Ever wondered who decides on your syllabus ?
The National Curriculum Framework (NCF) is a pivotal document shaping the educational landscape in India. It serves as a comprehensive guideline for schools, educators, and policymakers, aiming to provide a unified vision for developing and delivering quality education across the nation.
The NCF plays a crucial role in defining what students should learn, how learning should be assessed, and what educational experiences should be provided to ensure holistic development.
In this article, we will delve into the evolution of NCF, its core principles, the latest developments, and its broader implications on Indian education.
So, what exactly is (NCF) National Curriculum Framework

Contents
- What is National Curriculum Framework (NCF)
- Importance of NCF in Indian Education
- 1. Mirrors Education with Stages of Development
- 2. Attention towards Competency-Based Learning
- 3. Supports Multilingualism and Culture Context
- 4. Promotes Inclusive and Equitable Education
- 5. Brings about Flexibility and Student Choice
- 6. Accentuates Assessment on Learning
- 7. Improves Teacher independence and Training
- 8. Curriculum Development and Textbook Writing
- 9. Capability Building and Autonomy of Teachers
- 10. Inclusive Equitable Education
- The Evolution of the National Curriculum Framework: Historical Perspective
- Practical Examples of How to Implement the 5+3+3+4 Structure in Existing Schools
- NCF 2005 vs NCF 2023
- Difference Between NCF 2000 and NCF 2005
- National Curriculum Framework (NCF) 2022: An Overview
- NCF vs NEP (NCF 2023 and NEP 2020)
- Checklists for Transitioning from Rote Learning to Experiential Learning
- Detailed Analysis of the Newest National Curriculum Framework (NCF 2023)
- 1. Foundational Literacy and Numeracy
- 2. Redesign School Organization: 5+3+3+4 structure
- 3. Interdisciplinary and Practice Learning
- 4. Language and Multilingualism
- 5. Holistic and Competency-Based Assessments
- 6. Vocational Education and Skill Development
- 7. Value and Ethics Based Education
- 8. Textbook Reform and Teacher Control
- 9. Equity, Inclusion and Accessibility
- Competency-Based Education in NCF 2023
- Sample Lesson Plans Showing Competency-based Teaching
- How Parents Can Support Competency-Based Learning at Home
- National Curriculum Assessment Framework
- Templates for Formative Assessment Methods
- The National Curriculum Framework for Teacher Education (NCFTE) 2009 and Beyond
- Challenges and Criticisms of the National Curriculum Framework
- Future of the National Curriculum Framework in India
- Conclusion
What is National Curriculum Framework (NCF)
The NCF or the National Curriculum Framework is a set of guidelines issued by NCERT (National Council of Educational Research and Training) as a policy document concerning curriculum construction and general educational tactical actions in different schools of India.
It provides a system of academic learning which puts emphasis on attainment of Education sector objectives as well as qualities found in the international market.

Vision and Mission of NCF
The NCF has the vision of providing for a vibrant and effective system of education to equip the learners to cope with the future learning environment.
Its work is to make this curriculum internationally competitive but at the same time traditionally Indian oriented.
- Aligning Curriculum with Global Standards: The objectives are intended to narrow the gap between the level of existing Indian education and the level of education that will enable Indian students to successfully compete with students from the rest of the world.
- Promoting Inclusive and Holistic Education: According to the NCF, the education system should accommodate every kind of child regardless of physical disability, among them being children with special needs.
Importance of NCF in Indian Education

National Curriculum Framework (NCF) is a guiding curriculum framework document used in India at all levels of school education. The NCF was devised in the light of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 and is expected to help reshape the Indian education system into a more inclusive, flexible, and learner-centered model. The essentiality of the NCF lies in the following:
1. Mirrors Education with Stages of Development
- Split education into Foundational, Preparatory, Middle, and Secondary phases united on the basis of child development (5+3+3+4).
- Makes curriculum and pedagogy age-friendly, which enhances learning.
- Enhances early childhood learning and formalizes learning at age 3 and above.
2. Attention towards Competency-Based Learning
- Shifts emphasis on rote learning to conceptual learning, use and problem solving .
- Fosters the ability to think critically, to be creative and to collaborate.
- Focuses more on real-life learning and skills, as opposed to textbook learning.
3. Supports Multilingualism and Culture Context

- Supporters of mother tongues or regional language as the language of instruction up to at least Grade 5.
- Incorporates the Indian culture, heritage, and local knowledge systems in the curriculum.
- Accommodates language skills development and readies students in the global arena.
4. Promotes Inclusive and Equitable Education

- Guarantees quality education to every learner including those with disabilities and the marginalized groups.
- Promotes gender sensitivity, value-based education and inclusive classroom practices.
- Reinforces the community in the educational process by localizing the content.
5. Brings about Flexibility and Student Choice
- Enables students to select subjects in each stream (arts, science, vocational) in the secondary school.
- Encourages multidisciplinary studies, which break the hard boundary between academic fields of study.
- Allows students to develop interests at an early stage and create their own learning itinerary.
6. Accentuates Assessment on Learning
- Substitutes high stakes exams with formative assessments, diagnostic assessments and competency-based assessments.
- Incorporates projects, portfolios and peer-assessments to develop roundly.
- Eliminates exam stress and develops a more ongoing and self-assessing mind to the evaluation process.
7. Improves Teacher independence and Training

