The Indian curriculum is meant to offer a systematic educational method. This comes with the addition of a national curriculum framework, cultural values, and global competitiveness.
However, parents and students are frequently faced with the challenge of finding the right ways to select the appropriate curriculum. In keeping with their academic inclination, career goals, and learning abilities, the process becomes daunting.
Read on to have a detailed understanding of the Indian curriculum at length, including its types, stages, characteristics, and comparisons with other international boards in india .
Go through the easy tips on choosing the correct curriculum and the increasing popularity of homeschooling curriculum in India.
Contents
- 1 What is the Indian Curriculum?
- 2 Key Stages of Indian Education
- 3 Types of Indian Curriculum
- 4 Comparison of CBSE, ICSE, NIOS & State Boards
- 5 Key Features of the Indian Curriculum
- 6 Career & Higher Education Pathways
- 7 Indian Curriculum Vs International Curriculum
- 8 How to Select an Optimal Curriculum for Your Child?
- 9 Why Online Schooling for the Indian Curriculum?
- 10 To Sum Up
What is the Indian Curriculum?

The Indian curriculum is the formal educational system covering the different subjects and learning stages from class 1st to class 12th.
It is practiced by the majority of Indian schools. It covers different subjects like Humanities, Science, or Mathematics along with different options for physical education, performing arts, and others.
It is regulated by national and state education boards. This justifies its adherence to guidelines from the National Education Policy (NEP) and concerned authorities.
It puts emphasis on academics, skills, education, and proficient development. This curriculum majorly focuses on subjects such as mathematics, science, social sciences, and language.
The syllabus also encompasses the importance of extracurricular activities and vocational training so that students are prepared for life after school.
The curriculum in India has various stages:
- Primary Education (Grades 1-5)
- Middle School (Grades 6-8)
- Secondary Education (Grades 9-10)
- Senior Secondary Education (Grades 11-12)
Each level emphasizes learning appropriate for the age group, cognitive growth, and skill development.
Learn more about the advantages of Indian education system .
Key Stages of Indian Education

To ensure that every student of the nation gets a uniform and structured form of learning, Indian education was categorised in the following sequence:
1. Primary Schooling (Grades 1-5)
Age duration- 5-12 years
At the primary stage, students are exposed to core subjects like math, language, and environmental studies. Hence, leading online primary schools emphasizes reading, writing, and the importance of communication skills.
Storytelling, drawing, and experiments are also a part of the curriculum to foster integrated growth.
2. Middle School (Grades 6-8)
Age duration- 12-14 years
Middle school adds to knowledge foundations, advancing to more rigorous subjects such as science, history, geography, and other languages.
While co-curricular activities like games, arts, and computer courses contribute immensely towards the overall growth of the individual, especially in online middle school .
3. Secondary Education (Grades 9-10)
Age duration- 14-16 years
This phase is important as students get ready for board exams. The curriculum becomes more formalized, with emphasis on core subjects like science, mathematics, social sciences, and languages.
Career guidance and vocational education are also initiated to guide online high school learners toward possible career options.
4. Senior Secondary Education (Grades 11-12)
Age duration- 16-18 years
At this level, students specialize in opted streams like Science, Commerce, or Humanities. The course is planned in a way that prepares the students for professional courses and higher education while ensuring that these stay relevant for them.
Read how higher education is becoming increasingly irrelevant.
Students also begin preparations for entrance tests like JEE, NEET, CLAT, and more depending on the career path chosen by them.
Read on to learn more about key benefits of higher education.
Types of Indian Curriculum
There are several educational boards in India. And each of them has a distinct curriculum format, testing mechanisms, and learning targets. There are four major categories of curricula in India, which are:
1. CBSE (Central Board of Secondary Education)

