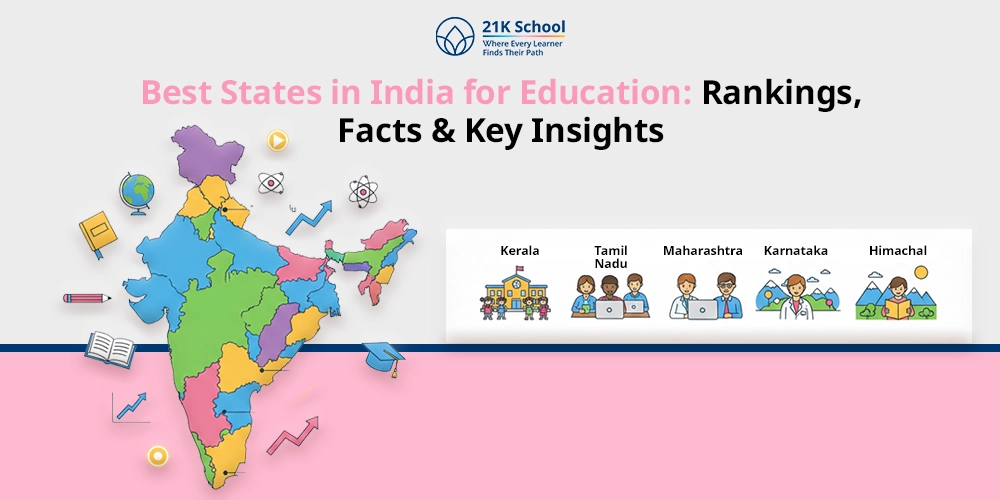
Have you ever wondered why the old 10+2 Indian education system was discredited and presented as the new 5+3+3+4 system?
The latest National Education Policy, 2020 introduced the 5 3 3 4 educational system.
The new structure is more focused on holistic performance and interdisciplinary questioning to tackle the challenge of real life.
In this paper, the implications of the 5+3+3+4 scheme, its phases, key reforms, and benefits have been given.
The later section also covers the comparison of the new system with the older system, and challenges to provide a full picture of the new structure.
Contents
- What is the 5 3 3 4 Education System?
- The Four Stages of 5+3+3+4 System
- Comparison Between New 5+3+3+4 Education System and Old 10+2 System
- Key Features and Reforms of NEP 2020
- How the 5+3+3+4 System Prepares Students for the Future
- Advantages of the 5+3+3+4 Education System
- Challenges in Implementation of the 5+3+3+4 Education System
- Concluding Comments
What is the 5 3 3 4 Education System?
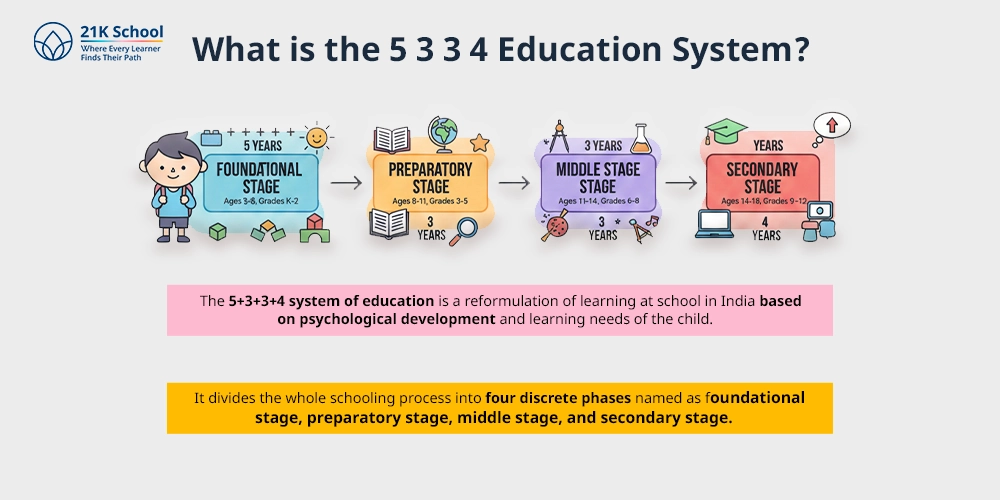
The 5+3+3+4 system of education is a reformulation of learning at school in India based on psychological development and learning needs of the child.