- Offers a flexible guideline to ensure that teachers creatively construct their lessons.
- Insists on life-long professional growth and application of technology in instruction.
- Promotes teacher participation in curriculum development and innovation.
8. Curriculum Development and Textbook Writing
- Textbooks would be less intense, more interesting, and locally-based.
- Foster customization of resources by schools and teachers depending on the needs of the learners and regional applicability.
9. Capability Building and Autonomy of Teachers
- Enables teachers to come up with lesson plans that fit their students.
- Advocates continued professional learning and reflection teaching.
10. Inclusive Equitable Education

- NCF lays stress on universal access, varied learning needs and mainstream inclusive practices.
- Particular attention to gender equality, inclusion of people with disabilities, rural outreach.
The Evolution of the National Curriculum Framework: Historical Perspective
The evolution of the National Curriculum Framework can be understood by going through the following stages:
1. NCF 2000

The NCF 2000 envisaged to make the education across India more child centred and child friendly.
It sought to call for a decrease in the sets of information that learners were required to learn and make learning more interesting to students.
It aimed at de-emphasizing the formal academic approach and put a lot of the concentration on the practical approaches.
Key Features and Focus Areas:
- Emphasis on value education and ethical development, back then referred as holistic development of students for a brighter future.
- Incorporation of cultural diversity into the curriculum, introducing major and minor languages was a major part of this change.
- Introduction of experiential learning to engage students better, and grab their attention.
2. NCF 2005

Specifically, the NCF 2005 replaced traditional methodologies of teaching with the constructivist approach often referred to.
This approach highlighted the facts that learners build their knowledge congruent with the experience they undergo.
Emphasis on Constructivist Approach:
- Focus on understanding concepts rather than memorization, focusing on quality over quantity and concentrating on learning with a hint of innovation .
- Encouraged interactive and participatory learning methods .
Key Takeaways and Impact on Education:
- Shift from teacher-centred to student-centred learning .
- Integration of life skills and critical thinking into the curriculum, for students to be taught manners, disciplines and skills that make them ready for the future and that can make them individuals with strong will-power.
- Widespread implementation of Continuous and Comprehensive Evaluation (CCE).
3. NCF for Teacher Education 2009

To meet the emerging classroom needs and the new teaching pedagogy, the NCF for Teacher Education 2009 was being formulated.
It emphasised the preparation of teachers as instructional leaders rather than merely as transmitters of information.
Core Principles and Pedagogical Shifts:
- Emphasis on teacher empowerment and professional growth, to ultimately use it for betterment of students.
- Introduction of reflective practices in teaching, to maintain engagement and boost the interest of students towards more skill based practical learnings.
This framework has been particularly influential in informing the development of teacher education programmes to ensure development of necessary teaching skills that support an exciting learning environment.
4. NCF 2022 and 2023

Among the many revolutionary components of NCF 2022 and 2023, in the broader NEP 2020 vision, is the 5+3+3+4 curricular format, which will replace the previous 10+2 format.
The basis of this new framework is the principles of developmentally appropriate learning, which strives to match the educational phases with cognitive, emotional, and physical development of children.
The 5+3+3+4 plan presents the school years in four important stages:
- Foundational Stage (5 years): Ages 3- 8 years, three years of pre-school plus Grades 1 and 2. It puts emphasis on play-based, discovery-oriented learning and provides the foundation of language, numeracy, and social skills .
- Preparatory Stage (3 years): Ages 8 -11 (Grades 3 -5), the preparatory stage starts to get more formal and activity-oriented learning and curiosity, storytelling, and foundational ideas of subjects are encouraged.
- Middle Stage (3 years): Targeting 11-14 (Grades 6-8), the Middle Stage is all about experience learning and opening up the inter-disciplinary subjects, critical thinking and basic exposure to vocational training and digital literacy .
- Secondary Stage (4 years): Ages 14-18 (Grades 9-12), the students will have more flexibility in choice of subjects, and a deeper learning experience, focused on multidisciplinary learning, project-based learning , and higher education / Careers preparation.
The purpose of such a structure is not just academic re- alignment but pedagogical and psychological re-orientation. It promotes a child-based orientation, lessens content overload and incorporates real life learning hence, makes education more inclusive, holistic and significant.
Focus on Competency-Based Education, Digital Integration, and Skill Development:
- Promotion of 21st-century skills , also referred as soft skills: including problem-solving, creativity, and digital literacy.
- Greater focus on personalised and adaptive learning methods, mainly focusing on skill based learning .
The National Curriculum Framework (NCF) has introduced many changes due to the growth in technology, with the use of ICT being embraced in the teaching-learning process.
The integration of the solution in question is expected to enhance the experience students get in their learning institutions, fostering engagement, interaction, as well as making it easy for learners across the country to access resources and content that enriches their studies.
With the help of technologies such as AI, augmented reality and applications in education, the NCF picture the modern classroom as one that is intelligent and responsive to individual learning needs.
It also transforms education to make the students ready for the 21st century through developing skills in the endeavours of technology, making students literate in technology solutions in the future.
Practical Examples of How to Implement the 5+3+3+4 Structure in Existing Schools
Shifting from a 10+2 model of learning to 5+3+3+4 structure in schools can be effectively implement in given ideas:
1. For Foundational Stage (Ages 3 to 8, Pre-school + Grades 1 to 2):