CBSE is a Government of India-controlled board at the national level. It adheres to the syllabus of the NCERT (National Council of Educational Research and Training) and is among the most recognized boards across the nation.
The CBSE curriculum is well-designed and emphasizes conceptual learning, preparing students for national-level competitive exams such as JEE, NEET, and UPSC. It combines academics with extracurricular activities .
It is deemed an apt option for students who want to pursue professional courses in India. Moreover, CBSE schools are easily accessible across the nation, which makes it an easy option for families who move frequently.
- Overview: The Union Government of India ruled the national board.
- Syllabus: Emphasizes science, math, and application-oriented learning.
- Exams: Conducts board exams for AISSE (Class 10) and AISSCE (Class 12).
- Advantages: It is the most well-known for competitive exams such as JEE and NEET. The same syllabus is taught across India, which helps students whose parents transfer often.
- Disadvantages: In certain schools, there is too much focus on rote learning . This derails from the courses’ core value of a flexible education .
2. ICSE (Indian Certificate of Secondary Education)

The ICSE curriculum is administered by the Council for the Indian School Certificate Examinations (CISCE). However, it is renowned for its thorough and elaborate method of education.
ICSE places great stress on the importance of the English language, making it suitable for students who want to pursue higher studies abroad. ICSE has a more vast syllabus when compared to CBSE. With a more practical and simulated form of learning, ICSE stands out.
Besides, it promotes analytical skills and thorough concept understanding. ICSE is academically demanding because of its large syllabus.
- Overview: It is governed by the Council for the Indian School Certificate Examinations (CISCE).
- Syllabus: Wider than CBSE, with a similar emphasis on languages, arts, and science.
- Exams: Holds Indian Certificate of Secondary Education (ICSE Class 10) and Indian School Certificate (ISC Class 12) exams.
- Benefits: It stresses English proficiency and analytical abilities. It is also accepted internationally for higher studies.
- Drawbacks: The syllabus may be larger and more demanding.
3. NIOS (National Institute of Open Schooling)

NIOS is an open board of learning intended to impart education to students who can’t attend school. It is acknowledged by the Government of India and provides academic and vocational courses.
NIOS offers a self-learning framework. And thus, it is most suitable for working professionals, differently-abled students, and students who need an alternate learning style.
The board gives the students an option to write exams when they are prepared, hence, a customized learning process.
Though it is popular for higher studies and competitive examinations, the absence of a regular classroom setup might be a disadvantage for certain students.
- Overview: An adaptable, open schooling network for distance and alternative education .
- Syllabus: Provides both academic and vocational courses.
- Exams: Enables students to take exams at their convenience.
- Advantages: Suits students unable to attend normal school (sports persons, working students). Besides, it is approved by CBSE and other boards.
- Disadvantages: It offers limited peer communication and classroom learning .
4. State Boards
Every Indian state has a State Education Board, which is responsible for running schools in the state. Every region has a different curriculum, with textbooks supplied by the concerned State Council of Educational Research and Training (SCERT).
State board syllabi are prepared in accordance with regional requirements, generally focusing on the local language and history. State boards offer a low-cost mode of education and are ideal for students who want to study at higher levels in the state.
State board syllabi might not be as competitive as CBSE or ICSE for national entrance exams. Hence, many look forward to the benefits of state boards shifting to CBSE.
- Overview: Every state in India has its board (e.g., Maharashtra Board, Tamil Nadu Board).
- Syllabus: Designed according to regional languages and state-specific educational requirements.
- Exams: Hold state-level Class 10 (SSC) and Std 12 (HSC) exams.
- Advantages: Emphasis on local culture and language. Less difficult for students who intend to study within the state.
- Disadvantages: Less standardized than CBSE/ICSE for national-level competitive exams.
Comparison of CBSE, ICSE, NIOS & State Boards
CBSE and ICSE are India’s best-known national-level boards, but the difference lies in academics.
CBSE puts a great emphasis on conceptual knowledge. ICSE is a more detailed and tough syllabus with language development and prioritizing practical application.
It suits students for the entrance examinations at national levels, while ICSE suits those intending to go to foreign countries.
State boards, however, offer localized education with a syllabus customized to the regional language and history. State boards are more accessible and economical, but might not prepare students well for competitive exams such as CBSE and ICSE.
Also Read, Importance of Regional Language.
NIOS is a flexible option where students can learn at their own pace, making it ideal for non-traditional learners. NIOS, however, does not have the structured setting of traditional schooling.
| Aspects | CBSE | ICSE | NIOS | State Boards |
| Established | Established in 1952, and the oldest central educational board in India. | Established in 1956 and widely accepted by private schools. | Established in 1990 and provides open learning. | Different establishment dates, however, the first state board in India was established in Rajasthan in 1921. |
| Exam Pattern | Secondary and senior secondary exams for class 10th and 12th, known as All India Secondary School Examination (AISSE) and All India Senior School Certificate Examination (AISSCE) | Exams for class 10 and Class 12 students. There are Certificate exams for Vocational Education. | The secondary exams and senior secondary exams for classes 10th and 12th. | The SSC exams for class 10th and the HSC exams for class 12th. |
| Curriculum | NCERT curriculum to prepare students for the national exams. Students were given the choice of selecting streams after the board exams. | ICSE curriculum offers three streams to students, along with Science, Arts, and Commerce, they were also provided with Vocational education and language learning. | NCERT curriculum allows students to choose Science, Arts, and Commerce after class 10th. | Some state boards use the government-recommended curriculum and textbooks to prepare students for the national exams. |
| Objective | To improve teaching knowledge and application so that students can improve their social, intellectual, and physical skills. | Provides excellent training through practical experience. The curriculum places a strong emphasis on knowledge that is applied. | To improve literacy and flexible education by providing all societal segments with accessible education. | To help students teach the state language and get ready for state exams by facilitating a regionally based curriculum and syllabus. |
| Practical Ratio | 60:40, which means 60% is theoretical learning and 40% is the practical approach. | 70:30, which means 70% is theoretical learning, whereas 30% is practical learning. | Offers a flexible approach to learning, with mostly theoretical learning and 30 to 20% of practical learning. | Every state board has its own practical ratio. However, the practical ratio depends upon 70:30 or 60:40. |
| Affiliation | Affiliated to (National Council of Education Research and Training) NCERT. | Affiliated to private or non governmental councils. | NIOS board comes under the Ministry of Education. | Affiliated to their respective states council and CBSE board. |
Key Features of the Indian Curriculum
Proving its versatility, Indian Curriculum especially the CBSE can be defined well with its certain features. these are as follows:
1. Technology Integration

