
Entering a school, college, or university is the start of an exciting journey for each student.
But, before entering, how to check the quality standard and an institute provides.
Here come “accreditation” and “affiliation” the two important terms often used to ensure quality and build relationships.
To understand the concepts and key differences between accreditation and affiliation, go through the following blog.
Contents
What is Accreditation?

Accreditation is a kind of grant given to educational institutions or programs that meet the pre-set criteria or standards.
There are many parameters that confirm the learning quality standard like teaching quality, curriculum, infrastructure, faculty qualifications, student outcomes, and many more.
Learn what is accredited online school .
What is Affiliation?
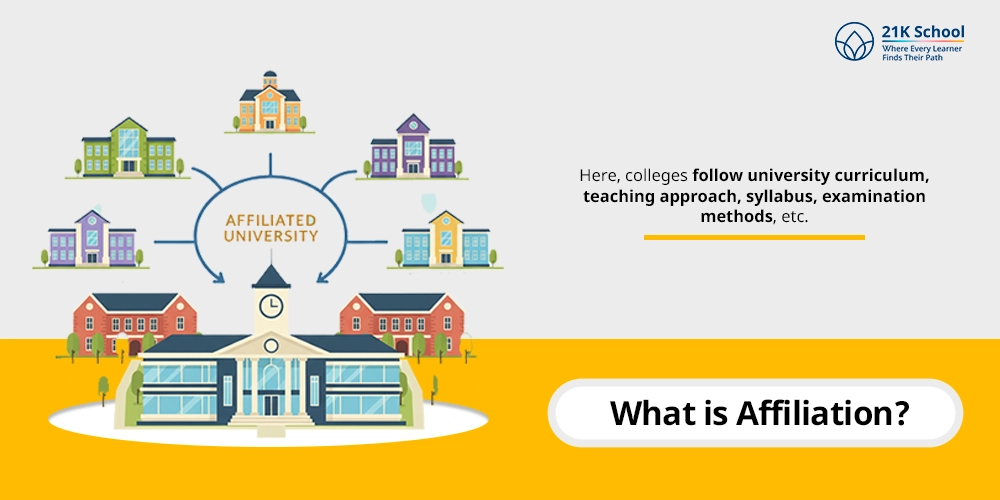
Here, colleges follow university curriculum , teaching approach , syllabus, examination methods, etc.
For focusing on quality education it is an effective opportunity.
10 Key Difference Between Accreditation and Affiliation
Accreditation and affiliation both are important for institutions. The given details showcase a key comparison of both the terms.
| S No. | Aspects | Accreditation | Affiliation |
| 1. | Definition | To maintain the quality standards, it is a recognition given to institutions. | It is a procedure in which an institution connects with a board or university to conduct courses/exams. |
| 2. | Core Purpose | The core purpose is to maintain the quality and standard of an institution. | It offers courses, follows a curriculum and conducts exams to grant permission for an institution. |