Adoption of playful and discovery-oriented classrooms are ideal for the foundational stage.
Various approaches such as outdoor play, sand/water play, storytelling, phonics, counting with manipulatives can be implemented.
As a teacher, re-designing the daily schedule to provide un-structured activities increases interactions.
2. Preparatory Stage (Grades 3 to 5):

Including simple project work in the stage for example, local environment project, group reading, basic science labs, simple Math problem solving help kids to grow in a better learning environment.
Using various languages and guiding them in multilingual instruction improves their thinking, analysing and responding abilities.
3. Middle Stage (Grades 6 to 8):
For grade 6 to 10 students implementation of delivering interdisciplinary modules is beneficial.
Kids can also connect with vocational skills such as digital skills, local crafts or technologies etc.
4. Secondary Stage (Grades 9 to 12):
In the secondary stage let students choose, encourage deeper learning, project-based and research work.
Implement different kinds of assessments
instead of rote learning or memorisation techniques.
Also, prepare them for higher education by enhancing critical thinking, internships,, ethics.
NCF 2005 vs NCF 2023

NCF 2023 and the National Curriculum Framework 2005 are the two significant landmarks in the development of education in India.
Although both are targeted at enhancing learning outcomes, their contexts, target areas and approaches are very different.
NCF 2005 was largely a reaction to issues of rote learning, exam stress and curriculum overload.
Conversely, NCF 2023 is in alignment with National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, which aims to achieve holistic, flexible, and competency-based education applicable in the 21st century.
| Features | NCF 2005 | NCF 2023 |
| Pedagogical Approach | Learner-focused, activity-based and constructivist | Holistic development focused on experiential learning and critical thinking |
| Method Of Assessment | Formative and continuous evaluations (CCE) for child development | Competency-based assessment, driven by feedback |
| Curricular Focus | Focuses on equity, inclusiveness, and multiple disciplines | Focused on Global competencies, environmental awareness, and developing latest skills |
| Incorporation Of technology | Encouraged use of technology | Dependency on AI, technological gadgets, etc. |
| Teacher’s Role | Facilitator and guidance for learning | Mentor, co-learner, guide, focused on self-regulated learning |
| Lingualism | Learning multiple languages, especial focus on regional ones | Emphasis on mother tongue, developing cognitive skills |
| Curriculum Design | Contextual and flexible | Varies in person-to-person, along with projects and digital integration |
| Global Competencies | Awareness about and multiple cultures and treatment with respect and equity | Critical thinking, problem-solving, and digital literacy for interconnected world |
1. Philosophical Foundation:

- NCF 2005 is grounded on constructivist learning, with its stress on learning through doing and linkage with real life.
- The priorities of NCF 2023 are competency-based learning, integration of digitals, and developmentally-appropriate pedagogy.
2. Curriculum Structure:

- NCF 2005 continued with 10+2 format.
- NCF 2023 proposes a new structure of 5+3+3+4, which means the restructuring of learning stages according to age and cognitive development .
3. Assessment Approach:

- NCF 2005 advocated continuous and comprehensive evaluation (CCE), which however did not have identifiable tools of implementation.
- NCF 2023 lays focus on formative, 360-degree feedback and progress monitoring via portfolios, peer/self-review and competency rubrics.
4. Technology Integration:
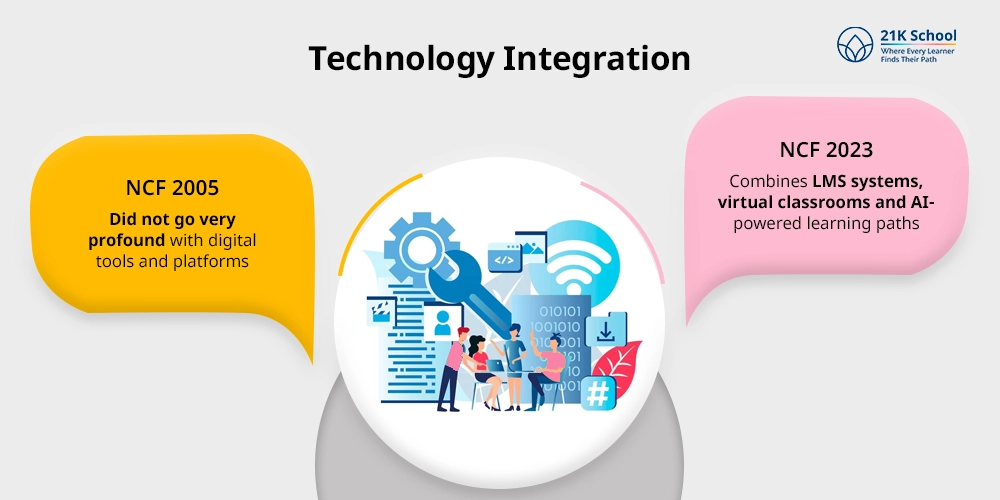
- NCF 2005 did not go very profound with digital tools and platforms.
- NCF 2023 combines LMS systems, virtual classrooms and AI-powered learning paths.
5. Teacher Role:

