In the 21st century, learning with technology is a necessity. Artificial intelligence and machine learning are some popular terms students need to implement in learning.
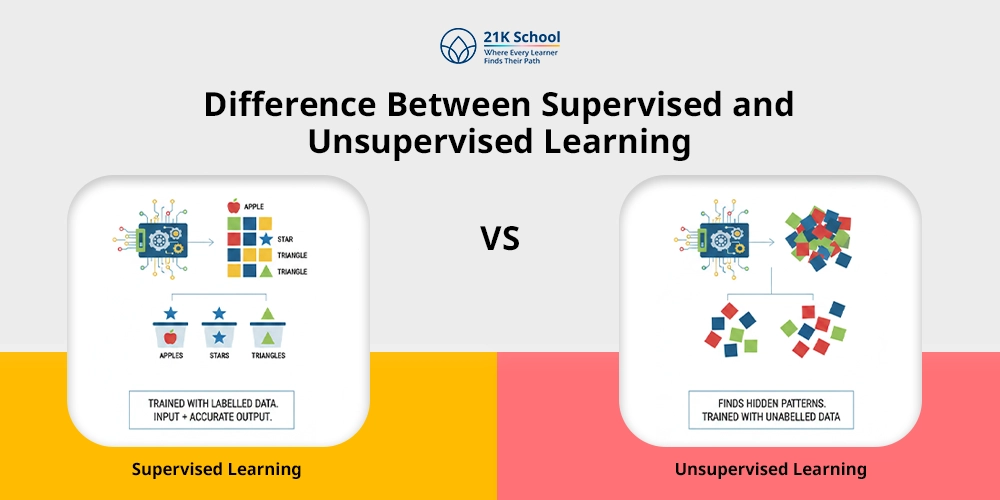
To understand the core of machine learning it’s important to know the difference between two fundamental approaches known as supervised learning and unsupervised learning.
These two approaches are ideal for students to learn from data in different ways.
In this blog, we will explore the 10 key differences between supervised and unsupervised learning and discuss their advantages and disadvantages.
Contents
What is Supervised Learning?
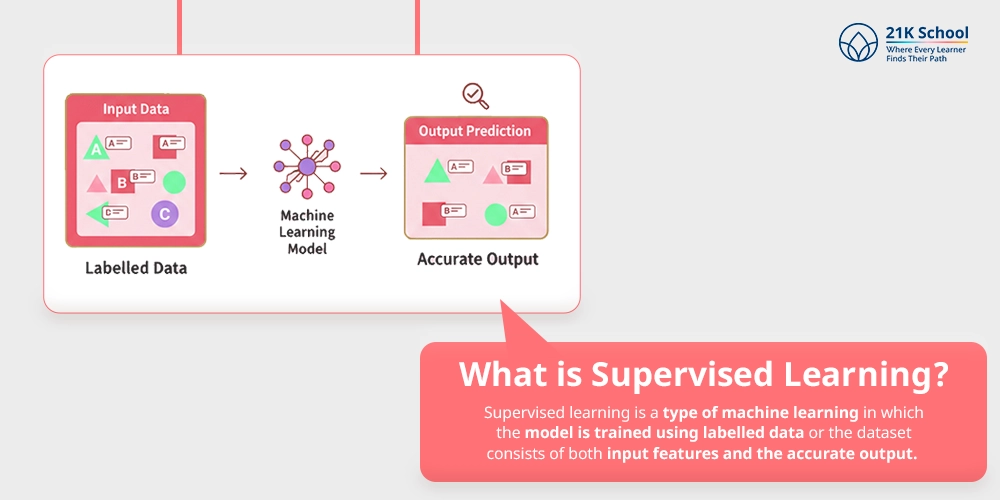
Supervised learning is a type of machine learning in which the model is trained using labelled data or the dataset consists of both input features and the accurate output.
What is Unsupervised Learning?
