Education is the foundation of students and national progress. In India, the education system is structured for different types of learners.
Learners from early childhood in pre-primary school through to advanced academic and vocational training of high school students.
With the introduction of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, the system is undergoing changes that match 21st century needs.
The aim is to make learning holistic , flexible, and aligned with global standards. And to do so, adapting behavior and continuous learning is crucial.
In this guide we are going to explore the different levels of education in India and understand their benefits, challenges and NEP.
Contents
10 Levels Of Education in India
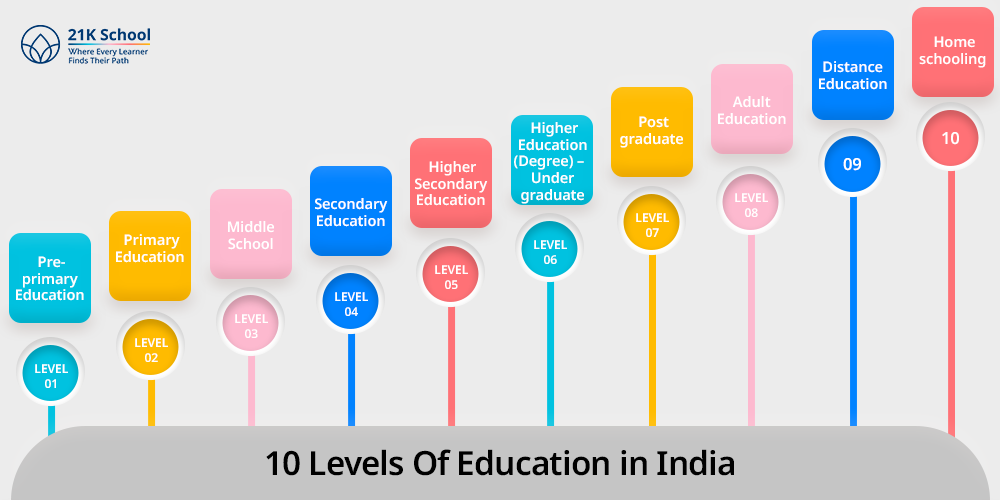
As we all know, the Indian education system is structured across several levels. But understanding these structures ensures clarity in both parents and students.
From pre-primary to higher education each structure can be further categorized into formal, non-formal, and informal education.
Here we will explore each structure in detail:
1. Pre-primary Education
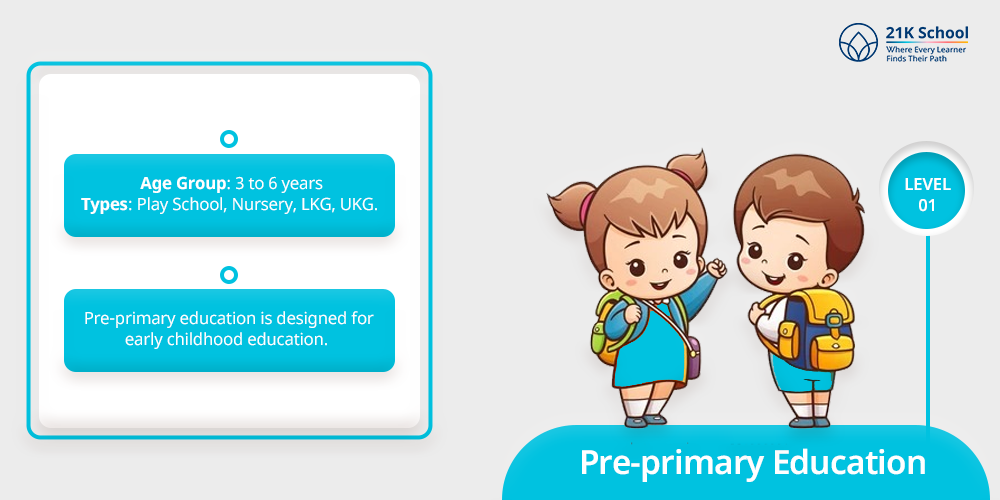
Starting with pre-primary education also known as preschool education for kids. Pre-primary education is designed for early childhood education.
The National Education Policy gives strong emphasis to Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE). It encompasses different kindergartens and even online preschools .
The aim of this stage is developing essential skills and preparing children for formal schooling. Skills such as gross and fine motor skills , basic literacy, and social interaction.
- Age Group: 3 to 6 years
- Types: Play School, Nursery, LKG, UKG.
2. Primary Education