The Indian curriculum uses modern technology for enhancing the learning experience with coding, robotics, online resources, and digital classrooms.
The inclusion of coding and robotics in the curriculum prepared learners for growing in innovation and technology. The availability of the interactive modules, video lectures, and e-books makes it easy for learners to unlock the contribution of technology in education.
The smart classrooms with digital tools and interactive boards makes the learning process engaging and effective. For more help and information on the need of coding, read the blogs focusing on the importance of coding for kids.
2. Holistic approach in designing curriculum

The Indian curriculum aims for a holistic approach with its equal focus on arts, culture, sports, and academics.
The academic framework helps in detailed understanding of the core subjects and development of critical thinking abilities . The schools are encouraged to integrate physical and sports activities for promoting healthy competition, teamwork, and fitness.
Learn more on the importance of sports in student life here.
Not only this, students get opportunities to explore their creativity and enjoy cultural diversity by offering programs in visual arts, music, or dance.
3. Flexible curriculum

The Indian curriculum allows flexibility in terms of different subjects and electives. It is highly effective and helps students develop a well-rounded skill set.
It helps trainers to adapt to the individual student needs, abilities, and interests. Not to miss is that the learning process is enjoyable and content.
Whether your child wants to go for arts, sciences, commerce, or humanities, the Indian Curriculum offers several options to choose from.
With the availability of different types of curriculum in education, the room for your learner to follow their interests and passion remains welcoming in the Indian curriculum.
Career & Higher Education Pathways