It divides the whole schooling process into four discrete phases named as foundational stage, preparatory stage, middle stage, and secondary stage.
This pattern cuts across the ages 3-18. And in the first instance, it establishes preschooler education as a part of the mainstream schooling sequence.
The system foreshadows play-based learning, discovery-based learning, experiential learning , and competency-based learning in place of rote memorisation.
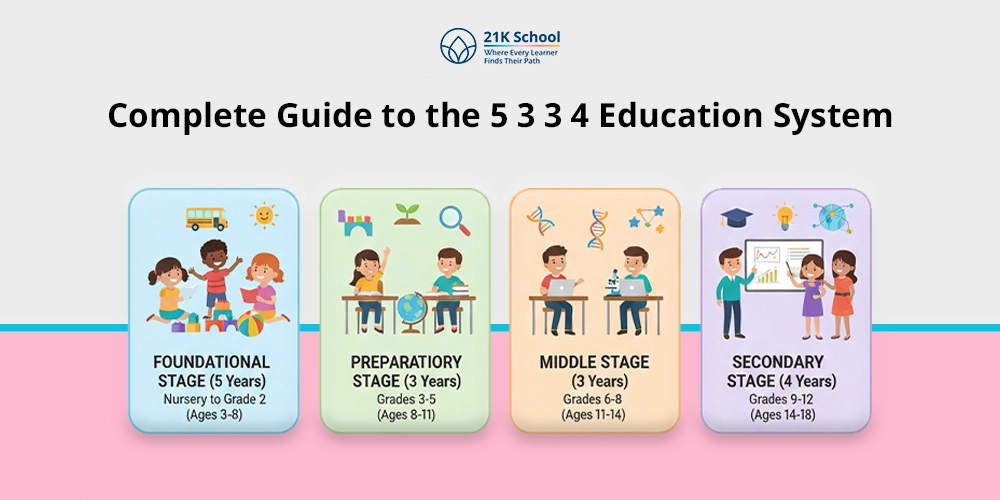
The Four Stages of 5+3+3+4 System
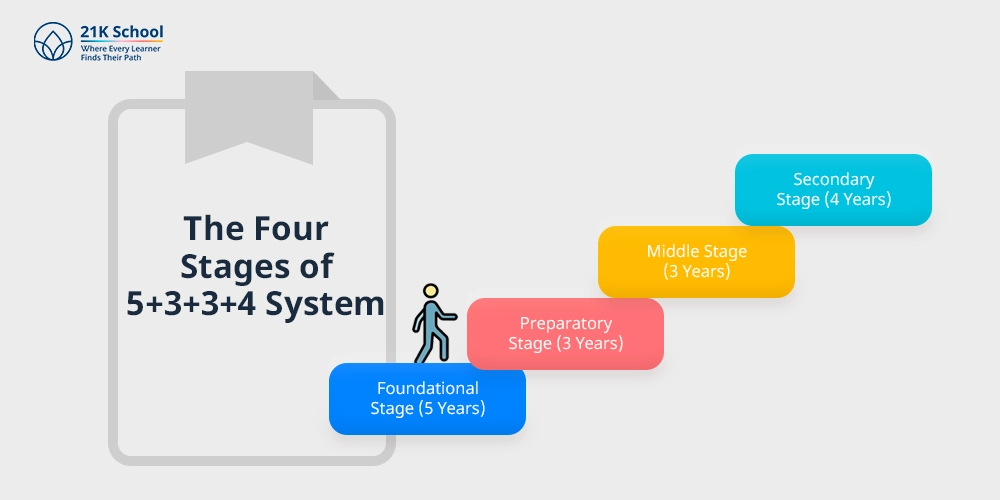
As mentioned in the previous section, the 5 3 3 4 education system comprises 4 functional stages for whole-round development of individuals.