Primary education is also called Elementary education. The first stage of formal education, typically encompassing grades 1 through 5 or 6 where kids age between 6 to 10 years old.
Hence, many online primary school focuses on the foundation for future learning by focusing on developing basic literacy, numeracy, and foundational skills.
Government initiatives like the Right to Education (RTE) Act support universal access to primary education.
- Age Group: 6 to 10 years (Classes 1 to 5)
- Types: Primary Stage.
3. Middle School
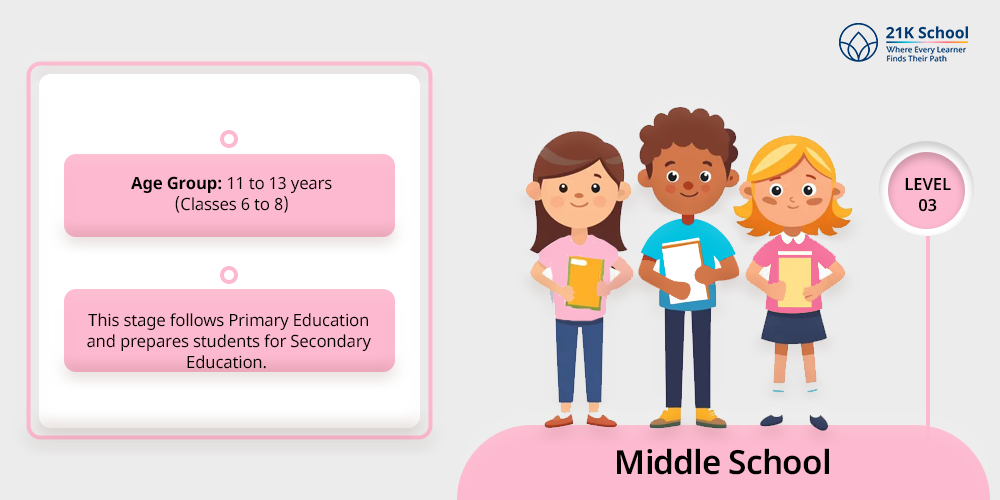
Middle School means the same level of schooling, spanning grades 6 to 8 where children age between 11 to 14
This stage follows Primary Education and prepares students for Secondary Education. So, even in online middle school , students learn subject-based learning and development of cognitive and analytical skills.
The key objective of schools is nurturing intellectual curiosity and fosters independent thought. Kids can dive deeper into topics while getting valuable guidance from experienced educators.
- Age Group: 11 to 13 years (Classes 6 to 8)
- Types: Middle Stage.
4. Secondary Education

Secondary education in India includes Classes 9 to 12. This level of education consists of students aged 14 to 18.
It is divided into two stages. First Lower Secondary which includes classes of 9 to 10 and other Higher Secondary which includes classes 11 to 12.
Here students can learn to strengthen academic concepts and prepare for board exams. Career awareness and selection starts at this level.
- Age Group: 14 to 15 years (Classes 9 and 10)
- Types: Lower Secondary (Classes IX-X) and Higher Secondary (Classes XI-XII).
5. Higher Secondary Education
Levels of education system in India includes Higher Secondary Education. It is also known as Senior Secondary Education.
The final two years of secondary education are of classes 11 and 12. In this stage students choose any academic stream.
Students have options like Science, Commerce, or Humanities. They also prepare for entrance exams and higher education.
- Age Group: 16 to 17 years (Classes 11 and 12)
6. Higher Education (Degree) – Undergraduate
Higher education is the undergraduate level which involves a 3 year Bachelor’s degree or a 4 or 5 year professional bachelor’s degree.
This stage is also popular as a graduation or undergraduate stage. Students after completing class 12 can opt for these undergraduate programs at universities and colleges.
- Age: No limit
- Types: BA, BSc, BCom, BTech, etc.
7. Postgraduate

Postgraduate education in the Indian education system play important role to make career. People also call it higher education.
Students choose the specialization in their chosen field at 11 class. Entry is usually through merit or entrance tests in most university.
It includes pursuing Master’s degrees on MA, MSc, MBA, etc. or doctoral degrees (Ph.D.) after completing a Bachelor’s degree.
These programs take 2 to 3 years which are offered primarily by universities.
- Age: No limit
- Types: MA, MSc, MBA, MTech, etc.
8. Adult Education
Adult education in India includes different levels of learning such as functional literacy, life skills development, vocational training, basic education equivalency, and continuing education.
Improving literacy among adults especially aged or who live in rural or underprivileged communities. Various programs focus on adult learning and basic education.
9. Distance Education

Distance education in India refers to access to education across various levels remotely or from anywhere.
Students from K-12 to postgraduate studies, and includes diplomas, career-oriented, and vocational courses can choose and learn freely.
This flexible learning option provides a cost-effective alternative to traditional campus-based education. It is ideal for students who travel a lot or online high school learners.
As per date distance education in India is regulated by govt bodies like the University Grants Commission (UGC) and the Distance Education Bureau (DEB).
10. Homeschooling

Homeschooling is an emerging concept of India that is legal and follows the same levels of education as traditional schools .
Students opting homeschooling can choose to follow the Indian education system like CBSE or ICSE. Know more about homeschooling curriculum .
However, they are free to choose international boards like IGCSE or open education programs like NIOS .
Recent Reforms & New Education Policy 2020