| 3. | Authority | NAAC for colleges/universities and NBA for technical programs. | It is granted by educational boards or universities. |
| 4. | Focus | The main focus is to enhance the quality, environment, and student outcome. | The main focus is to follow rules, curriculum standards, and exam process. |
| 5. | Process | In accreditation, the process is an independent, often periodic, evaluation and validation process. | In affiliation, the process includes application, inspection, and approval. |
| 6. | Nature of Relationship | Independent. | Dependent. |
| 7. | Evaluation Criteria | It is mainly depends on: teaching-learning qualityresearchinnovationstudent supportgovernance. | It depends on:infrastructurestaff qualificationsfacilities etc. |
| 8. | Outcome/Impact on Students | Here, students receive high quality education. | Here, they receive valid certifications and degrees. |
| 9. | Duration and Renewal | It is valid for a fixed period for example 5 years and needs periodic renewal after re-evaluation. | It continues as long as the institution requires. |
| 10. | Example | “A college accredited by NAAC or an engineering program accredited by NBA.” | “A college affiliated to Mumbai University or a school affiliated with ICSE board.” |
1. Core Purpose
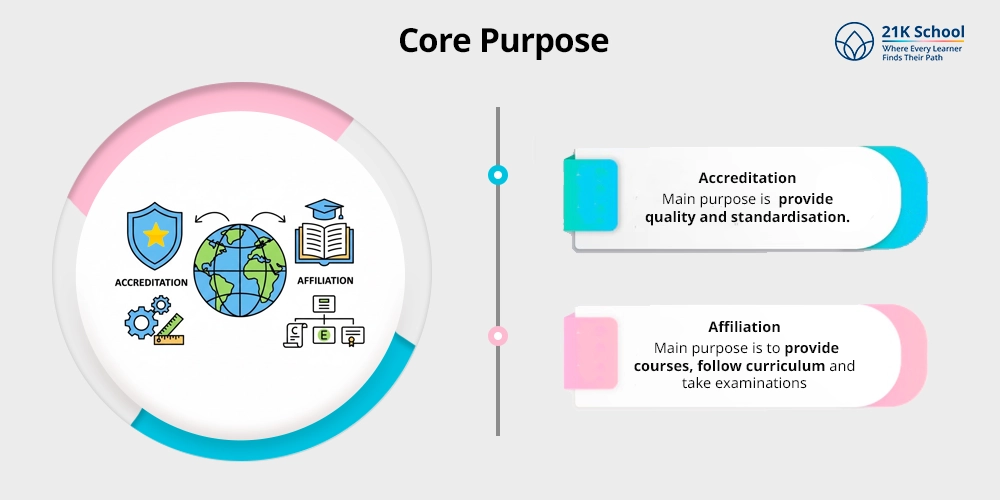
- Accreditation: The main purpose of accreditation is to provide quality and standardisation.
- Affiliation: While in affiliation the main purpose is to provide courses, follow curriculum and take examinations to grant permission to conduct effectively.
2. Authority
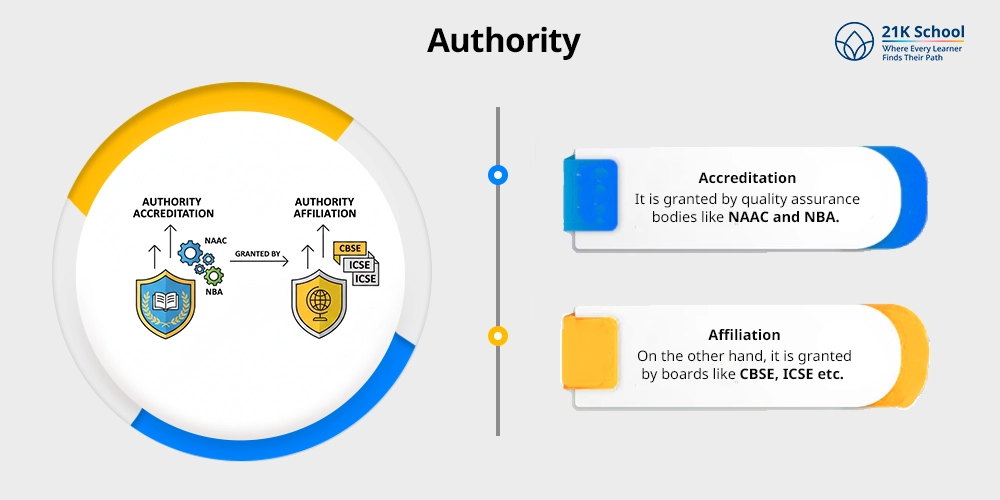
- Accreditation: It is granted by quality assurance bodies like NAAC and NBA.
- Affiliation: On the other hand, it is granted by boards like CBSE, ICSE etc.
