Today, activities that happen outside the classroom contribute much to a learner’s education. The activities let students learn abilities that might be lacking in the regular academic program.
Have a read on top 10 fun and engaging educational activities for kids.
Since holistic education is becoming more relevant for development. That is why schools are putting more energy into making sure students achieve academically and personally.
The article discusses why these activities are essential, and the differences between them. Read on to know the positives they add to a student’s education while also contributing to their growth.
Contents
What are Co-curricular Activities?

Co-curricular activities are built into the school curriculum to work with academic learning. They often match the subjects in class and are meant to improve a student’s learning overall.
Although co-curricular activities focus on building leadership, communication, and teamwork skills, they are generally assessed as part of a student’s whole education.
Examples of Co-curricular Activities
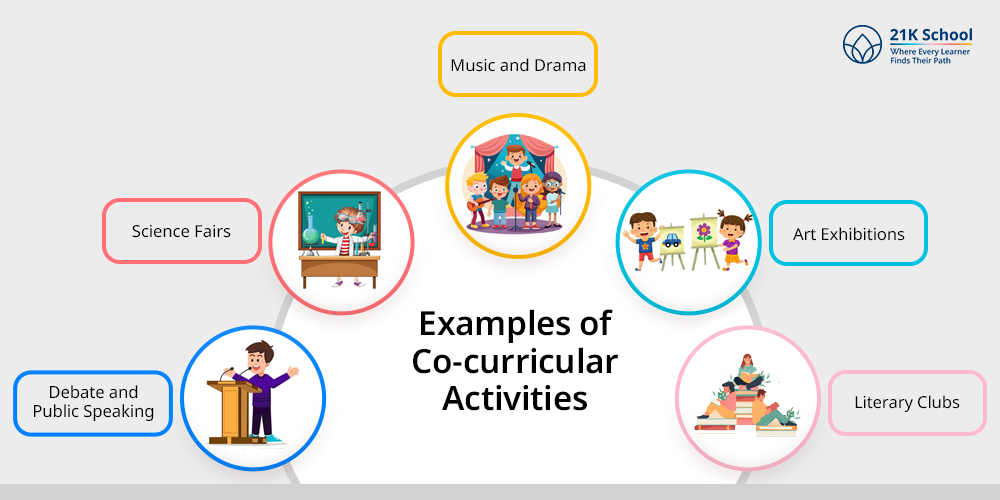
- Debate and Public Speaking: Usually connected to language arts and communication studies, these activities enhance a student’s ability to speak clearly and use logic.
- Science Fairs: Most of the time, students create and present scientific projects that are related to their science education.
- Music and Drama: Usually, such activities link with music and theater classes, where students get creative as they continue to learn.
- Art Exhibitions: In their curriculum, students make art and occasionally display it at school shows.
- Literary Clubs: Being attached to literature classes, these clubs let students try creative writing and learn about literature apart from their daily studies.
What are Extracurricular Activities?