Recent reforms in education have changed the way of learning. NEP 2020 aims to modernize India’s education system.
It’s objective is emphasizing inclusivity, foundational literacy, and a restructured learning framework. Let’s explore the crucial points in depth:
1. Structural Changes (5+3+3+4 Model)
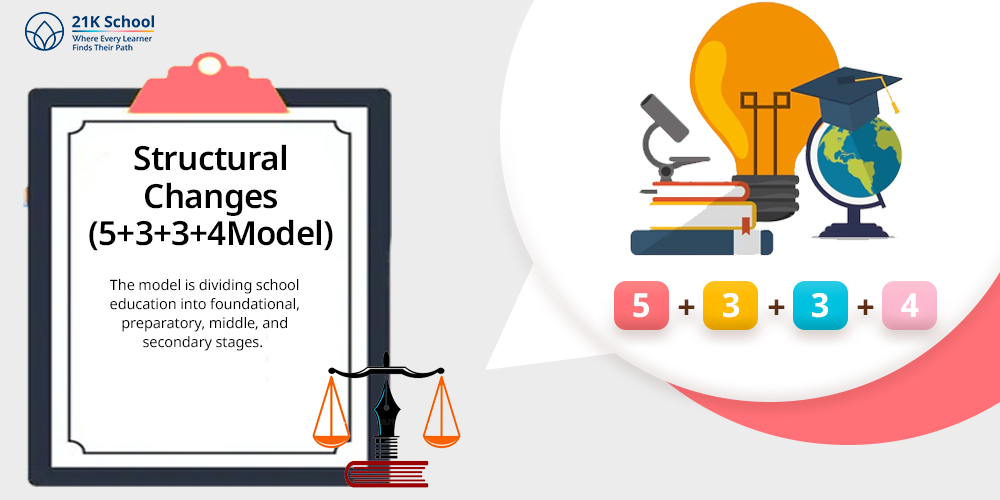
Starting with structural changes in the new education system in which the 5+3+3+4 model is introduced by New Education Policy 2020.
The model is dividing school education into foundational, preparatory, middle, and secondary stages.
Here the replacement of the old 10+2 model by new model.
Stages Includes:
- Foundational (5 years): Nursery to Class 2
- Preparatory (3 years): Classes 3 to 5
- Middle (3 years): Classes 6 to 8
- Secondary (4 years): Classes 9 to 12
2. Multidisciplinary Approach

NEP 2020 promotes a multidisciplinary approach to education, moving away from traditional, compartmentalized learning.
It helps students to discover new subjects without any stream boundaries. Multidisciplinary approaches enhance students critical thinking , creativity, and problem-solving .
3. Emphasis on Skill Development and Flexibility

The recent reforms in education in India and the latestly adopted National Education Policy (NEP) lays strong emphasis on skill development and flexibility.
The skill development is achieved with focus on vocational education, development of 21st century skills , project-based learning, and continuous teachers training.
The flexibility is offered to learners with multidisciplinary education, allowing students to explore different areas of interest, modular approach, and smooth technological integration.
Importance of Structured Educational Levels in India
Today’s education system is crucial to shaping kids’ futures. It is important for developing well-rounded individuals, ensuring a skilled workforce, and fostering societal progress.
Explore the advantages of Indian education system for career growth. Here we will discover the importance of structured educational levels in India:
1. Progressive Learning
Progressive learning means each level of education builds on the previous one.
This ensures holistic development and equipping students with essential skills for the 21st century
2. Standardized Curriculum

A structured and standardized curriculum in India ensures consistent, equitable education for all students.
It supports logical learning progression and enables fair, objective assessment of their development. Understand National Curriculum Framework designed to fulfill students’ needs.
3. Lifelong Learning

Lifelong learning helps learn continuously and increase curiosity from young age to adulthood.
The positive point is to keep individuals updated with current knowledge and trends.
4. Social and Economic Progress

Social and economic progress leads to access to better employment opportunities, higher incomes, and overall economic stability.
It empowers individuals’ education, reduces poverty and promotes social justice.
Challenges in the Indian Education System
In the Indian education system challenges faced by 21st century students like outdated curricula, inadequate infrastructure, and unequal access to quality education.
Some specific challenges:
1. Outdated Curriculum

Outdated curriculum can be a big challenge for students’ preparedness for modern education in the 21st century.
However, focusing on practical skills and critical thinking rather than rote learning and theoretical knowledge can be the solution.
2. Unequal Access
Unequal access means in India there are many individuals due to various reasons still do not get equal access to education.
It happens due to socio-economic disparities, limited infrastructure in rural areas, and the quality of education available in different regions.
3. High Dropout Rates

High dropout rates are a significant challenge in the Indian education system . It impacts different levels of education.
Due to various factors like socioeconomic challenges, lack of access to quality education, and societal issues encourage dropout rates.
Conclusion
With time the Indian education system is evolving. To meet the needs of a dynamic, globalized world it is important to understand the different levels of education.
From preschool to postgraduate and other learning methods students appreciate how each stage contributes to building a more professional, educated and empowered society.
Implementation of NEP 2020 brought a big difference in India. It is moving toward a learner-centered, skill-oriented, and inclusive education model.
Adopt the 21st century Indian education system and start your learning journey with the right approach with a positive learning environment .
To do so, 21K School is here for you.