1. Foundational Stage (5 Years)
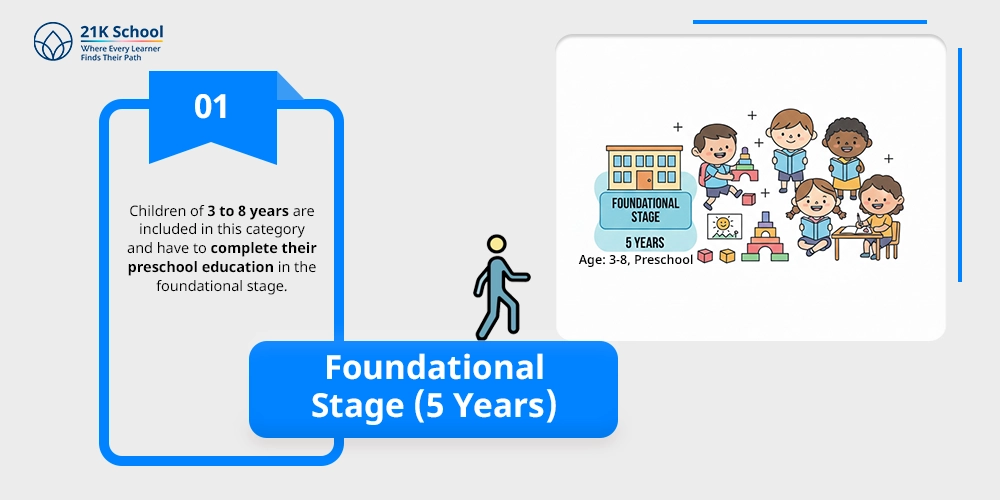
Children of 3 to 8 years are included in this category and have to complete their preschool education in the foundational stage.
This stage is based on activity or can be said to be a play-based learning, where numeracy and basic literacy is prime focus.
Students learn better when they are taught with stories, songs, games, or fun-learning activities .
There is least pressure on students to pass with best marks in assessments.
Teachers teach social-emotional learning , foundation of curiosity, communicational abilities, motor abilities and the early cognitive abilities.
2. Preparatory Stage (3 Years)
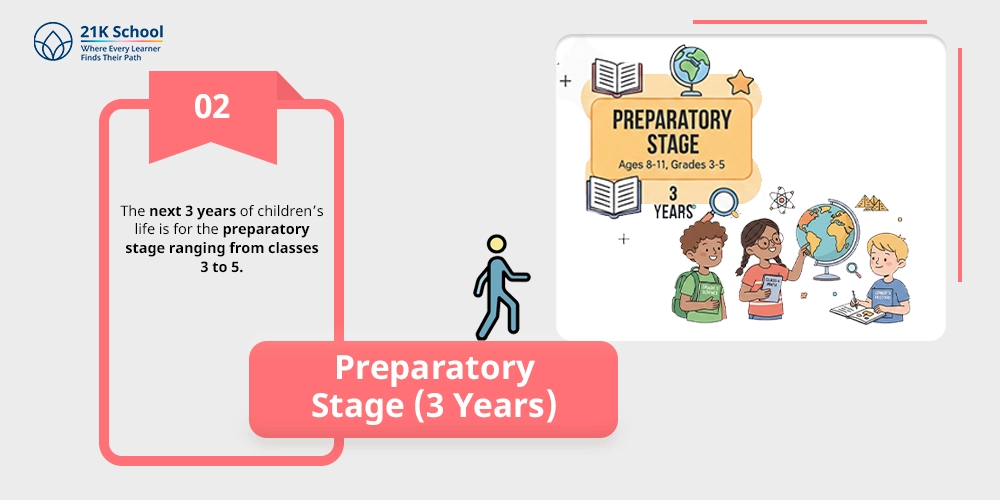
The next 3 years of children’s life is for the preparatory stage ranging from classes 3 to 5.
Learners are shifted from play-based to restricted academic education, where practice-based learning in a less informal classroom setting is first introduced.
This is the first education in reading, writing, mathematics, and languages with practice of art, music, and craft.
This level prepares the students to learn further to internalize knowledge of environmental science, primitive computational thinking , rational problem-solving , and conceptual proficiency.
