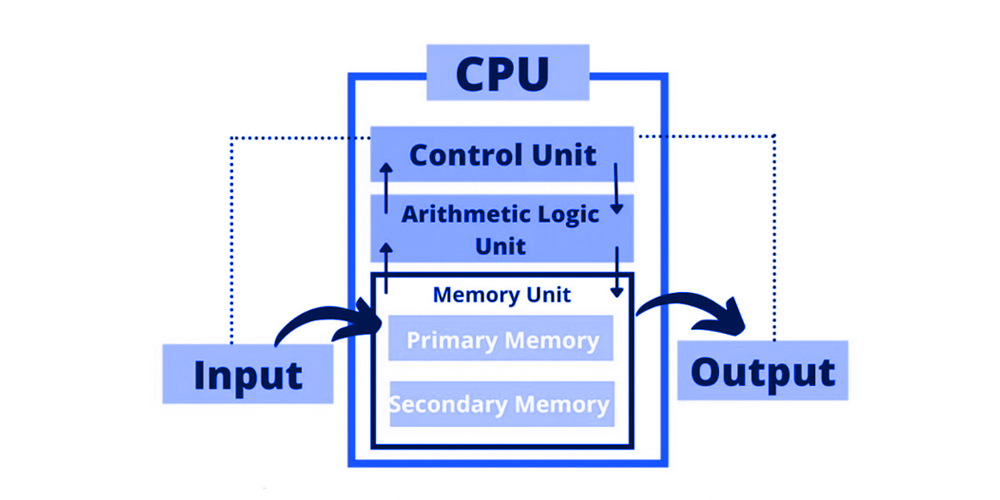
A computer system, which is the centre of modern technologies, works with certain organizational systems that help them to perform their required task.
The best method to comprehend the behavior of a computer is always by assessing its block diagram of it. This diagram gives the basic structure of a computer system and how the various features perform functions on the system.
This way the complex goings on inside a computer are broken down into relatively easy-to-understand units using the block diagram.
If you want to know what a block diagram of a computer is and examine the major parts of the block diagram such as the input unit, output unit, control unit, and memory unit, then you are at the right place.
In this blog, we will talk about each part of the block diagram in detail. By the end of the lesson, you will have understood how computers process, store, and manage data.
Explore five generations of computer you should know about.
Contents
What is a Block Diagram Of a Computer?

This is a graphical view of a computer wherein the main parts of the computer system are depicted and the relationship between them indicated.
Conveys an easy method on how some of the substructures like the Input Unit, Central Processing Unit, and Memory Unit jointly work to undertake computing operations.
Each block or unit of the diagram performs particular tasks for an integrated system whereby all blocks or units are well coordinated to run the system.
This diagram simplifies the intricate organizational structures of a computer by bringing out the main functional blocks to help in understanding computer architecture and operations.
Starting from inputting data into the system, calculating, and storing data, this block diagram gives a fundamental knowledge of how a computer processes commands.
Read, Programming Languages For Kids- Learn to Code From Scratch to know how you can make your kids learn the essential coding skill.
The Major Components of the Block Diagram of Computer System Are:
1. Input Unit
The input unit is that central component in the computer through which all data to be processed must pass.
As an intermediary between the user and the computer system, it enables the user to feed instructions and data into the computer system.
Major Functions of the Input Unit:
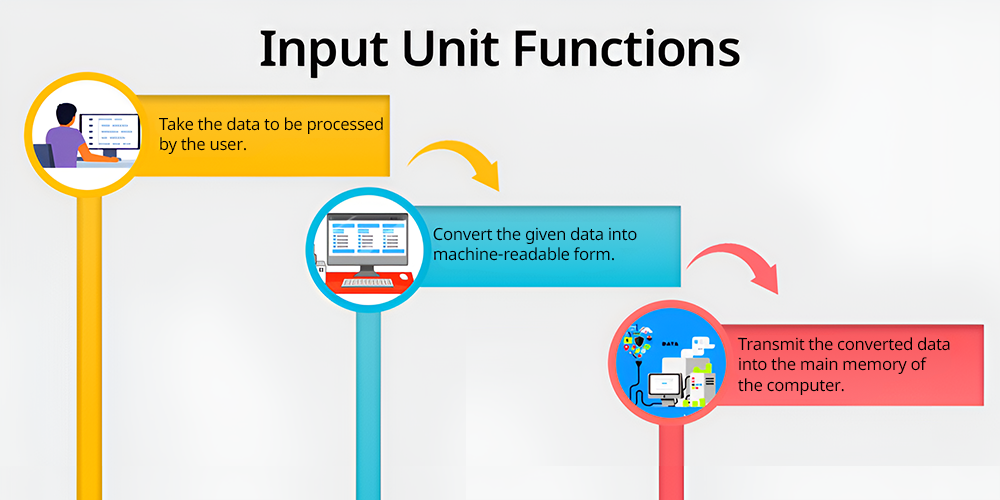
The input unit serves three main functions:
- Take the data to be processed by the user: The input unit takes data, commands, and programs from the user in one or the other manner through a keyboard, mouse, scanner, or even through the microphone.
