
Competency-Based Education (CBE) is an educational approach that prioritises the mastery of specific skills and knowledge over traditional time-based learning.
Instead of focusing on the number of hours spent in a classroom, CBE emphasises the development of competencies that are essential for success in the 21st century.
Unlike the conventional systems that focus on grade levels and SAT scores, CBE focuses on students acquiring competencies and then providing them with individual learning plans comprehensively.
Contents
- What is Competency-Based Education?
- What is the Need for Competency-Based Education (CBE)?
- Characteristics of Competency-Based Learning
- Principles of Competency-Based Education
- How Competency-Based Education Differs from Traditional Models?
- Core Components of Competency-Based Education
- Competency Based Education Curriculum
- Examples of (CBE) Competency-Based Education
- Benefits of Competency-Based Education
- Challenges and Solutions in Competency-Based Education
- Implementing Competency-Based Education
- Future of Competency-Based Education
- Conclusion
What is Competency-Based Education?
Competency Based Education (CBE) is an individualised learning system where a student passes from one level to the other based on what tutors perceive that the student is capable of doing rather than a fixed period they spend in class.
In CBE systems of education, learners progress through educational episodes, when he/she is ready to do so after proving competency in the relevant domain.
This system is based on routinised competencies and results while offering a clear and quite open pattern for accomplishing genuine and functional capacities. It is somewhere co-related to skill based learning.
What is the Need for Competency-Based Education (CBE)?
The traditional education system offers a one-size-fits-all approach for students, that is often criticised, and it doesn’t cater to individual learning styles, needs, preferences or paces.
(CBE) Competency-Based Education tries to fill the gap by prioritising skill acquisition, providing practical knowledge, and promoting a better engaging and effective learning environment for students .
So, how does fun learning work for students?
Characteristics of Competency-Based Learning
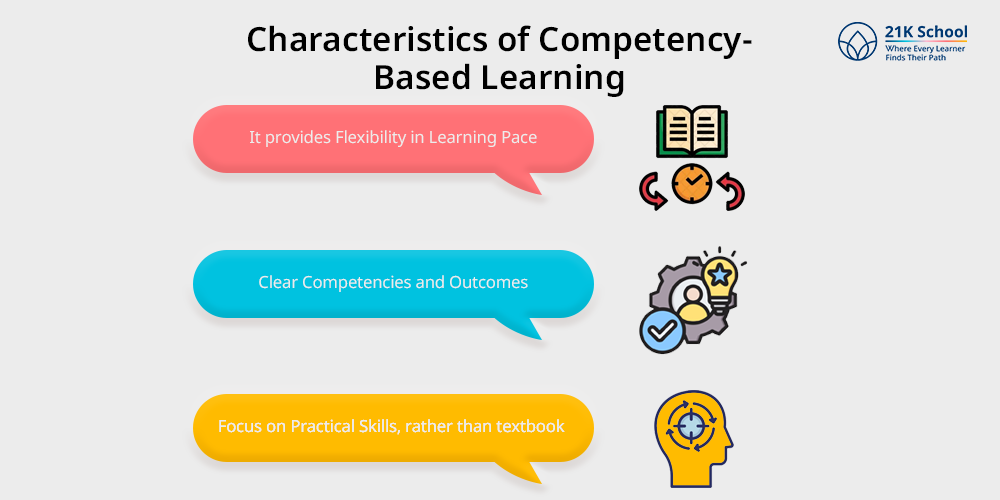
CBE has several defining characteristics that set it apart, and is proven to be a successive strategy for the overall development and academic glorification of a student :
- It provides Flexibility in Learning Pace: Students progress upon demonstrating competency, not based on time spent, demonstrating mastery in subjects.
- Clear Competencies and Outcomes: Each course has well-defined competencies students need to achieve based on a structured curriculum, stating definite and achievable learning goals, set within a time frame as per the students pace and skill sets.
- Focus on Practical Skills, rather than textbook-oriented knowledge and standardised assessment process: The curriculum includes real-world skills, education & applications, preparing students for workforce challenges.
Principles of Competency-Based Education
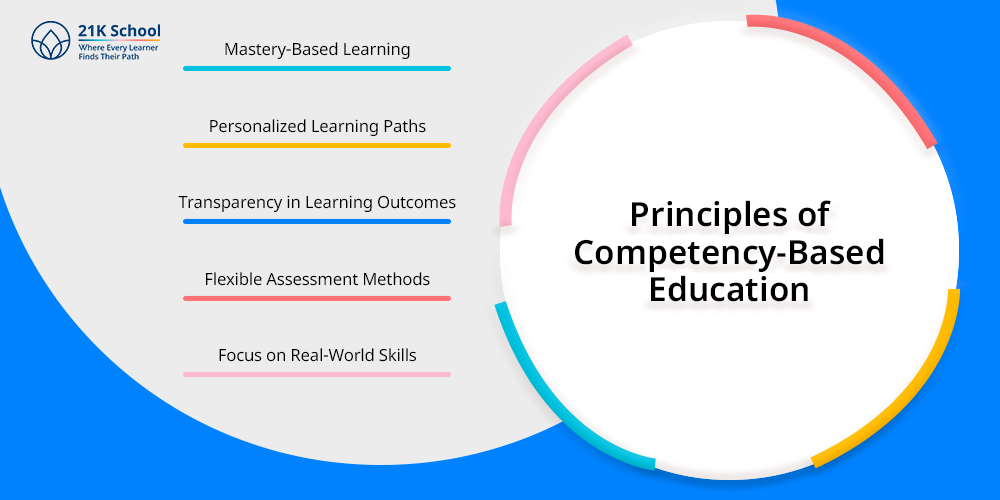
1. Mastery-Based Learning