- Both models urge teachers to act as facilitators.
- NCF 2023 takes it a step further, offering flexibility, digital content and support of on-going professional development .
6. Vocational Education:

- NCF 2005 made some references to life skills, and little reference to learning skills.
- NCF 2023 will start vocational exposure as early as Grade 6, and Skill development will be the core of the curriculum.
7. Inclusivity and Flexibility:

- NCF 2005 talked about inclusion in theory.
- NCF 2023 gives it effect through multiple pathways of learning, multilingual facilitation, and materials that are contextualized to different regions.
Difference Between NCF 2000 and NCF 2005
NCF 2000 to NCF 2005 transition was a move towards replacement of conventional content based education systems to one which gave credence to child centered learning . NCF 2000 upheld traditional standards and emphasized mostly on content and exam preparation.
Contrarily, NCF 2005 brought in a newer, more democratic prospect of education.
| Aspect | NCF 2000 | NCF 2005 |
| Pedagogical Approach | Mostly teacher-based rote learning. And content is too heavy | Mostly child-centred, constructive content. And activity-based learning |
| Assessment | Summative assessment, exams, and tests | Formative assessments, and Continuous evaluation |
| Curriculum Focus | Focused on basically theories, and academic subjects | Focused on holistic development of child with experiential learning and multiple disciplines |
| Inclusion Factors | Addressed differences, but not much emphasis on inclusion | Highly focused on inclusion besides socio-economic disparities, gender, disabilities. etc. |
| Role of teachers | Mostly as instructors | As facilitators providing guidance |
| Language inclusion | Focus on english and hindi, minimal multilingualism | Also include multilingualism, fostering culture development |
| Use of Technology | Not much use of technology | Dependency on technological assets and gadgets |
Important modifications brought about in NCF 2005:
1. Curriculum Philosophy:
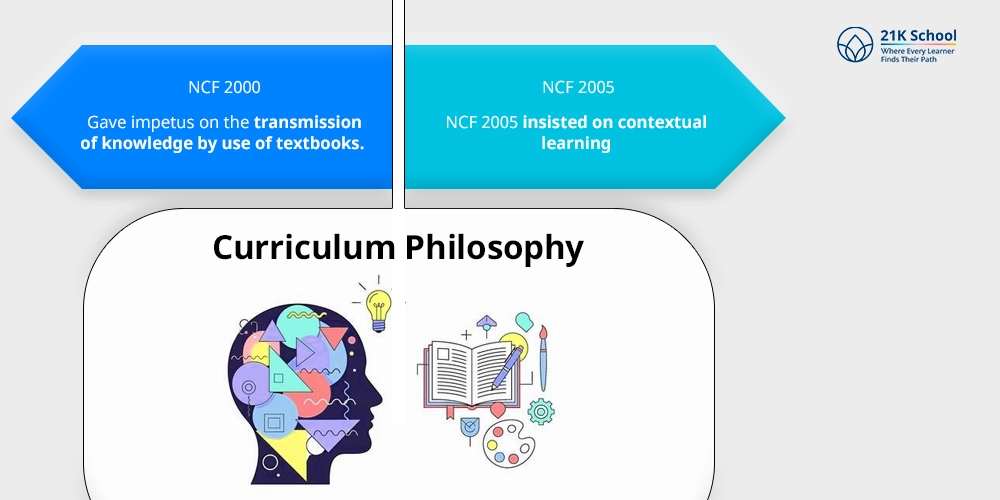
- NCF 2000 gave impetus on the transmission of knowledge by use of textbooks.
- NCF 2005 insisted on contextual learning in which the experience and background of the students were part of the classroom learning .
2. Learning Environment:
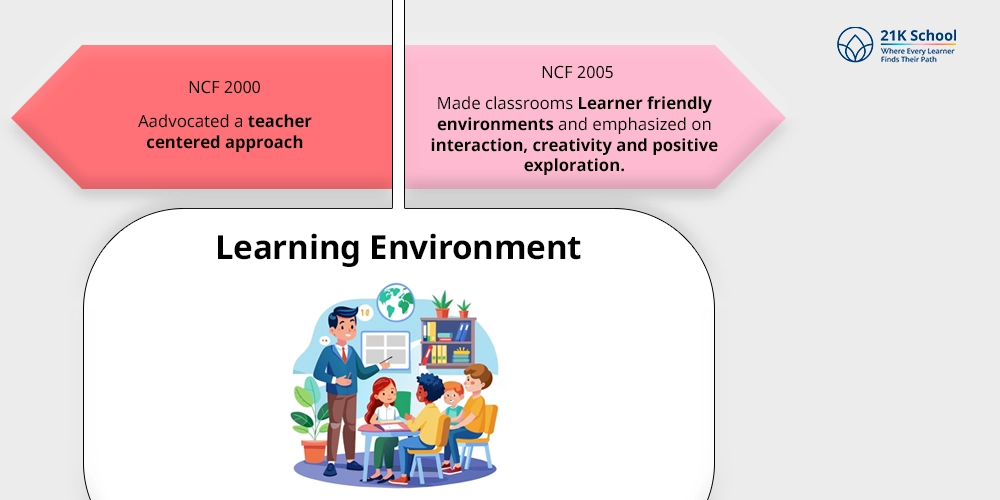
- NCF 2000 advocated a teacher centered approach.
- NCF 2005 made classrooms Learner friendly environments and emphasized on interaction, creativity and positive exploration.
3. Pedagogical Focus:
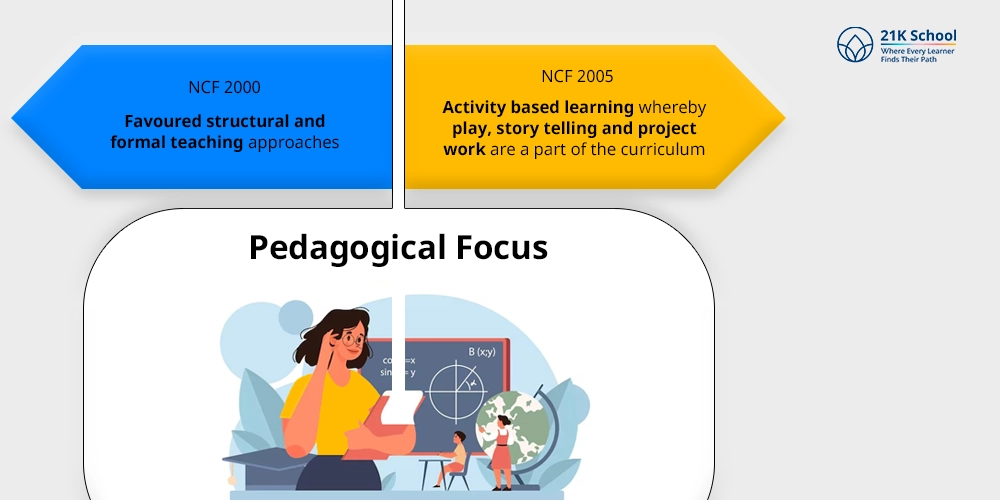
- NCF 2000 favoured structural and formal teaching approaches .
- NCF 2005 has introduced activity based learning whereby play, story telling and project work are a part of the curriculum.
4. Assessment:
- NCF 2000 had a great dependence on summative exams.
- To evaluate the holistic development of a child, NCF 2005 had suggested CCE (Continuous and Comprehensive Evaluation).
5. Social Inclusion:

- NCF 2000 did not pay much attention to inclusion.
- NCF 2005 emphasized quite a lot on gender sensitivity, diversity and inclusion of children with special needs.
NCF 2000 was structural although it was mostly rigid and discipline based. NCF 2005 was radical in moving the discourse to a whole person development, learning with joy and empowerment of the child.
These structural shifts formed the basis of a far more comprehensive and systemic change that would be subsequently suggested in NCF 2023.
National Curriculum Framework (NCF) 2022: An Overview
NEP 2020 is a comprehensive policy paradigm of India’s education structure, which lays the foundation of vision and policy framework for the National Curriculum Framework (NCF) 2022.
It is hoped that the framework will help to transform the current system of education by introducing a student-centered approach, competency-based system, and the full development of the learner.
1. Key Changes in NCF 2022
- Competency-Based Learning: Unlike the traditional methods of learning that teach the students through rote the NCF 2022 focuses on the competency and skills acquired by the student. The new approach is designed to foster actual grasp of the content, problem-solving skills , and application in the real world situations.
- Holistic Education: NCF 2022 encourages development of students holistically, not only their intellectual, but physical and psychological development as well. It introduced the use of life skills, environmental issues and aspects and digital literacy as part of the curriculum as part of a preparation for the future.
- Flexible and Inclusive Curriculum: This flexibility of the NCF 2022 makes it unique to implement in favour of diversifying learning needs and preferences of students. This conceptual framework of curricular programs is to include all children with learning ability and/or socio-cultural diverse needs.
- Focus on Foundational Literacy and Numeracy: Not surprisingly, the NCF 2022 lays significant stress on foundational literacy and numeracy, for the former years of schooling. This corresponds with the government’s vision in the NEP 2020 of attaining 100 percent basic competency in literacy and numeric by grade three.
- Integration of Indian Knowledge Systems: The framework aims at integrating indigenous forms of learning, indigenous languages and indigenous values to provide education to students which have Indian origin but have global orientation.
- Revised Assessment Methods: According to the NCF 2022, there has been a recommendation that over-reliance on achievement tests should be done away with and replaced with a better method of assessing learning. Assessment of the new methods is based on competencies, and skills as well as knowledge rather than rote learning.
2. Implementation of Teacher Training Under NCF 2022

The extent to which the NCF 2022 will be successful will depend on its implementation which entails the process of reviewing and policy, writing and development, reviewing and revising curriculum, texts and teachers.
Teachers’ professional practice is continuously developed further when implementing the curriculum, which enables them to create the learning environment that accords with the mentioned framework.
NCF vs NEP (NCF 2023 and NEP 2020)