The Indian curriculum is as deep as an ocean, which gives the children of this nation to upskill themselves with whatever stream they choose.
The following pathways lead students to become whatever they want to, while supporting their families:
- Science Stream: Students get the chance to join the different streams like Engineering (JEE), Medicine (NEET), Research after completing the Science stream in the Indian curriculum system.
- Commerce Stream: For students opting to commerce stream in the Indian curriculum, it is easy to select the different options like CA, BBA, Economics, Business Management.
- Arts Stream: Indian curriculum ensures that learners interested in Literature, Law, Civil Services, and Humanities can go ahead with the Arts stream.
Indian Curriculum Vs International Curriculum
The Indian curriculum, mainly exemplified by CBSE and ICSE, varies considerably from international curricula such as IB (International Baccalaureate) and Cambridge.
CBSE and ICSE have a methodical, exam-based system that focuses on academic achievement and national entrance exams. These boards have a greater emphasis on theory and lesser subject flexibility.
IB and Cambridge, however, have a skill-based and inquiry-based system. They are more concerned with critical thinking, creativity, and research, making them ideal for students who wish to pursue global universities.
IB and Cambridge also have greater subject freedom and focus more on continuous assessments in place of ultimate board examinations. However, these global curricula are costly and less popular in India than CBSE and ICSE.
Explore the process of shifting from cbse to icse .
| Sr.No. | Features | Indian Curriculum | International Curriculum |
| 1 | Focus of curriculum | The focus of CBSE is on the academic achievement | ICSE focuses on the skill development and inquiry-based |
| 2 | Type of learning | The learning methodology adopted in the CBSE is theory-based learning. | ICSE adopts a critical thinking, creativity, and research learning methodology. |
| 3 | Flexibility in learning | CBSE allows reduced flexibility when it comes to syllabus selection and compared to ICSE. | ICSE allows highly flexible learning with good subject freedom. |
| 4 | Affordability | CBSE is highly affordable for a major section of students. | ICSE is costly when compared to the CBSE. |
Understand the difference between Indian and British curriculum , and Indian vs American curriculum .
How to Select an Optimal Curriculum for Your Child?
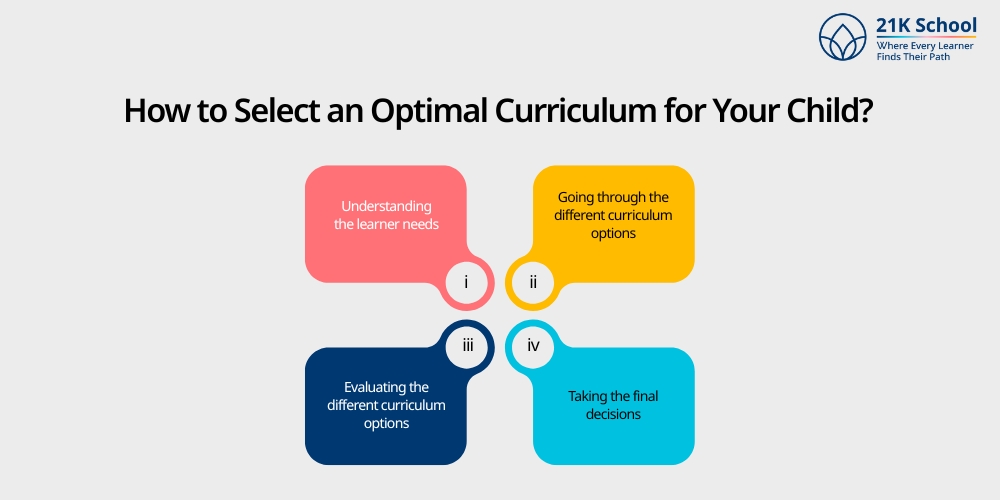
Choosing the right curriculum is subject to several criteria. Your decision to opt for one should be based on the following points:
- Understanding the learner needs:
It is important to go through the learner needs of your children before selecting the right curriculum.
Here, you must try to find out which subjects excites your child the most, what are their future career prospects, and what learning style they need.
- Going through the different curriculum options:
Once you’re clear with the learning needs of your ward, the next important criteria is to go through the different curriculum options.
You get the options of CBSE, ICSE NIOS or state boards and go through their key offerings.
- Evaluating the different curriculum options:
The available curriculum options can be evaluated based on the different factors like focus of curriculum, type of learning, flexibility in learning, and affordability.
It will bring you a step closer in your curriculum selection process.
Do understand what is curriculum vs syllabus here.
- Taking the final decisions:
To finalize the optimal curriculum for your ward, you can finalize one by visiting the different schools and taking reference from other parents.
Actively involve your child in the decision-making process so that they can feel comfortable in the process.
For quick selection, here are some of the key pointers for your help.
- For those seeking Indian competitive exams – CBSE is the best option as it is synchronized with national-level entrance exams.
- For those seeking extensive learning and excellent language proficiency – ICSE is a good option when compared to the other available counterparts.
- For those seeking foreign study – IB or Cambridge is the best option because they are internationally recognized.
- For those who require flexibility – NIOS is the best option as it is self-paced learning and hence suits working professionals.
- For those requiring state accessibility and state relevance – State Boards are a good choice. Especially for students who intend to pursue studies in their home state.
For more details go through the best ways to choose the right curriculum for your child.
Why Online Schooling for the Indian Curriculum?
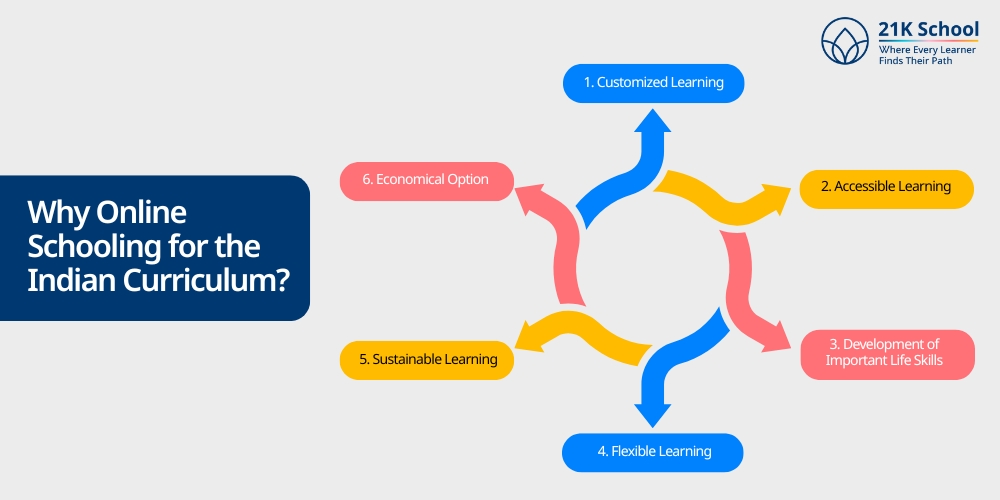
The top reasons for selecting online schooling for your kids in the Indian Curriculum are:
1. Customized Learning