3. Middle Stage (3 Years)
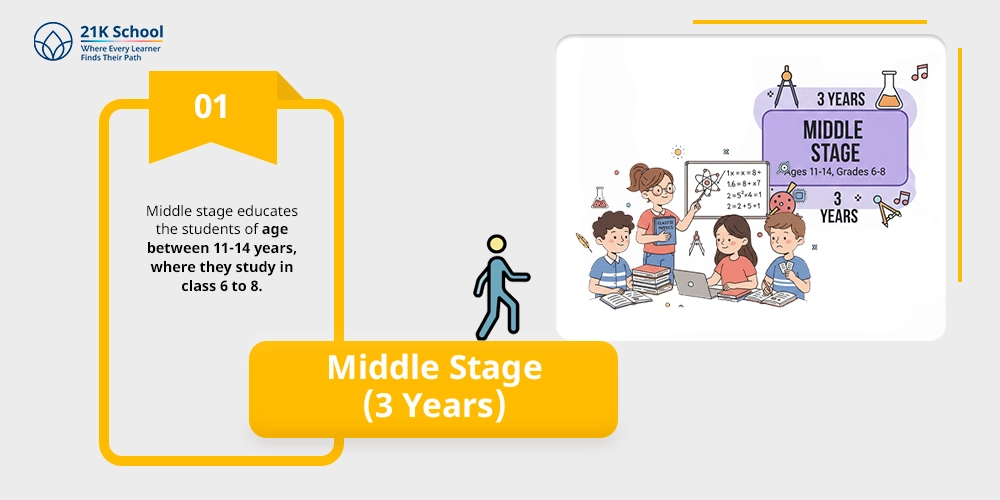
Middle stage educates the students of age between 11-14 years, where they study in class 6 to 8.
This phase is critical towards crystallising the academic inclinations and trying new career opportunities.
The main focus is towards experimentation and research to develop some real base for on-site learning (design, technology, information communication, farming, and coding).
Most common ways to experience education in this stage might include developing critical thinking and self-directed learning .
It simultaneously emphasizes interdisciplinary interconnection and flexibility in curriculum .
4. Secondary Stage (4 Years)
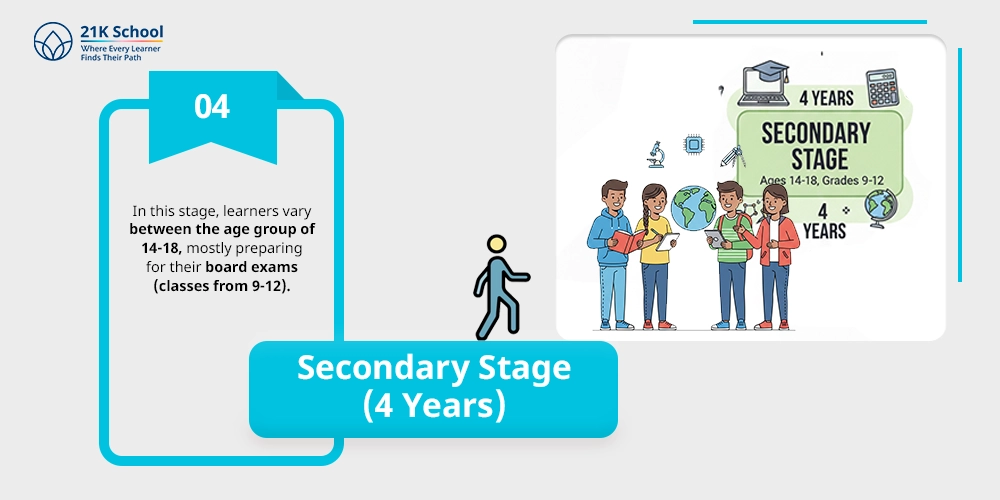
The last stage of the 5 3 3 4 education system is called the secondary stage, which can be said to be the most crucial one.
In this stage, learners vary between the age group of 14-18, mostly preparing for their board exams (classes from 9-12).
It puts emphasis on future preparation for career choices based on personal choices and interests comprising arts, science, and commerce streams.
This gives a multidisciplinary education choice revolving around research, higher-learning, and other internship opportunities.
