The process of simulation-based learning is interactive and experience-based in which learners can interact with a model or a real situation in order to enable them to gain knowledge and practical skills.
The approach will help close the gap between practice and theory and improve knowledge, problem-solving and thinking. Simulation-based learning is an application with numerous applications, such as the medical aspect, engineering, aviation and business, since simulation-based learning is a safe, effective and interactive method of acquisition of technical and soft skills .
Contents
What is Simulation-based Learning?

Simulation-based learning may be described as a form of learning that involves the application of a realistic interactive model or situations during teaching and learning. The students do not read textbooks, but listen to lectures to learn, and they imitate the conditions, which are similar to those in real life.
Through this, they are able to practise, make decisions, problem solve, and learn the mistakes in a safe manner.
It is also present in other fields like medicine, aviation, engineering, as well as business, so as to come up with an understanding, critical thinking , practical skills and confidence. However, it is important to note here that Simulation-based learning reduces risk but doesn’t eliminate all dangers entirely.
Top 5 Types of Simulation-based Learning
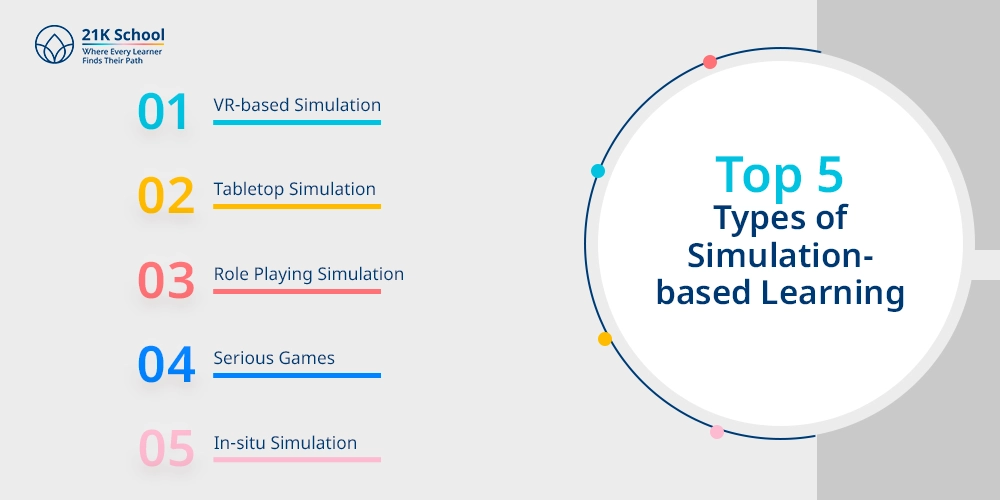
Simulation-based learning has many different modes of application, and they are all dedicated to the simulation of real and interactive experience. VR-based simulation, tabletop simulation, role-playing, serious games, and in-situ simulation are the top 5 most popular ones that offer various variations of skill practising, decision-making, and problem-solving.
These methods are participatory and confrontational to the learners and develop knowledge and prepare the learner for real-life situations in a controlled environment.
1. VR-based Simulation
The VR-based simulation is one of the modalities that assist the learners in being absorbed in a realistic and interactive environment with the assistance of virtual reality technology. It allows one to manage complicated activities, choices, and problem-solving skills without being exposed to the real world.
VR simulations may be used in any kind of medicine, aviation and engineering to enhance engagement, retention and acquisition of skills because of the simulation of scenarios that may be difficult or dangerous in practice.
2. Tabletop Simulation

Tabletop simulation is a diagram, map, or model-based discussion-based simulation, where the participants solve scenarios. It is applicable to emergency management, military and business planning, and it is aimed at strategic thinking, collaboration and decision-making.
Even though this is not physically immersive, it allows learners to learn processes, anticipate difficulties and practise solutions within a non-risky controlled environment.
3. Role Playing Simulation

Role-playing simulation involves the learners adopting some roles, and through the roles, they play a scenario. The practice enhances communication, empathy , teamwork and problem-solving. It has widespread use in medical and customer care training as well as management training.
Learners are able to acquire practical skills, enhance interpersonal knowledge, and have an understanding of the implications of their judgment by undergoing situations through alternative perspectives.
4. Serious Games