3. Focus
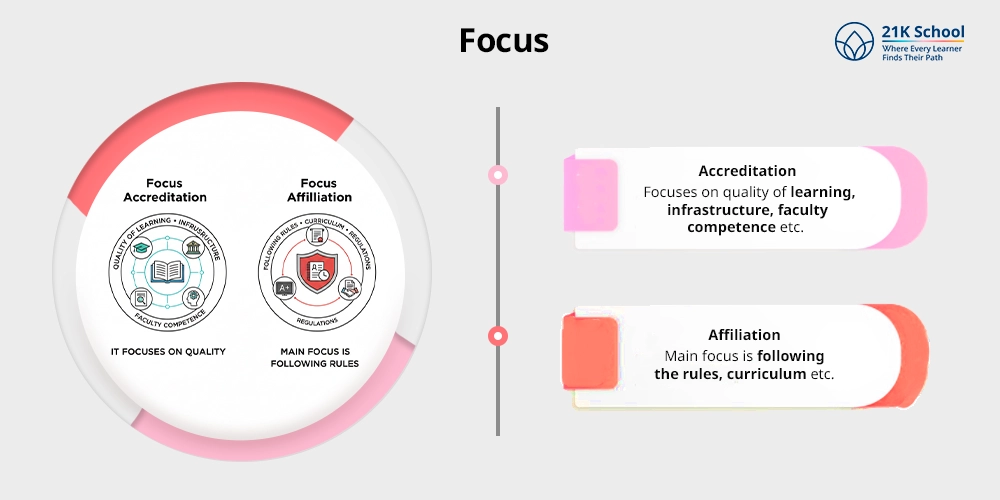
- Accreditation: It focuses on quality of learning, infrastructure, faculty competence etc.
- Affiliation: While here the main focus is following the rules, curriculum etc.
4. Process
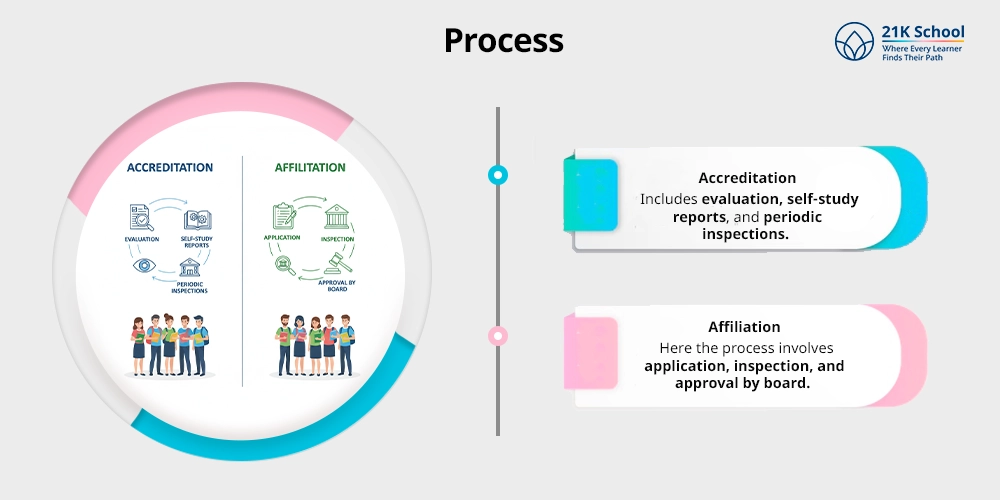
- Accreditation: The process simply includes evaluation, self-study reports, and periodic inspections.
- Affiliation: Here the process involves application, inspection, and approval by board.
5. Nature of Relationship
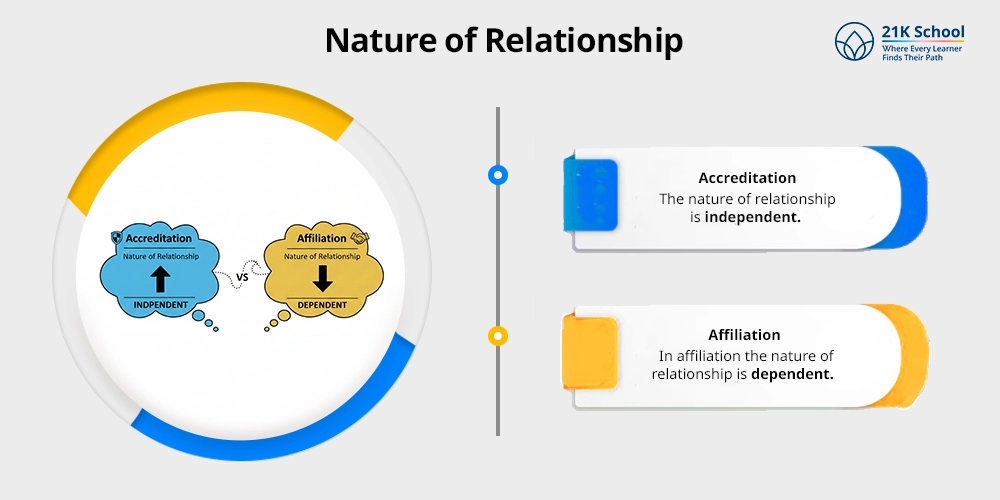
- Accreditation: In accreditation, the nature of relationship is independent.
