
In education many people often interchange a few terms that do not really mean the same. These are the terms such as “Skill” and “Knowledge”.
With time each individual works on their both personal and professional learning at some time. Terms like knowledge and skill are often used by learners.
Are you someone confused about the difference between skill and knowledge?
If yes, then this guide will help you to understand the real difference between skill and knowledge. And a quick comparison table, examples, importance and many more. Let’s begin!
Contents
6 Key Differences Between Skill and Knowledge
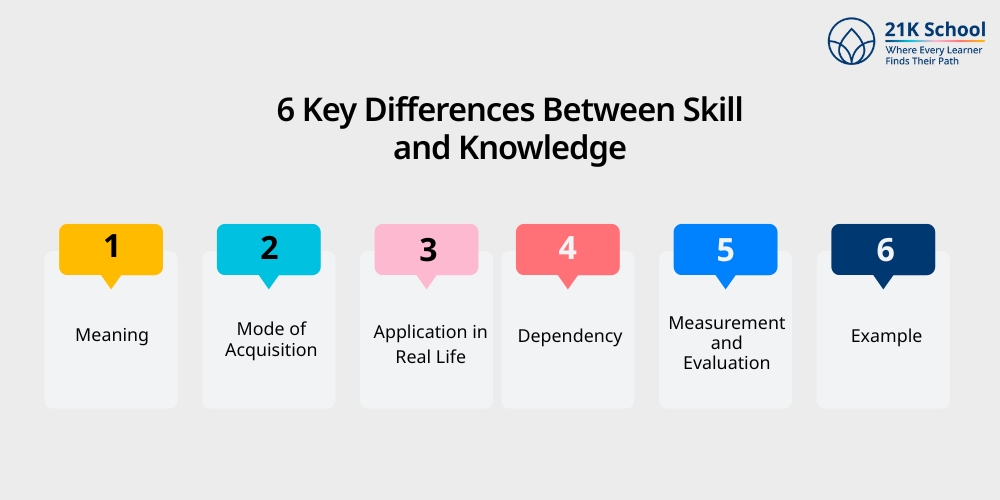
Given below is a quick overview of key difference between skill and knowledge in the form of table comparison and important insights one must know:
| S No. | Particulars | Skill | Knowledge |
| 1. | Meaning | Skill refers to the ability to perform tasks effectively with the help of knowledge and practice. | Knowledge includes different types of awareness, facts, topics, concepts and information gained through education or experience. |
| 2. | Mode of Acquisition | Skill is acquired through practice, training, and real-world application. | While knowledge is gained via learning, reading, studying, or observing. |
| 3. | Application in Real Life | Skill helps in executing tasks, solving problems and achieving results. | On the other hand, knowledge helps in understanding concepts and making informed decisions. |
| 4. | Dependency | Skill depends on knowledge for guidance but requires practice to master. | Knowledge can exist without skills. For example, theory without practice can be useful. |
| 5. | Measurement and Evaluation | Skill is evaluated through performance, execution and outcomes. | Knowledge is measured through exams, tests or discussions. |
| 6. | Example | Examples such as writing a grammatically correct and engaging essay. | Examples such as knowing grammar rules of English. |
Go through a detailed explanation of comparison between skill and knowledge:
1. Meaning

Knowledge: Knowledge simply means that information or theory present in an individual’s mind or memory. It’s about “What you know?”
Skill: Skill simply means a practice or practical ability of an individual who performs a task successfully. It’s about “What you can do?”.
2. Mode of Acquisition

Knowledge: The mode of acquisition of knowledge is based on classes, books, novels, videos or audio listening.
Skill: However, skills are developed in a different way for example regular practice, training programs, internships and implementation in real world experience.