Serious games have a primary purpose beyond entertainment (education, training, health, etc.) and hence are used in learning. They interrelate, challenge and provide feedback to impart skills, ideas or processes.
Students are engaged, make decisions and endure repercussions in a safe e-learning environment. These simulations can be utilised in the education, corporate training and medical fields to promote motivation, critical thinking and knowledge retention.
5. In-situ Simulation

In-situ simulation is done in the actual working environment, e.g. a hospital ward or an industrial establishment. It will provide the learner with an opportunity to practise authentic processes, collaborative and crisis management within the framework, to be better prepared and minimise mistakes.
It is one of the most efficient methods of training professionals since it is employed in the high-stakes industries to introduce changes, define existing gaps in the workflow, and create practical skills and realistic decision-making.
6 Characteristics of Simulation-based Learning
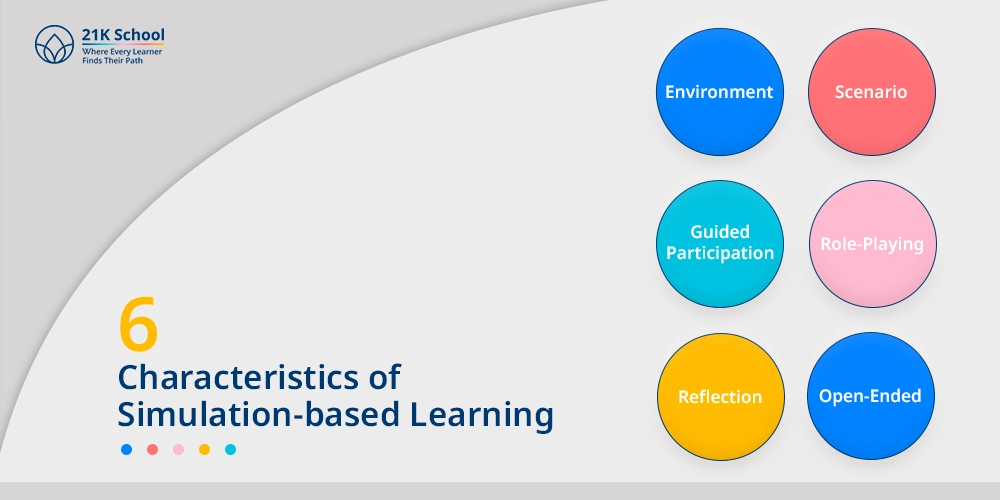
Simulation is a type of learning, but it is characterised by certain features that precondition its efficiency and interest. These are realistic environments, circumstantial, role play, facilitated and rumination and unstructured findings.
All this will provide engaging and immersive experiences that can be used to understand, and skills can be developed and critical thinking to narrow the divide between theory and practice.
1. Environment

Environmental simulation is almost close to real-life, which allows the learner to learn in a realistic or controlled setting. It may be both physical and virtual, where the learner is provided with a touch and a sense of being in the place.
A good environment enables the players to rehearse in a safe environment, experiment and actively participate in the process to make learners capable of being able to relate theory and practice. The property is important in making the learning process meaningful, focusing and equipping the learners to handle situations in real life.
2. Scenario
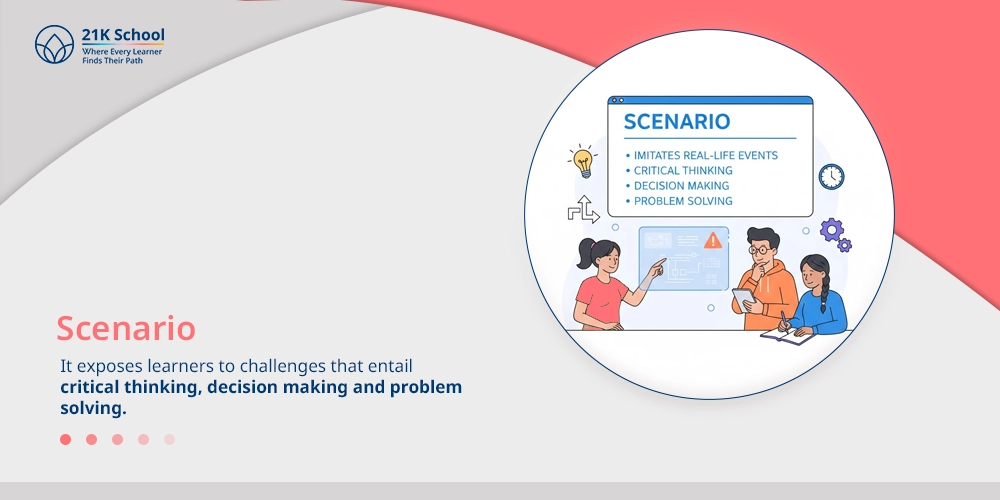
A scenario is an ordered situation or a problem which aims to imitate real-life events. It exposes learners to challenges that entail critical thinking, decision making and problem solving.
Scenarios provide the context and a reason, and demonstrate to learners the course of action and the identification of consequences. A well-written scenario will give the learner some active learning, exploration of different strategies and reinforcement of the learning exercise since it will give the learner the knowledge in a real-life scenario, as it will make the skills more memorable and in practice.
3. Role-Playing