The customized learning tailors to the unique needs, strengths, and interests of each student in the Indian curriculum.
It eliminates the one-size-fits-all learning approach and ensures that learners can access quality education catering to their specific learning pace and style.
2. Accessible Learning

Accessibility is ensured in the online schooling for the Indian curriculum. It confirms that every learner with or without special needs has access to academic growth.
The special education department at the 21K School focuses on equal opportunities for all learners based on their accessibility requirements.
3. Development of Important Life Skills
The development of essential life skills is a key point of attraction in delivery of the Indian curriculum using online learning.
It not only focuses on academic development but ensures that students can be proficient in the use of digital tools. It further allows independent learning, and inculcates self-discipline.
4. Flexible Learning

Indian curriculum when delivered using online methods offers the best flexibility where learners can study at their own pace and as per their availability.
It eliminates the rigid schedules and fixed location requirements and helps in online mode. Hence, it suits the needs of learners looking to achieve academic excellence amid tight schedules.
5. Sustainable Learning

The delivery of the Indian curriculum online makes the learning process highly sustainable when compared to the traditional physical learning methodology.
It reduces the carbon footprint of the learner, eliminates the big campus needs, and limits the use of physical resources.
6. Economical Option

Online learning is an economical option when compared to the traditional learning solutions in the Indian curriculum.
It saves on infrastructure and is an affordable option for most families. Moreover, AI-based platforms offer adaptive learning, enabling students to gain a better understanding of ideas.
To Sum Up
The Indian education system provides multiple curricula to suit different learning requirements. CBSE and ICSE offer systematic learning, and State Boards provide regional convenience. NIOS is an option for non-conventional learners.
With the introduction of global curricula such as IB and Cambridge, parents are now presented with more options based on the child’s intentions.
Making an informed decision demands aligning future intentions, and learning styles after careful considerations of problems in the Indian education system.
To gain a more thoughtful perspective on Indian curricula, online education , and other international courses, reach 21K School today!
Enjoy the benefits of virtual education for students, the best faculty, and interactive learning in the Indian curriculum for your child from 21K School!