- Convert the given data into machine-readable form: The data input from the user is often in human-readable format while the input unit translates it to binary form, which can be processed by computer.
- Transmit the converted data into the main memory of the computer: If it is converted to binary form it moves to the main memory and remains inactively waiting for the CPU to process it.
The input unit is essential to the system because without it the user will not be able to exercise any control over the computer.
Explore about basic computer skills for students.
2. Central Processing Unit (CPU)
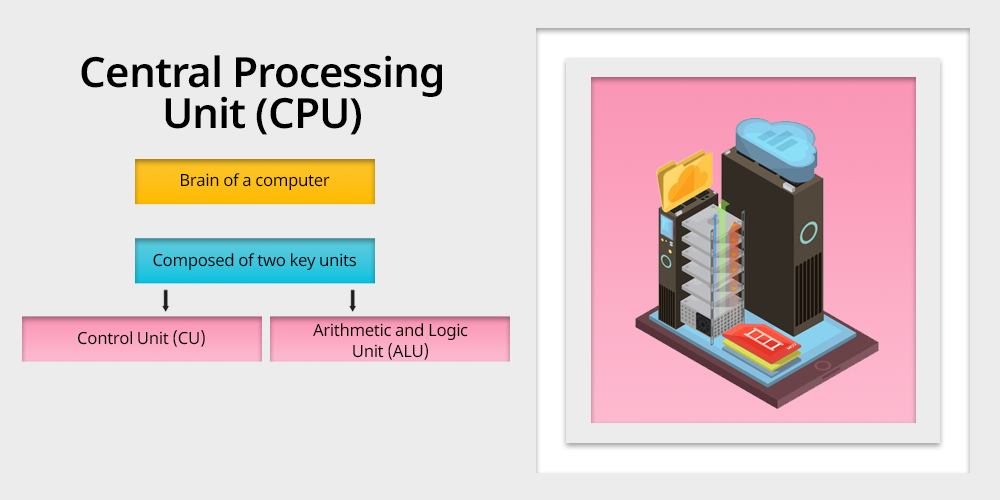
Let’s start by defining some key elements of a computer: the Central Processing Unit, commonly called CPU – is the brain of a computer.
It is mainly used for fixing instructions as well as for processing the data. The CPU is composed of two key units: those are the Control Unit (CU) and the Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU).
The acronyms mentioned above work hand in hand to control all activities of the computer.
(1) Control Unit (CU):
CU controls and supervises all operations within the computer.
As we know, it indicates what the several components of a microprocessor including the ALU and memories should do when supplied with certain instructions.
The CU does not perform calculations, but it breaks in the appropriate instructions within the stipulated time.
(2) Arithmetic And Logic Unit (ALU):
The Arithmetic and Logic Unit performs all the mathematical calculations (such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division) and logical operations (such as comparisons).
The ALU is crucial for tasks that require decision-making, as it helps the computer compare values, compute outcomes, and make logical deductions.
Altogether, the CU and ALU are responsible for data processing within a CPU as the last ones bear all the loads of the work.
3. Memory Unit
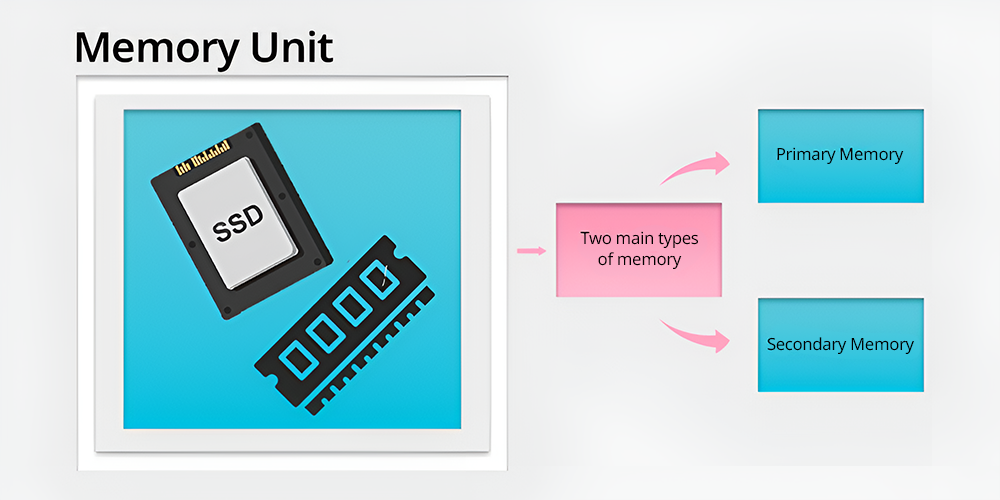
The memory unit of a computer is the unit where data and instructions are stored. This storage can be short-term or long-term depending on the nature of the memory circuit used for storage.