One of the methods is role-playing, which involves the learners performing a simulation by showing particular examples. It fosters communication, teamwork and good decision-making. The learners are in a position to understand the roles, the expectations and the nature of people dynamics through the exposure.
The interactive nature of role-playing and the chance of student engagement provide the learners with the possibility of trying actions and strategies safely to help them practice the behaviours and responses that can be applied to real-life situations.
4. Guided Participation

Guided participation directs learners to some degree, and feedback is provided by instructors, mentors or facilitators in the simulation process. It is the advice that will make learners go through the proper procedures and remain within the frame of the learning objectives, as well as overcome barriers in a safe manner.
It uses a balance between independence and supervision that allows the learners to achieve confidence, real-time correction of mistakes and efficiency in the learning of hands-on skills. The facilitated learning improves the process of learning, fosters thinking, and improves decision-making in real-life contexts.
5. Reflection
Instructional reflection involves reflection and assessment of experiences at some point in the middle or at the end of a simulation. The students can examine the options, behaviours, and outcomes to discover what they are doing and, what they are not doing well and what they should enhance.
It allows the learners to integrate theoretical and practical knowledge, to understand the implications and put the acquired lessons into practice and apply them in real-life scenarios, which would make the learning process more practical and meaningful.
6. Open-Ended

In an open-ended simulation, the learner can search through a variety of strategies/solutions and not follow one correct path. This promotes innovation, ideas, and problem-solving. Learners become flexible and resilient by trying out various methods and trial and error.
The open-ended designs are more realistic concerning the uncertainty and complexity in the world, in which learners should acquire their abilities in making decisions, strategic planning and critical thinking in the context that can be compared to the real-world environment crisis and unpredictability.
5 Best Benefits of Simulation-based Learning

The learning methods using simulations are both interesting and practical in learning. It promotes retention, decision-making and problem-solving and enables individualised learning experiences.
Its interactive and safe learning environment, based on such features as quick feedback and peer evaluation, makes the theory more compatible with practice and makes the process more effective and applicable to real-life scenarios.
1. Enhances Knowledge Retention

Learning in a simulation environment improves knowledge retention by actively involving the learners in the actual situation. It is also unlike passive learning since it enables one to have repetitive practice, on-the-job experience, and application of concepts in a context.
When theory and real life are intertwined, learners have a deeper processing of information and better retention of information and can recall and apply information in real life or professional practice.
2. Promotes Decision-Making Skills

Simulations put the learner in a situation where they are expected to make decisions and solve problems, and this teaches critical thinking and problem-solving. Through a safe environment, learners get to learn how to analyse information, weigh options and make informed judgments.
Continuous practice in diverse scenarios builds their confidence, flexibility and capacity to react well to pressure in real-life settings.
3. Personalised Learning

With simulation-based learning, one can customise it to suit the needs of the individual learner, the pace, and the ability level of the learner. Students are able to concentrate on their areas of weakness, repeat activities where necessary and be involved in situations where their objectives are concerned.
Personalisation increases knowledge, effective skills acquisition, and supports different learning styles, which makes education more efficient and student-centred learning .
4. Quick Feedback