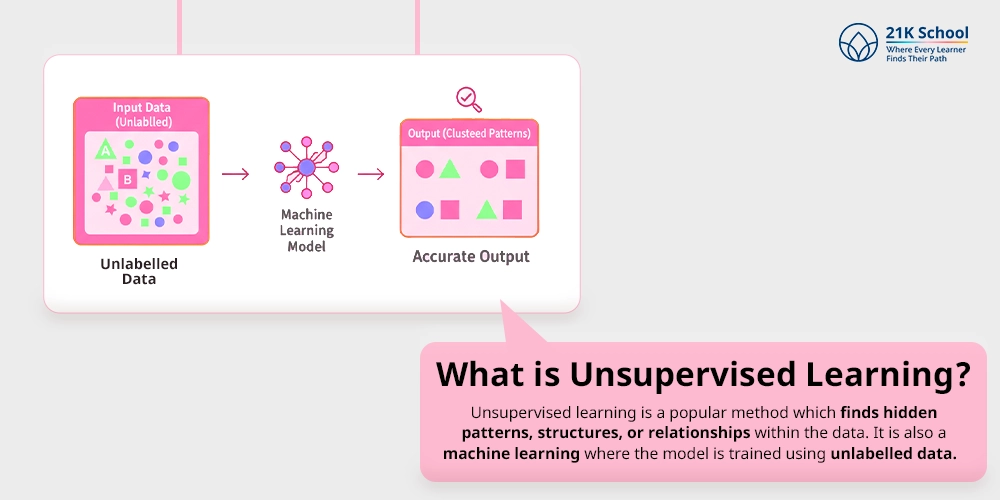
Unsupervised learning is a popular method which finds hidden patterns, structures, or relationships within the data. It is also a machine learning where the model is trained using unlabelled data.
It is often used to seek unknown data, discovering patterns, and building recommendation systems.
12 Key Differences Between Supervised and Unsupervised Learning
Mentioned below table provide a quick analysis of differences between supervised and unsupervised learning:
| S No. | Particulars | Supervised Learning | Unsupervised Learning |
| 1. | Meaning | Supervised learning means an algorithm learns from labelled data with predefined outputs. | Unsupervised learning means an algorithm learns from unlabelled data without predefined outputs. |
| 2. | Goal | Here, the goal is to predict outcomes accurately. | Here, the goal is to explore data and identify hidden patterns. |
| 3. | Data Requirement | Supervised learning requires large labelled datasets. | Unsupervised learning mainly uses unlabelled datasets. |
| 4. | Algorithm Type | Classification and regression. | Clustering, association and dimensionality reduction. |
| 5. | Accuracy | Accuracy here is generally high due to labelled data. | On the other hand, accuracy in unsupervised learning is lower because patterns are inferred. |
| 6. | Complexity | Supervised learning is more complex due to labelled training. | Unsupervised learning is comparatively simpler than supervised learning. |
| 7. | Use Cases | It is used for spam detection, fraud detection. | It is used for customer segmentation, anomaly detection. |
| 8. | Output Type | The output is predictive. | The output is descriptive. |
| 9. | Training Time | Training time is usually longer. | Training time is comparatively faster. |
| 10. | Dependency | It depends on labelled data quality. | It depends on hidden structures in data. |
| 11. | Classification | Supervised learning classifies data based on trained labels. | Unsupervised learning automatically divides data into groups. |
| 12. | Example | Predicting house prices. | Grouping shopping behaviour. |
1. Meaning
Supervised Learning: It is an algorithm in which individual train models by using labelled data.
Unsupervised Learning: It is an algorithm where individual train models by using unlabelled data.
2. Goal
Supervised Learning: The main goal of supervised learning is to identify correct outputs for new data.
Unsupervised Learning: The main goal of unsupervised learning is to discover the hidden structure of the dataset.
3. Data Requirement
Supervised Learning: In supervised learning, large labelled datasets are required.
Unsupervised Learning: In unsupervised learning, unlabelled data is needed.
4. Algorithm Type
Supervised Learning: The type of algorithm used in supervised learning are classification and regression problems.
Unsupervised Learning: The type of algorithm used in unsupervised learning are clustering, association, and dimensionality reduction.
5. Accuracy
Supervised Learning: It is highly accurate and offers a clear outcome.
Unsupervised Learning: It is comparatively low in accuracy.
6. Complexity
Supervised Learning: It is more complex than unsupervised learning.
Unsupervised Learning: It is simpler and flexible to use.
7. Use Cases
Supervised Learning: Spam filters, fraud detection, medical diagnosis, stock price prediction etc.
Unsupervised Learning: Market segmentation, anomaly detection, pattern recognition.
8. Output Type
Supervised Learning: The output is predictive.
Unsupervised Learning: The output is descriptive in case of unsupervised learning.
9. Training Time
Supervised Learning: It usually takes longer due to accuracy.
Unsupervised Learning: It requires comparatively less time.
10. Dependency
Supervised Learning: Supervised learning depends on accurate labels.
Unsupervised Learning: On the other hand, unsupervised learning depends on the natural structure of the data.
11. Classification
Supervised Learning: It classifies data into predefined classes.