In contrast, extracurricular activities have nothing to do with official school subjects. Most studies are chosen by students because they are interested in them.
Although activities outside of school do not usually count toward academic scores, they help form students’ identities.
Further assisting them to develop time management skills, and help them try passions that may not appear in their academic work.
Examples of Extracurricular Activities
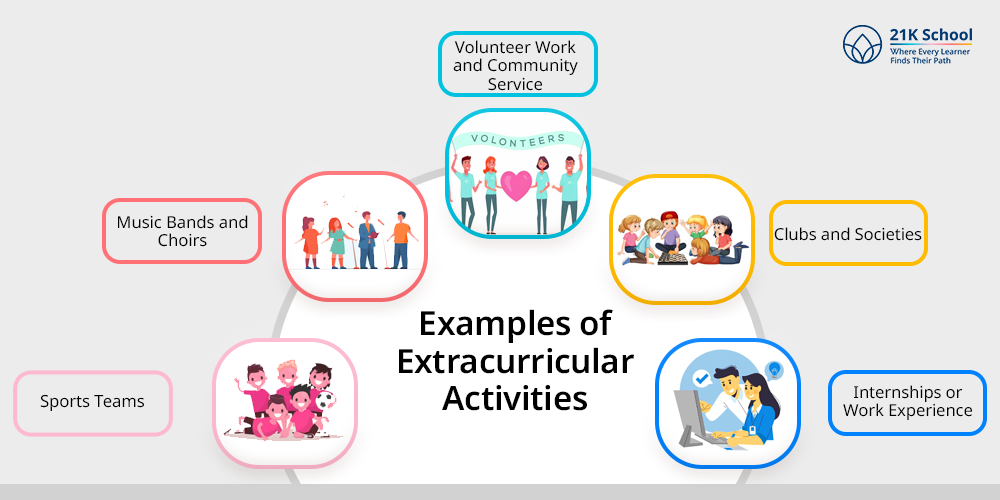
- Sports Teams: These can come from the school as organized activities such as basketball, soccer, or track and field.
- Music Bands and Choirs: Co-curricular and extracurricular music activities are not the same. The latter is often run apart from the regular school program and does not carry credit.
- Volunteer Work and Community Service: Volunteering in any environment—shelter, hospital, or local charity—helps a student grow socially responsible.
- Clubs and Societies: Among these are clubs for photography, coding, chess, and films, led by students who are interested.
- Internships or Work Experience: Internships offer students opportunities to learn and gain experience that support their preparation for future jobs.
Difference between Co-curricular Activities and Extracurricular Activities
Both co-curricular and extracurricular activities are important for developing a student. Still, they have different roles and results for a student’s education.
A detailed look at what each operating system offers is listed below.
| Features | Co-curricular Activities | Extra curricular Activities |
| Integration in Curriculum | Included into academic disciplines and intended to enhance learning. | Not part of the syllabus or subjects. |
| Academic Relevance | Improves topic understanding and is closely related to academic content. | Driven by student interests, not related to academic content. |
| Objective | To add in students’ academic learning. | To add in personal interests and character development. |
| Contribution in Academic Grades | May indirectly affect grades through debates, etc. | No relation with academic performance. |
| Frequency | Mostly scheduled between school hours. | After school hours mostly. |
| Supervision | Teachers and coordinators organise under supervision. | Bit more flexible as organised by students. |
| Effect on Personal Development | Improves intellectual growth and academics as well. | Enhances social skills, communication, etc. |
| Instances | Debates, school plays, art exhibitions, science fairs, etc. | Dance, music clubs, drama, sports,etc. |
| Role in School Settings | More focused on school academics. | Free of school curriculum, flexible as student-operated |
Co-curricular Activities