Comparison Between New 5+3+3+4 Education System and Old 10+2 System
Now, since the basic introduction of the 5 3 3 4 system is completed, we should understand what difference this system brings in comparison to the old 10+2 education model.
We will do this differentiation with the help of a table.
| Aspect | New 5+3+3+4 System (NEP 2020) | Old 10+2 System |
| Structure | 5 years (Foundational) + 3 years (Preparatory) + 3 years (Middle) + 4 years (Secondary) | 10 years (General Schooling) + 2 years (Higher Secondary) |
| Age Group | 3–8 yrs (Foundational), 8–11 yrs (Preparatory), 11–14 yrs (Middle), 14–18 yrs (Secondary) | 6–16 yrs (Class 1–10), 16–18 yrs (Class 11–12) |
| Entry Age | Starts at age 3 (includes preschool/Anganwadi) | Starts at age 6 (no preschool included) |
| Focus | Holistic, skill-based, flexible learning | Primarily academic and exam-focused |
| Foundational Stage (5 years) | Includes 3 years of preschool + Classes 1–2; play-based and activity-based learning | No official preschool stage included |
| Assessments | Continuous, competency-based, includes formative assessments | Mostly summative (annual exams, board exams) |
| Board Exams | Taken in Classes 10 & 12 but redesigned to test application & analysis | Traditional memory-based board exams in Classes 10 & 12 |
| Subject Choice | Flexible subject combinations; no rigid science–commerce–arts streams | Rigid streams (Science, Commerce, Arts) from Class 11 onwards |
| Curriculum Flexibility | Multiple entry/exit points; interdisciplinary approach | Limited flexibility; fixed curriculum |
| Vocational Education | Mandatory exposure from Grade 6 onwards | Minimal vocational training |
| Technology Use | Strong focus on digital learning, coding, computational thinking | Limited emphasis on technology integration |
| Report Cards | Holistic Progress Card including skills, values, extracurriculars | Traditional marks-based report card |
| Language Policy | Emphasis on mother tongue/local language as medium of instruction up to Grade 5 | No fixed policy; varies by school |
| Teacher Training | New National Professional Standards for Teachers (NPST) | Traditional teacher training with fewer reform measures |
| Outcome Goal | Critical thinking, creativity, life skills, flexibility, and employability | Exam scores and content knowledge |
Key Features and Reforms of NEP 2020
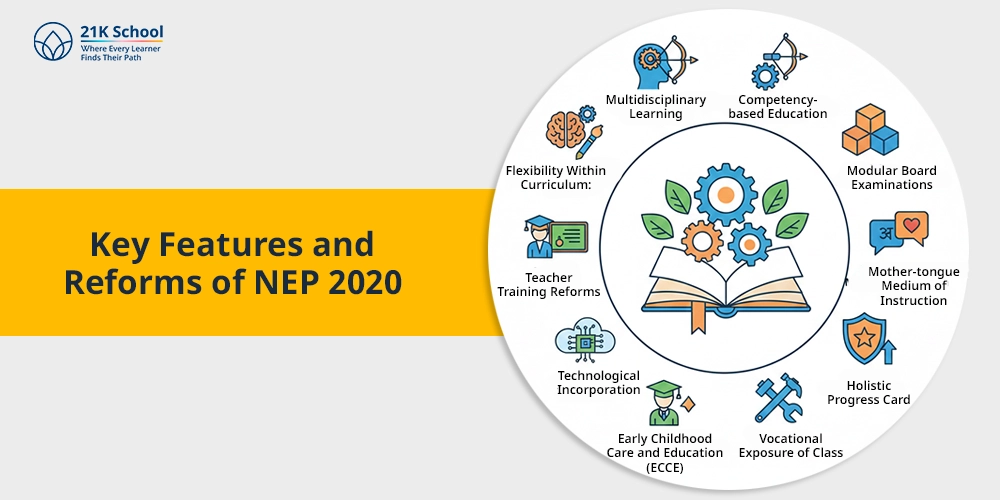
The 5+3+3+4 framework is a single aspect of National Education Policy , (NEP 2020). Principal reforms include:
- Multidisciplinary Learning: The students are free to choose subjects that cut across arts, commerce, and science.