3. Application in Real Life
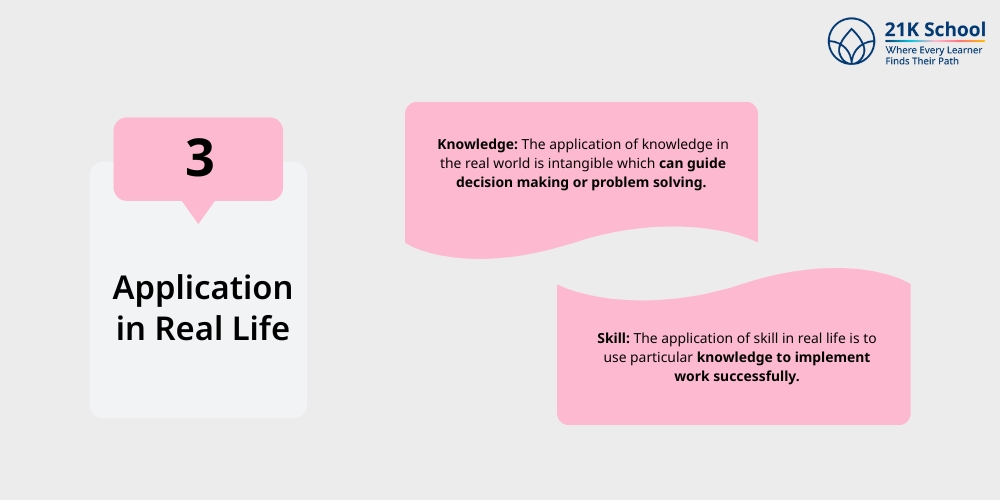
Knowledge: The application of knowledge in the real world is intangible which can guide decision making or problem solving .
Skill: The application of skill in real life is to use particular knowledge to implement work successfully.
For example, the medical information of a doctor is knowledge. However, treating a patient effectively is a skill.
4. Dependency
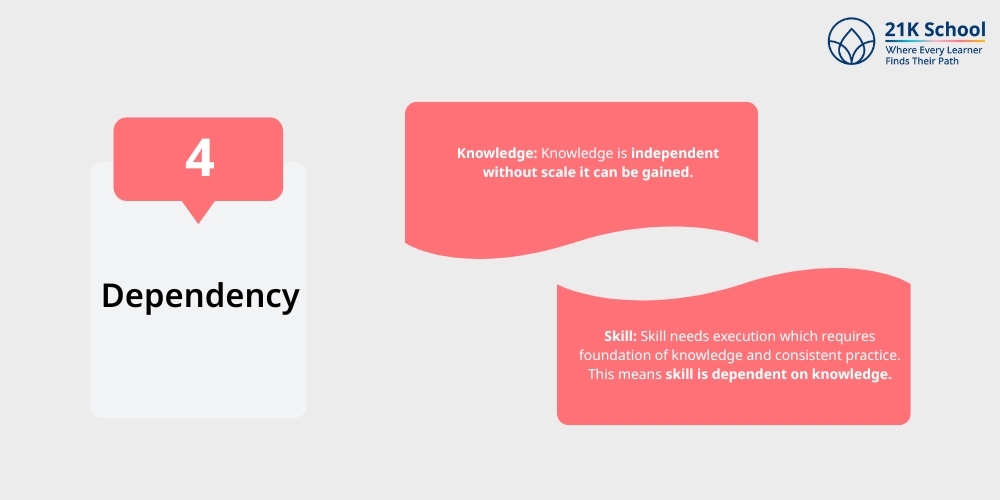
Knowledge: Knowledge is independent without scale it can be gained.
Skill: Skill needs execution which requires foundation of knowledge and consistent practice. This means skill is dependent on knowledge.
5. Measurement and Evaluation
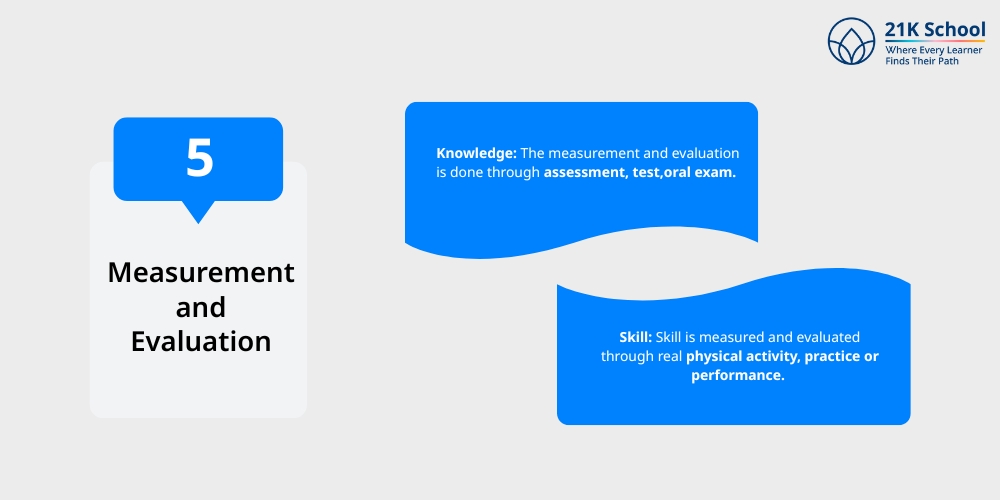
Knowledge: The measurement and evaluation is done through assessment , test,oral exam.