The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 is a policy document that envisages the goals and broad principles to transform the Indian education system. It presents goals, values, and structural reforms required in all levels of education- early childhood to higher education.
On the contrary, the National Curriculum Framework (NCF) 2023 is a solid implementation document of the NEP 2020. It gives the elaborate pedagogical roadmap, learning outcomes, subject structures and classroom practices that will bring the vision of NEP to the school level.
Whereas NEP determines the what and why, NCF describes how. They work together like a blueprint and architectural plan that would change the future of education in India.
| Aspects | NEP 2020 | NCF 2023 |
| Nature | It’s a document of policy. | It’s a curriculum framework for implementation. |
| Aim | It confirms broad goals, visions, and targets education systems | It provides a framework for guiding the execution of curriculum of NEP |
| Structural form | Only the 5+3+3+4 plan of education | Pedagogy and content along with 5+3+3+4 structure |
| Scope | Focuses on school to higher education as well (all levels) | Focused only on school (3-18 age) |
| Language Policy | Emphasizes 3 language formula, mother tongue promoted | Operates on multilingual formula in early stages |
| Pedagogical Approach | Enforces experiential and critical thinking-based learning | Details are student-centered and pedagogically categorised for different stages of education |
| Assessment Reform | Suggests shifts for formative assessments and competency-based tests | Proposes biannual exams, CCE, and best-score retention |
| Curriculum Flexibility | Suggests multidisciplinary learning | Defines flexible subject combinations and cross-discipline themes |
| Inclusion & Equity | Advocates for inclusive education and equity | Provides content and classroom strategies for diverse learners |
| Tech in Education | Promotes digital literacy, online learning | Details digital tools, coding, AI basics in curriculum |
| Integration of IKS | Encourages inclusion of Indian Knowledge Systems | Provides guidelines on integrating IKS into subjects |
| Teacher Role | Emphasizes teacher training and professional development | Specifies teacher support systems, capacity building |
| Environmental Education | Calls for ecological awareness | Incorporates sustainability and life skills into curriculum |
| Legal Status | Policy recommendation (not legally binding) | Official framework adopted by NCERT for curriculum development |
1. Policy Framework

The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 is a forward-looking document presenting the aspirations and path of the Indian education system in the 21st century. It gives the what – the ideals, goals and reforms needed in school and higher education.
The National Curriculum Framework (NCF) 2023 on the other hand is the how. The practical guide, organized and structured to give the means and methods to carry NEP suggestions into actual classrooms.
NCF interprets the intentions of NEP into definite curricular forms, content of subjects, teaching methodology and evaluation models.
2. Coverage and Scope

Whereas NEP addresses the full range of education, including preschool, adult education and higher learning, NCF 2023 addresses school education. It particularly addresses the Foundational to Secondary level curriculum planning, which is in line with the 5+3+3+4 framework suggested in NEP.
NEP talks of broader reform issues such as equity, access and lifelong learning . But NCF makes sure that these issues are operationalized in terms of text books, classroom curriculum, lesson plans and teacher training modules.
3. Execution and Purpose

NEP was initiated in 2020 to lead to long-term educational policy in India. According to its principles, NCF has been created in stages between 2022-23, and the feedback was taken in by teachers, parents, students, and academic experts across the country.
NEP preconditioned the shift to such changes as competency-based education, multilingual learning, and the decreased curriculum load. NCF provides these concepts with implementation clarity, outlining what learners are expected to get at every stage and how teachers can facilitate the process.
In effect, NEP is the vision; NCF is the working blueprint.
Checklists for Transitioning from Rote Learning to Experiential Learning
Go through a quick checklist for for schools and teachers for transitioning from rote learning to experiential learning:
✅ Detailed review on latest curriculum to understand rote-based modules or materials.
✅ Introduce strategy based on practical knowledge or competency-based learning.
✅ Incorporate educational activities and learning as a team to implement discussion instead of lectures.
✅ Include hands on activities different kind of projects relevant to subject matter.
✅ Use of engaging teaching techniques like stories, case studies, local examples to contextualise learning.
✅ Reducing assignments related to memorising and implementation of application based learning.
✅ Facilitators should families about inquiry-based, activity-based, and project-based methods to implement experiential learning effectively.
✅ Provide needful resources for experiential learning to avoid rote learning.
✅ Gather information from learners about which activity is favourite and help them to implement in daily life.
✅ Monitor facilitators teaching technique for correct execution.
Detailed Analysis of the Newest National Curriculum Framework (NCF 2023)

National Curriculum Framework (NCF) 2023 is a historic educational reform document formulated keeping in tune with the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020. It brings about a learner-centered, adaptive and competency based school education in India.
NCF 2023 is based on the new 5+3+3+4 structure, and incorporates the learning needs of children between the ages of 3 and 18, in four stages- Foundational, Preparatory, Middle, and Secondary.
Its framework focuses on basic literacy and numeracy, holistic development, experiential learning, representation of Indian systems of knowledge, multilingualism, life skills and environmental awareness.
Being relatively keen on the inclusive, culturally situated and technology-inclusive education, it disregards rote learning and fosters critical opinion, creativity and health.
Though it holds the promise to change the Indian education system into an equitable and future-ready pattern. Iits realization will depend on the ability of teacher training, infrastructural reinforcement and wise dissemination in various regions.
1. Foundational Literacy and Numeracy