Unsupervised Learning: While it finds groups within data.
12. Example
Supervised Learning: Examples such as predicting exam scores based on students’ study hours .
Unsupervised Learning: Examples such as grouping individuals in the classroom by learning styles .
Advantages and Disadvantages of Supervised Learning
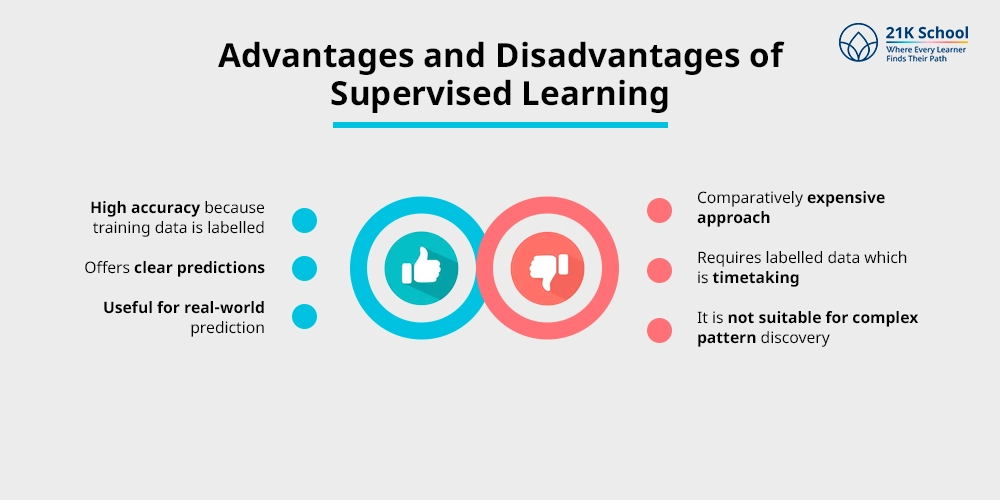
Some common advantages of supervised learning includes:
- High accuracy because training data is labelled.
- It offers clear predictions.
- Useful for real-world prediction tasks like business.
Some common disadvantages of supervised learning includes:
- Comparatively expensive approach.
- Requires labelled data which is timetaking.
- It is not suitable for complex pattern discovery.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Unsupervised Learning
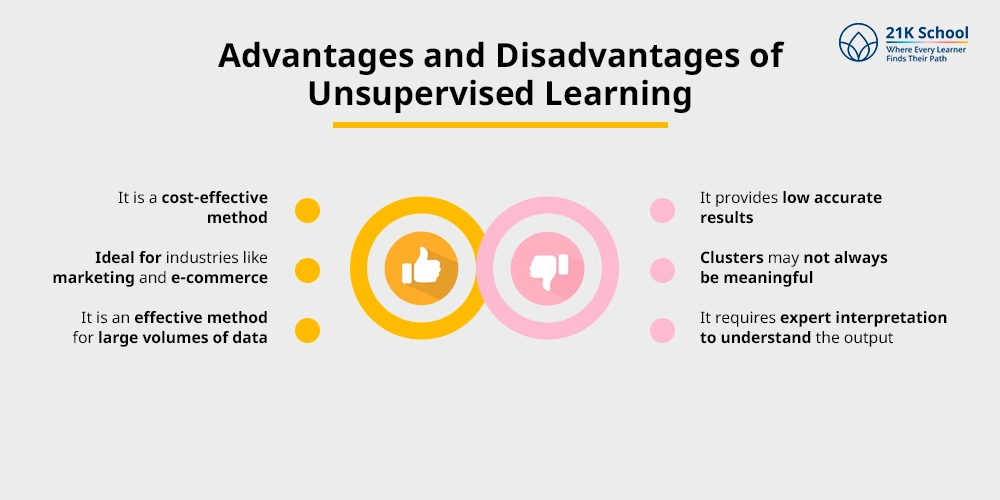
Some common advantages of unsupervised learning includes:
- It is a cost-effective method.
- It is ideal for industries like marketing and e-commerce.
- It is an effective method for large volumes of data.
Some common disadvantages of unsupervised learning includes:
- It provides low accurate results.
- Clusters may not always be meaningful.
- It requires expert interpretation to understand the output.
Conclusion
Machine learning has become an integral part of education in the 21st century. From schools to universities, machine learning implementation enhances students’ learning experiences.
By understanding the meaning, examples, advantages and disadvantages of supervised and unsupervised learning help to choose the right approach.
Remember, for solving data-driven problems select the most appropriate method.