The memory unit itself is needed for storage of both the data that is being processed and the instruction that the CPU is required to execute.
There are two main types of memory:
(i) Primary Memory:
Primary memory is sometimes called RAM or Random Access Memory, it is primary and also volatile, which means that all data stored in it will be forgotten when the computer is turned off.
Cache memory also known as primary memory is accountable for storing data and instructions in the CPU that are frequently used while processing.
This one has a high speed to allow fast retrieval of data, thus making the system efficient.
(ii) Secondary Memory:
Secondary memory includes; hard disk drives, flashes, CDs or DVDs, and USB drives. This is a volatile type of memory and is not able to store data when the computing device is switched off.
Secondary memory holds a vast quantity of data that is not directly accessed by the CPU at any time but often calls for eventual use.
It is slower compared to primary memory but is used for storing files, applications, and operating systems for the long term.
4. Output Units
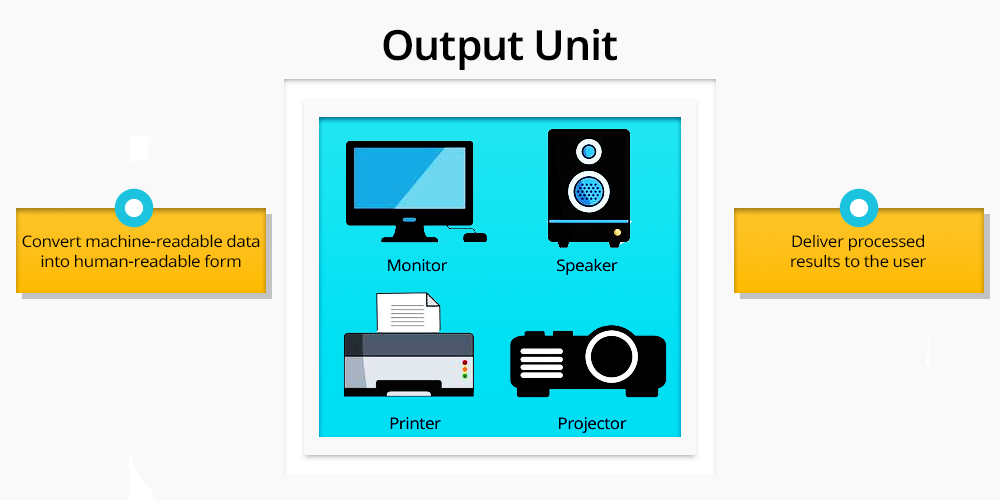
This unit consists of presenting the results of data processing on a computer to the user or the end consumer of the product.
The output unit takes the data that has been processed in the machine-understandable form and translates it into a form comprehensible to the user.
Examples of output devices are monitors, printers, and speakers. It means that the output unit is a part of the computing process and is an interface that provides information about the result of the computing process.
Functions of the Output Unit:
- Convert machine-readable data into human-readable form: After the data has been analysed in the CPU it is reformatted in the output unit to form items that can be understood by the user in the form of text, images, sound, etc.
- Deliver processed results to the user: Converted data is then presented to the output device that shows the user the result of the commands they gave the computer.
This unit closes the loop between the user and the computer, ensuring effective communication between them by delivering the final product of the computational process.
Read on to learn more about, how many computer characteristics are there.
Conclusion
Block diagrams of computer systems are considered essential knowledge and as a basis for understanding how a computer works.
Understand the factors to consider before buying a computer for your children.
It breaks down the complex inner workings into easy-to-understand units: The Integral System is composed of the Input Unit for feeding data in the system, the CPU for handling that data, and the memory unit for holding both active and long-term data.
Together, these units work seamlessly to execute the operations that are commanded by a user, thus eliminating any hitch and ensuring smooth, efficient operation.
Understanding the block diagram makes the users understand how the computers work, transform the data, and perform instructions where each unit is significant in the working process.