The simulations provide direct feedback regarding the performance that allows the learners to know their mistakes, consequences and correct their errors within a short period.
On-the-job instructions allow for accelerating the learning process, inculcate the appropriate behaviour, and reduce the risk of developing harmful habits. The fast feedback will allow the learner to think of the options, alter plans and concentrate on the skills at all times in a supportive and realistic environment.
5. Peer Evaluation

Simulation learning gives learners the chance to have peer evaluation that allows them to see, review and provide feedback to fellow learners. This is an interactive learning activity that contributes towards acquiring new knowledge, instilling teamwork and inculcating the evaluation skill.
The different perspectives also allow the learners to learn from the experiences of failures and successes of other learners, communication skills and interpersonal skills , which subsequently assist in improving personal and group learning outcomes.
5 Common Disadvantages of Simulation-based Learning
Simulation-based learning has numerous benefits, but there are a few limitations to this learning. It might not be easily implemented due to its high costs, duration requirements and technicality.
It can also be inappropriate in some subjects as well as in some learners, and the analysis of results can be challenging. The knowledge of such drawbacks will enable teachers and students to make wise choices in their proper application.
1. Expensive
Simulation learning could be costly in terms of equipment and software employed to simulate learning, and also trainers. The finest virtual learning systems, elaborate simulators and model systems are costly.
It can be counterproductive to smaller institutions or even individual students, and this implies that this cost cannot work on a large scale, although it has educational benefits.
2. Time-Consuming
Simulations and designs, and set-ups can be costly to design and execute compared to conventional teaching methods . This may be laborious, developing scenarios, training facilitators, and even running the sessions.
Neither is it as efficient a decision as simulations in a scenario, whereby there is a necessity to transfer knowledge fast, since students cannot afford to wait before fully investing in the simulation and the ability to contemplate the outcomes.
3. Limited Applicability
Simulation-based learning cannot be applied to all subjects and skills in general. It is pragmatic and procedural or decision-making, but with abstract concepts and theoretical knowledge or fields that easily do not adapt to reality, it might not be as effective. Its benefits are less in cases when the real-life imitation is bothersome and unnecessary.
4. Not Suitable for Everyone
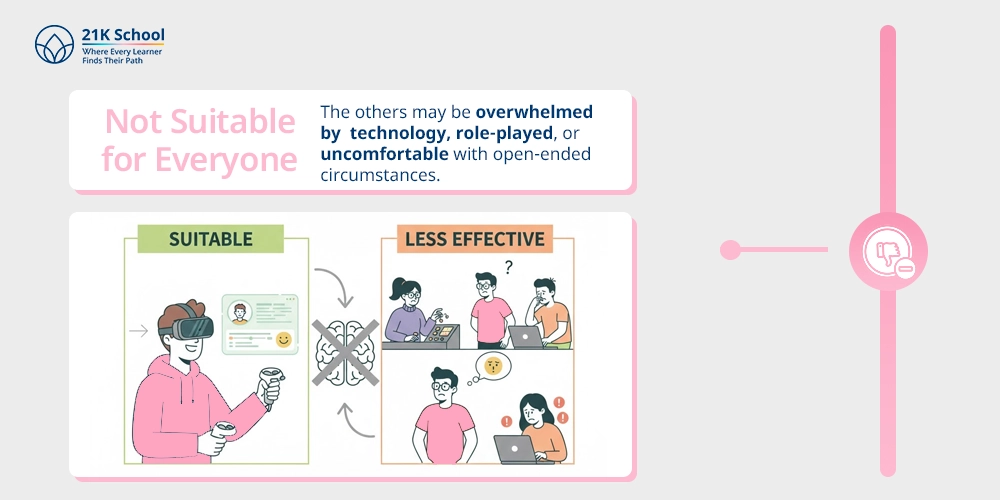
Not all learners find it easy to adapt to simulation-based approaches. The others may be overwhelmed by technology, role-played, or uncomfortable with open-ended circumstances.
Its engagement and effectiveness might be different in terms of the personalised learning styles, preferences and confidence level, which makes it not as universal as the traditional learning ideas.
5. Difficulty in Interpretation
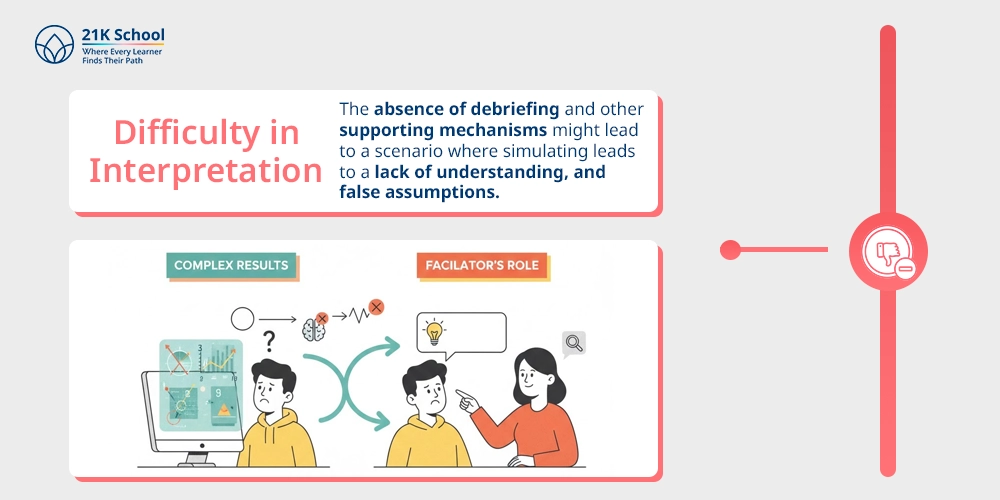
The results of the simulation may not be transparent and comprehensible. The analysis can be quite keen, and in some instances, the study will not help the students to match the simulated results with the real world, and this is where the facilitator plays a role.
The absence of debriefing and other supporting mechanisms might lead to a scenario where simulating leads to a lack of understanding, and false assumptions.
How Simulation-based Learning Works?