- Affiliation: On the other hand, in affiliation the nature of relationship is dependent.
6. Evaluation Criteria
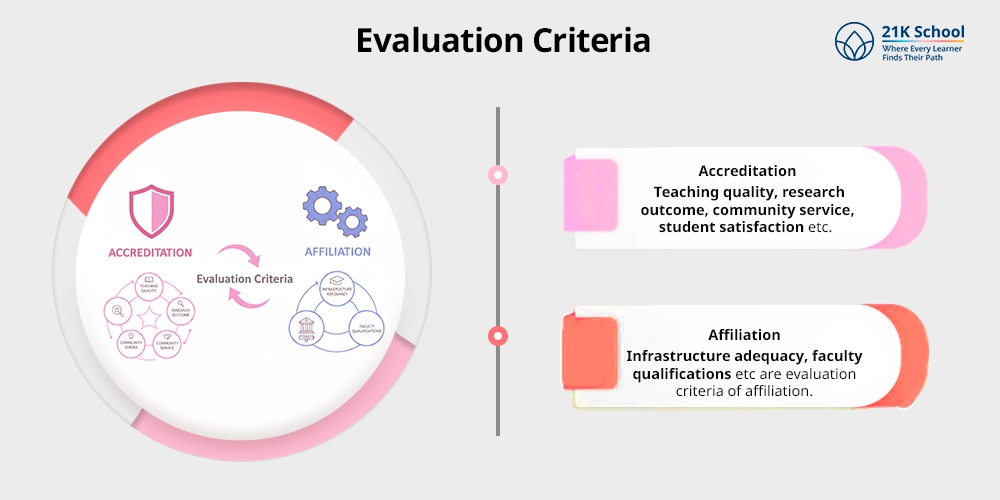
- Accreditation: Evaluation criteria considered in accreditation teaching quality, research outcome, community service, student satisfaction etc.
- Affiliation: infrastructure adequacy, faculty qualifications etc are evaluation criteria of affiliation.
7. Outcome/Impact on Students
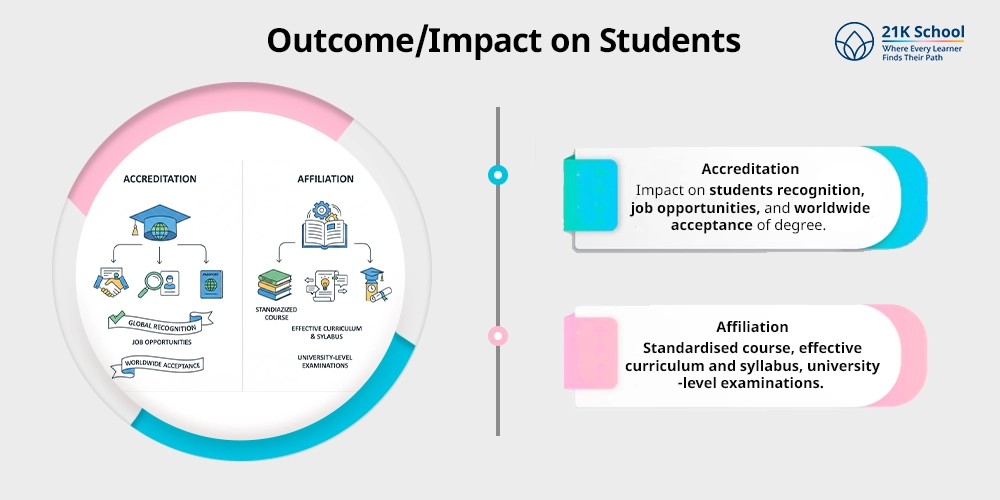
- Accreditation: Impact of accreditation on students recognition, job opportunities, and worldwide acceptance of degree.