Skill: Skill is measured and evaluated through real physical activity, practice or performance.
6. Example
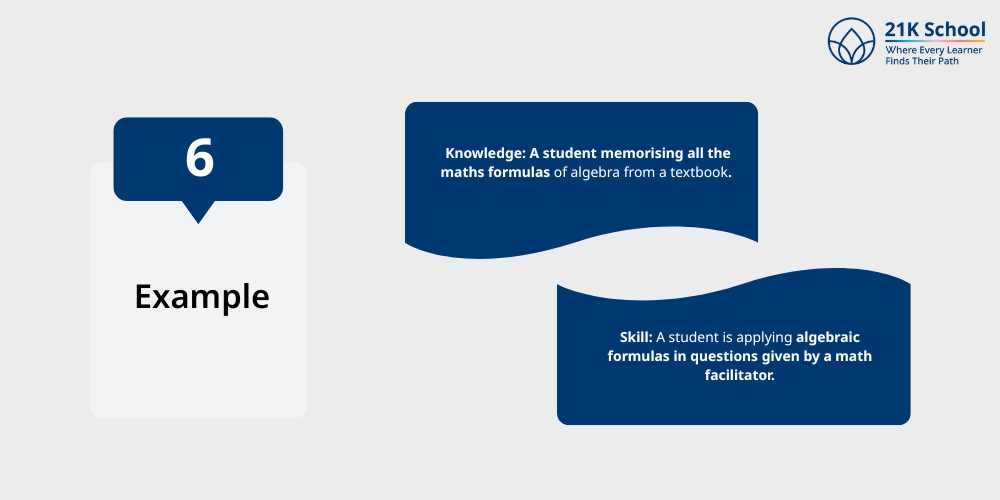
Knowledge: A student memorising all the maths formulas of algebra from a textbook.
Skill: A student is applying algebraic formulas in questions given by a math facilitator.
What Are Skills?

The physical expertise is to do a particular task known as skill. Skill depends on theoretical knowledge . It can be technical like ard skills or personal like soft skills.
1. Importance of Skills
1.1 Enhances Employability
Learners who focus on gaining multiple skills get more and more successful career opportunities.
For example 21st century skills like coding and programming problem solving skills and communication ability ensures better jobs.
1.2 Improves Adaptability
Highly skilled learners can easily adapt in the new environment or situation. For example, individuals with digital literacy can easily learn the latest technology without challenges.
1.3 Promotes Lifelong Learning
Skills are not static. It needs practice and improvement with time.
The knowledge of a doctor can be retained but to cure patients they need to practice everyday.
1.4 Examples
Graphic designing, coding and programming are some common technical skills one can gain.
What is Knowledge?

Knowledge is a combination of facts, information or data gained by different ways like classroom learning , self-study, experience or education. It is a foundation of skill.
1. Importance of Knowledge
1.1 Builds a Strong Foundation
To become expert in technical soft and life skills one must build a foundation of knowledge. Without knowledge, skill lacks its depth.
1.2 Helps in Problem-Solving
Knowledge and retention is a core of education which helps learners in problem solving, collaboration, communication and in-depth understanding of concepts.
1.3 Prepares for decision-making
By gaining knowledge from different sources one can make a reliable decision even in complex situations.
Whether it’s a financial decision, healthcare choices or business strategies it works everywhere effectively.
1.4 Examples
A simple example of knowledge is academic knowledge such as Mathematics and History. General knowledge like current affairs or medications.
Conclusion
The importance of knowledge and skill leads to a successful outcome but they both serve different purposes.
The theoretical foundation retained for the long term is known as knowledge. However, converting the knowledge into real life practices is defined as a skill.
Both knowledge and skill are crucial for higher education. The combination of both help them to become confident and future ready.