The simulation-based learning operates by exposing the learners to real-life scenarios where they can apply the information, practise their skills as well and develop an understanding of the action they are performing.
This method is the way theory can be connected to practice, as the practice is accompanied by active feedback and the ability to test something without fear, and it is possible to make the learning process more valuable, interesting and fruitful.
1. Provides a Realistic Environment

Learning through simulation is achieved by designing real-life-like scenarios which are real and close to real scenarios. Such an immersive environment will aid in contextualization, consequence observance and make learners become increasingly involved in the material.
The realistic environment, be it virtual or real, provides reinforcement on the practical knowledge , engages the learner to participate and prepares them to cope with such situations with confidence in real-life situations.
2. Enables Hands-on Practice

The simulations enable the learners to be active in what they are learning, and not merely observe and read about the task. The practical experience solidifies muscle memory, instils confidence and improves mastery of the skills.
By repeating the procedures or decision-making , learners can acquire practical experience, which reinforces the learning and prepares the learners against real-world challenges without the dangers of engaging in the actual practice.
3. Brings Theory and Practice Together
The simulation in learning is an integration of both the theoretical and practical aspects. The students get to apply the things they have learned in the practical environment, hence making the concepts clearer and easier to remember.
This integration helps them to know how ideas work in the real world, which creates awareness, instils a desire to learn more and makes the academic concepts meaningful, practical and easier to recollect when applied in real-life situations.
4. Include Reflection

Reflection is an important element by which learners discuss their actions and decisions and their results after the simulation. Through evaluation of what worked well and what did not, they know the strengths, weaknesses and improvement areas.
The reflective process helps to improve insight, critical thinking, and ensures that the lessons learnt are not disregarded, but they become incorporated and implemented into practice in the future.
5. Allows a Space to Make Mistakes

The simulation gives learners the chance to learn their lesson by making mistakes. This is an environment which is safe and supportive to experiment, to take risks and learn through trial and error.
As mistakes will become learning opportunities, learners will get confidence, sharpen, and, with time, learn to make better decisions. This will lower their level of student stress and equip them to face real-life situations better and in a more responsible manner.
Conclusion
The new and effective method of learning that is useful in bridging the gap between theory and practice is online simulation learning. It can be applied to improve the learning and retention of knowledge, critical thinking skills, decision-making and practical skills as it offers a realistic, positive learning environment .
In spite of the limitations of costs, time and availability, the tool is a priceless asset in the health care profession, engineering and aviation, among other professional sectors, due to its benefits that include customised learning experiences, instant feedback and practice in a risk-free setting.