- Competency-based Education: Focus on the skills that are demonstrable instead of the ability to just memorize.
- Modular Board Examinations: Two session tests that allow improving your score to make it easier.
- Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE): Preschool inclusion in formal education .
- Mother-tongue Medium of Instruction: It is held in the native language of the learner at least until Grade 5.
- Holistic Progress Card: The cognitive, social, emotional and physical development are covered for assessments .
- Vocational Exposure of Class: Skills for practice (coding, carpentry, gardening, and entrepreneurial practices).
- Technological Incorporation: Access to online education, artificial intelligence in education , virtual labs, and web-based applications.
- Teacher Training Reforms: A 4-year integrated B.Ed. course and continuous professional training.
- Flexibility Within Curriculum: Discontinuation of predetermined streams and increase in the range of elective options.
How the 5+3+3+4 System Prepares Students for the Future
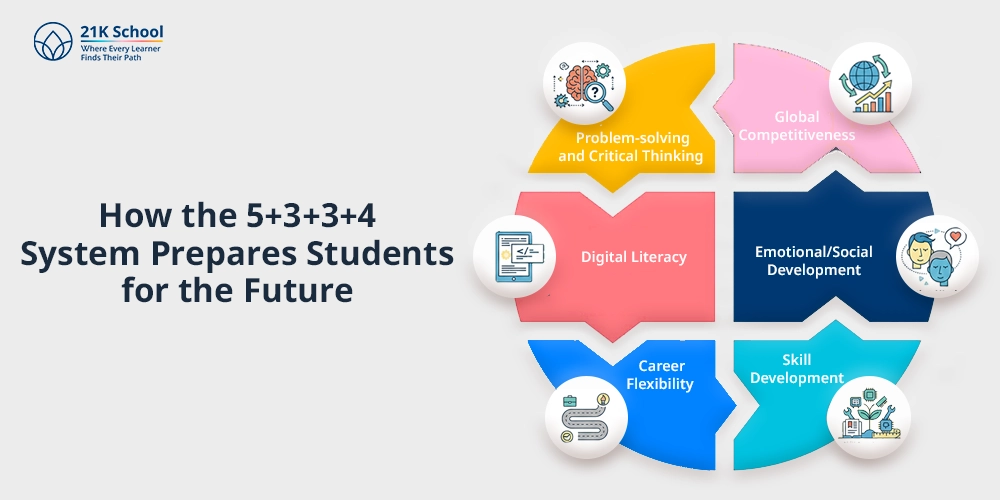
The new system tries to focus on nurturing futuremakers by ensuring that it emphasizes on:
- Problem-solving and Critical Thinking: Projects, problems and experiential learning enable critical thinking instead of rote learning .
- Global Competitiveness: There can be a correspondence with the global standard, including OECD frameworks, which improve the position of India in the world education market.
- Digital Literacy: Coding, robotics and online learning technologies exposure will provide students with modern careers.
- Emotional/Social Development: Holistic development guarantees the gain of empathy , and resilience.
- Career Flexibility: Before students undergo any form of specialization, they get the opportunity to learn various subjects, thus broadening their career horizons.
- Skill Development: Vocational education lays the foundation for entrepreneurship and work competency.
Advantages of the 5+3+3+4 Education System
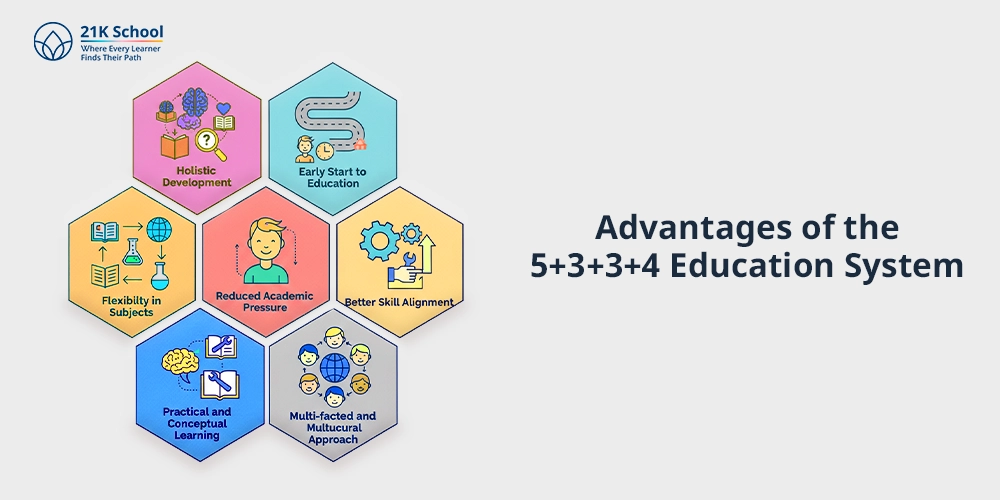
The advantages of the 5+3+3+4 education system are the following:
- Holistic Development: The 5+3+3+4 educational approach gives emphasis on emotional, cognitive, physical, and social development.