- Integration with the Curriculum: These activities undertaken outside the classroom are associated with the regular education program and add value to learning. These activities usually help students learn subjects better.
- Academic Relevance: The purpose of these activities is to help students improve what they learn outside of school. They use theory and help students practice using the knowledge they’ve learned.
- Purpose: Such activities are meant to help students improve their schoolwork by studying topics more broadly. And increasing their abilities with critical thinking, talking, and being part of teams.
- Impact on Academic Performance: Participation in co-curricular activities might affect a student’s grades. For example, debating in a competition can help someone build important skills for language arts assessments.
- Supervision: Teachers or academic instructors usually monitor these activities, and occasionally they are built into the school schedule.
Extracurricular Activities
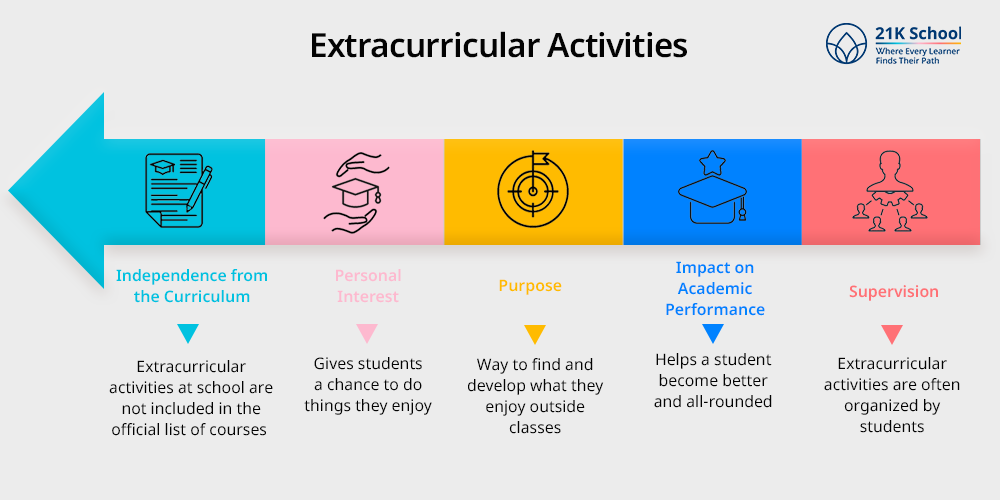
- Independence from the Curriculum: Extracurricular activities at school are not included in the official list of courses. They occur at times different from school hours and do not help with academic study or testing.
- Personal Interest: Students join activities outside of classes based on what they like doing, instead of what their school requires. They give students a chance to do things they enjoy, not connected to their studies.
- Purpose: Extracurricular activities are mainly used for growing as individuals, developing talents, and interacting with others. They provide students with a way to find and develop what they enjoy outside classes.
- Impact on Academic Performance: Extracurricular activities usually do not change academic grades, but they help a student become better and all-rounded. They can build a student’s confidence,
help with dealing with others, and aid when applying for colleges or jobs.
- Supervision: Extracurricular activities are often organized by students, under the guidance of faculty or outside helpers. Usually, educators arrange them after school or on weekends so that both students and members of the community take part.
Importance of Co-curricular and Extracurricular Activities
Students’ growth is greatly influenced by their participation in both kinds of activities. These activities focus on the whole student and greatly support their body, mind, and feelings. Let’s take a look at what makes them valuable:
1. Holistic Approach towards Education
Generally, holistic education does not focus on teaching subjects, but a student’s growth is bigger than just that. Activities outside the main lesson schedule offer students ways to improve their character.
Through these activities, students develop feelings and learn to be respectful and accountable, along with their school subjects.
Participating in group work teaches students how to collaborate, while doing things such as music or drama helps them grow more imaginative and caring. As a result, these activities help the child become equipped to deal with everyday life.
2. Building Network and Collaboration
Doing extra activities makes students learn to work cooperatively with others from both similar and different backgrounds. As part of these activities, students have chances to network with their mates, teachers, and occasional mentors.
Joining together with people from various backgrounds improves communication and helps people work well as a team.
No matter the team sport, project, or event, students have opportunities to learn how to work together. Further sorting out conflicts, and establishing useful professional relationships.
3. Learning Time Management

Being part of either co-curricular or extracurricular activities often means students have to handle several different jobs. Doing these things without sacrificing education teaches you to manage your time well.
Learning some of these activities encourages students to prioritize what needs to be done, organize their schedules, and meet deadlines.
Students must be able to use this skill both at school and at work. So they can tackle several jobs and not feel instantly loaded with obligations.
4. Leadership through Character Development

These projects let students step up and fill leadership positions. No matter if they are athletes, club presidents, or members of an organizing group, students learn how to lead.
Find out the best key leadership roles in schools for students.
By being in these roles, students see how important responsibilities, accountability, and leading by your words and actions are. They are able to build essential student leadership qualities such as making decisions, solving problems, and resolving disputes.
5. Boosts Critical and Creative Thinking

Being part of different activities outside classes encourages both our critical and creative thinking skills. By doing them, students become creative problem-solvers.
By experience in drama or art, students discover ways to look at things differently. Whereas in debate or science fairs, they improve their study skills.
Regular participation in various situations helps students find better solutions. It also improves their ability to think deeply about topics linked to subjects, relationships, and personal lives.
In Conclusion
Adding co-curricular and extracurricular activities to a student’s life helps them develop well. They help students grow important skills that they will use in all areas of living and learning.
They show students how to combine school work with personal development, and give them chances for leading, collaborating, and thinking critically.
All these subjects give students the skills needed to overcome difficulties and gain success in what they do.