A key area of concern of NCF 2023 is Foundational Literacy and Numeracy (FLN) by the end of Grade 3. This involves developing early reading, writing and calculating ability.
NCF encourages play-based learning and discovery-based learning in early years particularly in the Foundational Stage (ages 3-8).
Rather than imposing academic stress at a young age, the model emphasizes happy learning, communication, and storytelling as the main teaching tools.
2. Redesign School Organization: 5+3+3+4 structure

NCF follows and implements the 5+3+3+4 curricular framework that was presented in NEP. The initial five years ( Foundational Stage ) are concerned with play and early language/math growth.
The following three years (Preparatory Stage) bring formal education in an interactive way. The Middle Stage has more subject-specific instruction and the Secondary Stage (Grades 9-12) has more flexibility in choosing subjects.
The shift makes teaching developmentally appropriate, and students progress through the system in harmony with their mental, emotional and physical development.
3. Interdisciplinary and Practice Learning

One of the key ideas of NCF 2023 is to promote interdisciplinary ties and experiential learning. Rather than approaching each subject separately, the framework allows integrated learning experiences.
So that, for example, math and science may overlap in the real-life project.
Learning in classrooms is meant to be experiential and heavily focused on projects, field work and inquiry-based assignments. The students are required to make creative applications of the knowledge as opposed to memorization of facts.
4. Language and Multilingualism

The framework endorses the NEP suggestion that mother tongue or local language should be the medium of instruction up to Grade 5, and preferably thereafter as well. NCF points out that language learning at an early age in a familiar language develops understanding and cognition.
It also supports the slow introduction of other languages in addition to the regional languages instruction. Thereby supporting multilingual classrooms and language-enriched environments.
5. Holistic and Competency-Based Assessments

NCF 2023 offers a less rigid and skill-focused evaluation structure in lieu of the conventional rote-based testing system. The students are assessed based on their skills and knowledge and not mere recall.
These are formative assessment, 360-degree report cards, portfolios and peer/self-assessment. Assessment should be used to support students in their learning process, assisting the teacher to determine gaps and adjust accordingly.
6. Vocational Education and Skill Development

Beginning with Grade 6, NCF 2023 makes vocational education a part of mainstream curriculum. The students get exposed to more practical fields like agriculture, carpentry, electronics, tailoring, and even the current digital-related abilities like coding and AI.
This is meant to build life skills and work readiness that would prepare students towards many careers and life situations. Thus, indicative of a larger objective of the NEP to fill in the gap between theoretical and applied education.
7. Value and Ethics Based Education

The other critical component of NCF 2023 is the introduction of values education. The framework will enable sensitizing the students to the Indian Constitution, ethical conduct, empathy , accountability, and global citizenship.
It promotes education practices that enable children not only to be knowledgeable, but also dutiful and respectful members of the society. Important aspects that are introduced into the content of subjects are sustainability, an attitude to diversity, and civic awareness.
8. Textbook Reform and Teacher Control

The textbooks under NCF 2023 will be lighter, contextually relevant, and interactive. It is about making content more involving, overload less and the scope to adapt regionally.
Also, there is more freedom provided to teachers to interpret the curriculum, create learning experiences and employ various teaching methods. Therefore, teacher training and mentoring systems are highly recommended by NCF, so that the teachers are prepared to deal with diverse learning needs.
9. Equity, Inclusion and Accessibility

NCF 2023 is built on the concept of inclusivity. The framework supports quality education to all students irrespective of their gender, socio-economic status, and physical ability. Learning contents and plans are made to be dynamic and available.
It also encourages individualized learning with the view of accommodating children with special needs. Further helping learners who are marginalized, those who live in remote areas or underprivileged locations to get education.
Competency-Based Education in NCF 2023

It is important to understand what Competency-Based Education is or CBE for short. CBE can be defined as an education system that concentrates its delivery on competencies rather than on subject knowledge. This should come up with learners that are in a position to apply that knowledge in problem solving in real life.
Among the changes introduced to the latest NCF (2023), the concept of competency-based education (CBE) has a special place. Contrary to the strategies of memorised learning that are still employed in some of the institutions, CBE aims at the cultivation of competence competencies among the learners.
This means that a student is assessed on how well they are able to solve problems that are real life situations by coming up with solutions on their own.
The types of assessment have also changed with an emphasis on Those which are formative in that they provide information regarding the student’s performance for purposes of learning rather than for evaluation purposes like end of term examinations.
Sample Lesson Plans Showing Competency-based Teaching
Competency-based teaching shifts learners’ attention away from rote learning by providing specific skills or “competencies”.
Given below is a subject wise example one must look to understand in-depth:
Sample Lesson Plan: Grade 4 Science Subject: “Water Cycle”
| S.No. | Competency | Details |
| 1. | Competency | Students are able to explain different stages of the water cycle, its importance in the environment and design simple models to showcase evaporation, condensation, and precipitation. |
| 2. | Duration | 45 minutes |
| 3. | Learning Outcomes | Detailed explanation of evaporation, condensation, and precipitation.Understanding the impact of the water cycle in nature. Showcasing various factors that impact the water cycle. |
| 4. | Materials | Materials required include a ziplock bag, water, blue food colouring, sponge or paper towels, heat lamp / sunlight, glass bowl, plastic wrap. |
| 5. | Teaching Methods | By showing pictures, all videos ask learners what is going on in the process. Use a diagram to showcase each stage and ask them to make a model. Later discuss the process through the model and end up with its importance and ways to propose a solution for human negative affects. |
| 6. | Formative Assessment | To showcase all the three stages teachers can make small groups in the classroom and ask them to prepare a quick presentation for review. |
How Parents Can Support Competency-Based Learning at Home
At home, parents can support kids in competency-based learning (CBL) by taking care of the mentioned points:
1. Create a Supportive Learning Environment
Parents can help learners by stabilising a positive learning environment like quiet study space, providing the required resources like stationary, art supplies, educational games etc.
They can also set or monitor study routines for high productivity.
2. Promote a Growth Mindset and Self-Regulation