- Affiliation: Standardised course, effective curriculum and syllabus , university-level examinations.
8. Duration and Renewal
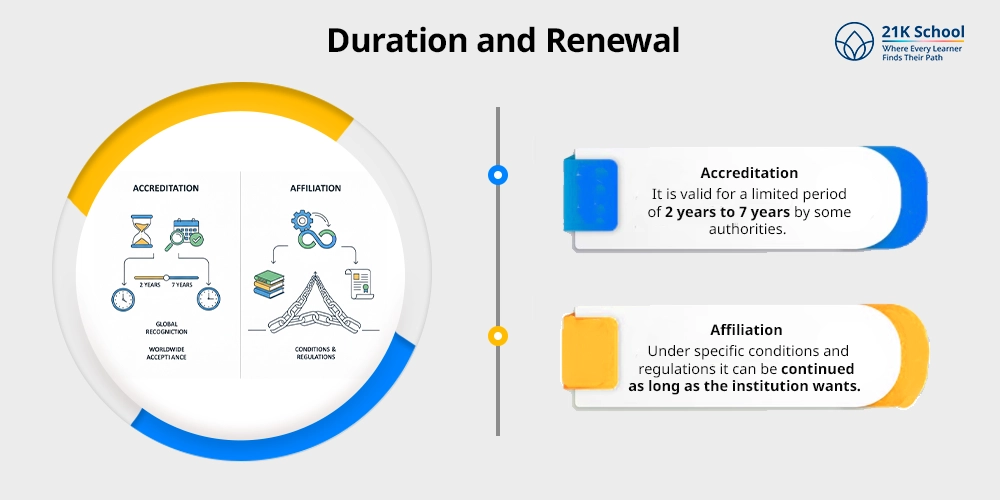
- Accreditation: It is valid for a limited period of 2 years to 7 years by some authorities.
- Affiliation: Under specific conditions and regulations it can be continued as long as the institution wants.
9. Example
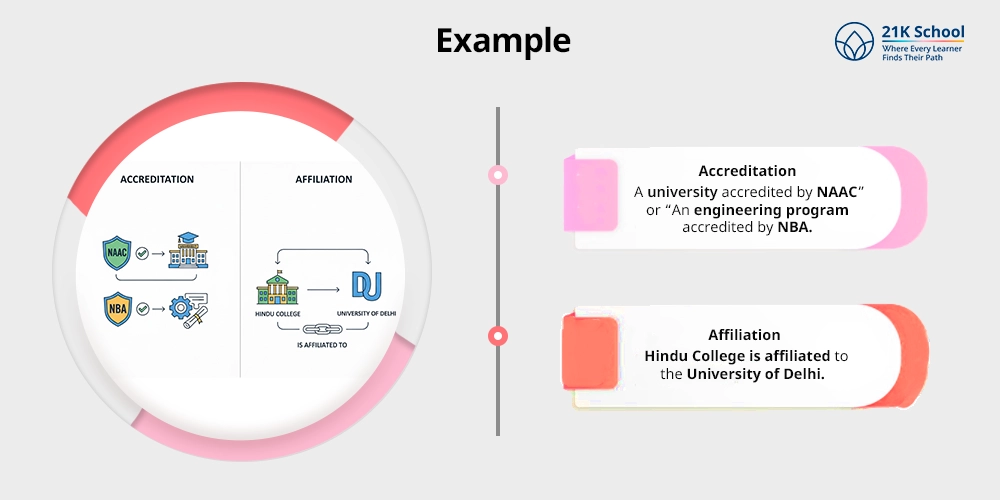
- Accreditation: A university accredited by NAAC” or “An engineering program accredited by NBA.
- Affiliation: Hindu College is affiliated to the University of Delhi.
Conclusion
The above-mentioned detailed blog consists of all the information about accreditation and affiliation.
To understand deeply must go through key differences between accreditation and affiliation.
It’s important to check accreditation and affiliation to ensure that an institute meets the necessary standards and requirements.
So, while choosing school, college or university one must look for accreditation and affiliation.