- Early Start to Education: Preschool education is established as part and outcome of formal learning from age 3.
- Flexibility in Subjects: A hard line between streams is removed and more flexibility of the curricular process is allowed.
- Reduced Academic Pressure: Academic stress is relieved by a transition to using modular board examinations and competency-based testing.
- Better Skill Alignment: Introduction of the competencies related to the industry, e.g., coding and vocational training, brings learning in line with the current needs of the labor market.
- Practical and Conceptual Learning: Students take part in practical enterprise projects, actual real-life studies, simulations, and multi-disciplinary training.
- Multi-faceted and Multicultural Approach: The mother tongue improves the understanding in lower grades.
Challenges in Implementation of the 5+3+3+4 Education System
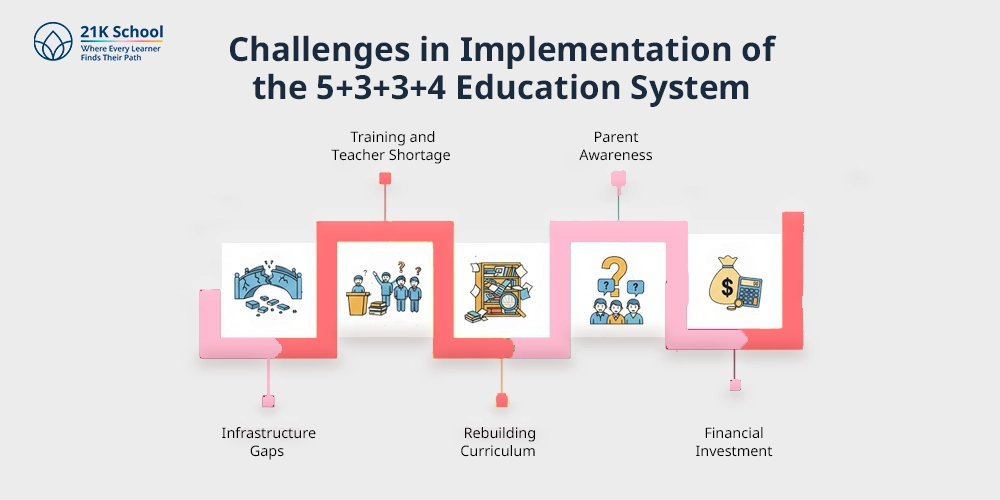
The following are challenges encountered in implementing 5+3+3+4 system of education:
- Infrastructure Gaps: In many schools, especially in rural areas, the schools lack proper laboratories, computers, infrastructure, and play-based learning activities.
- Training and Teacher Shortage: This new system needs a successful body of well-trained educators.
- Rebuilding Curriculum: Schools have to recreate syllabi, modes of instructions, courseworks, and mode of examination.
- Parent Awareness: The parents should be familiar with the new structure to be able to guide the children.
- Financial Investment: Since there is more emphasis on preschools, more investments are needed for infrastructure including play areas, digital equipment, teacher training, and supervision.
Concluding Comments
The 5+3+3+ 4 education system represents an historically important change to a modernized flexible and learner-centred schooling in India.
It is using developmental level-based alignment of education and learning systems with real-world skills, multidisciplinary opportunities.
NEP 2020 expects to produce a generation of confident, and future-ready students.