Promoting a growth mindset and self regulation encourages learner work with more concentration.
This encourages students curiosity and creates an environment for open ended questions. Motivation encourages self-regulation in children.
Remember, to praise efforts, not just outcome.
3. Engage in Active and Hands-On Learning

Including daily activities at home such as gardening, or shopping help learners to connect with real life situations.
Use various educational resources for example, learning apps, virtual libraries, and video tutorials. Monitor screen time and distraction.
4. Maintain Strong Communication
Parents can connect with teachers to understand kids’ academic progress, strength and weak areas that need improvement.
This will help them to set a clear goal on how to proceed and align tasks and routine to reach desired milestones.
National Curriculum Assessment Framework

- Shift from Rote Learning to Formative Assessments: The NCF 2023 proposes a significant shift in the education sector towards formative assessments, focusing on continuous evaluation rather than one-time exams, ensuring overall development and long lasting impact with better accountability and scope of improvement.
- Role of Continuous and Comprehensive Evaluation (CCE): CCE plays an important role in assessing both academic and non-academic aspects of a student’s development, based on soft skills, time management and even problem solving capabilities.
Templates for Formative Assessment Methods
Given below is a templates for formative assessment methods beneficial for teachers and facilitators use:
| Criteria | Excellent | Good | Satisfactory | Needs Improvement |
| Understanding of topic / concept | Shows deep understanding; can explain to others | Solid understanding; minor gaps | Basic understanding; some misconceptions | Many misconceptions; needs more help |
| Application / Problem solving | Applies concept in new contexts accurately | Good application with small errors | Can apply in familiar context; struggles with novelty | Struggles even in familiar context |
| Presentation / Clarity | Very clear, organised, well expressed | Mostly clear; small lapses | Somewhat confusing or disorganised | Needs improvement in organising & expressing |
| Creativity / Originality | Offers novel ideas or perspectives | Some creative effort | Limited originality | Copying, minimal creativity |
The National Curriculum Framework for Teacher Education (NCFTE) 2009 and Beyond

- Addressing the Needs of Modern Classrooms: The NCFTE 2009 was established with the aim of making teachers ready to face and control the changing nature of classrooms.
- Professional Ethics and Values: He endeavours to locate moralistic teaching principles put forth in the work: demonstrating that teachers should also follow the highest standards of conduct.
- Revised Frameworks and the Road Ahead (Post-2023): The post-2023 development priorities are concerned with the use of ICT and Other innovative pedagogy approaches.
The following are the consequences or outcomes of the implementation of NCF in Schools Self implementation of the components of NCF in schools In order to effectively implement the components of NCF in school, several outcomes mentioned below are expected to be achieved.
1. The New NCF Guidelines: How Schools are Implementing Them

Challenges in Implementation: Great difficulties experienced in schools are attributable to regional inequality, poor funding, and concern over autonomy from pre-specified conventional practices.
Role of Educational Technology: Various technologies and technologies have been helpful in promoting the standards provided for in NCF guidelines.
2. Concepts for Cognition and Knowledge and the Importance of Stakeholders

The implementation of NCF in the teaching learning process is the responsibility of teachers with the following functions;
It instructs that teachers play a role of a role model in the learning process, moving from being viewed as agents of knowledge transfer.
Role of Parents and Community
This paper agrees with the general notion that parental involvement plays an important role in the rendering of NCF. Such participation from the community is useful as far as development of curriculum is concerned due to creation of a favourable environment.
Challenges and Criticisms of the National Curriculum Framework

1. Challenges Faced in Implementing NCF

However, there are major challenges regarding teaching-learning infrastructure, interstate inequality, and the scarcity of qualified teachers in the implementation of the NCF.
2. Criticisms of NCF
Several scholars have pointed out that technology is becoming the leading mode of delivering education, yet many students cannot afford it.
Another challenge lies in finding the right balance between standardization and flexibility as a strategic emphasis.
Future of the National Curriculum Framework in India

What Lies Ahead for NCF?
The future NCF is expected to adopt the best practices from around the world and incorporate AI and other emerging technologies into teaching and the curriculum.
Conclusion
National Curriculum Framework is the most progressive change in the Indian system of education to hone young learners for the future towards sustainable education .
They believe it could help eliminate learning gaps and help design the curriculum of the future, thus developing an integrated one.