Students can only move to the next level if they have shown understanding of the competencies or information in question.
2. Personalized Learning Paths

Every learner has a certain learning path given his or her potential and preferences.
3. Transparency in Learning Outcomes

Student, facilitators and parental learning objectives are well articulated.
4. Flexible Assessment Methods

Learning assessment in CBE differs from the conventional system as it employs the use of diverse assessments usable to gauge on the application of test knowledge.
5. Focus on Real-World Skills

Student activities are designed to focus on instructional curriculum that can be implemented in client environments.
How Competency-Based Education Differs from Traditional Models?
Compared to a conventional learning environment, which sets the learners to a standard course curriculum within a given period, (CBE) competency-based education enables students to progress at their rate to learn.
Major learning outcomes commonly associated with traditional models are grades, examinations, etc, while competency based measures mastery in terms of utilisation or application of knowledge thus making students get a better appreciation of the subject.
| Aspect | Competency based education | Traditional education |
| Progression | Based on mastery of skills and knowledge | Based on time spent in class (e.g., semesters) |
| Pacing | Self-paced, flexible | Fixed pace, same for all students |
| Assessment | Focuses on mastery through continuous assessments | Relies on exams and periodic grades |
| Learning path | Personalised, adaptable to student needs | Standardised, same for all students |
| Focus | Practical skills and real-world application | Theoretical knowledge and memorization |
| Teacher’s role | Facilitator, guide, mentor | Instructor, knowledge deliverer |
| Student engagement | High, as students take ownership of their learning | Moderate, often passive learning |
Core Components of Competency-Based Education
1. Learning Outcomes and Skills Over Time-Based Progression
(CBE) competency-based education puts more emphasis on what has been learnt, and what skills or knowledge has been achieved rather than the period that was taken on the specific content area.
This change makes it important that the knowledge students acquire will be useful and relevant.
2. Mastery-Based Assessment
This is true since in competency-based education, assessment is always an ongoing process, which is informed by the capacity of the student, on how they can apply what they learn.
This assists students and educators in determining where one stands in terms of strengths and areas of weaknesses.
3. Personalized Learning Pathways

Technology enabled learning path approach enables students to proceed to the next level as they are prodded towards self responsibility in learning.
4. Student-Centred Approach
Students are central to any process in competency based education. This approach fits with learning styles, learner’s speed, and requirements and creates a learning atmosphere where every learner matters.
Competency Based Education Curriculum
The competency-based curriculum is intended to have content areas of human strengths it aims to deliver with emphasis on its application in practice. The curriculum typically includes:
Defined Competencies: These are laudable goals and objectives which must be clearly articulated as skills that students need to acquire.
Integration of Real-World Scenarios: Concepts that are taught as well as activities are associated with suitable, real life situations.
Personalized Learning Pathways, Flexible Pacing, Use of Technology: Resources are tailored to address understanding and learning needs of the students along the curriculum.
Examples of (CBE) Competency-Based Education
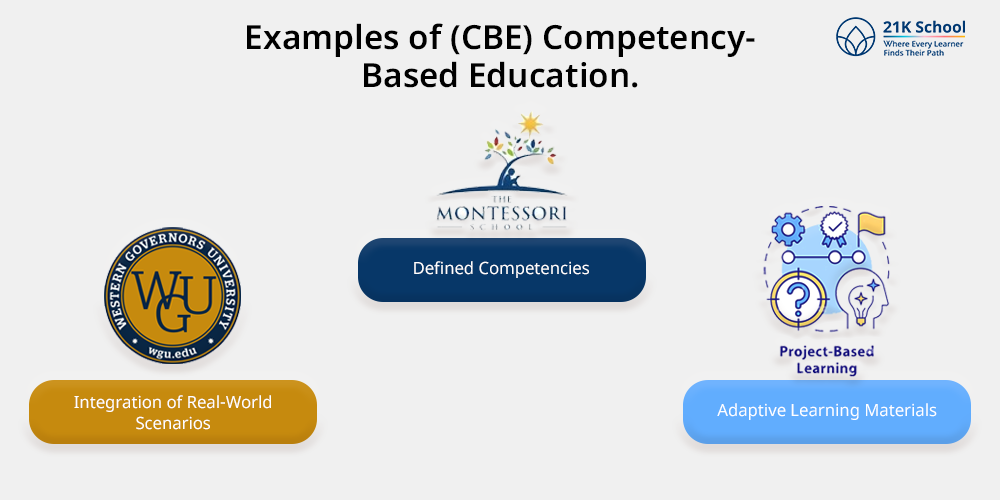
Many educational institutions have successfully implemented CBE models:
Western Governors University (WGU): An institution that offers fully online programmes with the ability for learners to move from one level to another based on competencies acquired.
Montessori Schools: CBE is also supported by a concept of these schools where the student is fully responsible and in control of his/her learning.
Project-Based Learning Programs: It is common in many high schools to have adopted a competency- based system where competencies are demonstrated by way of projects and presentations.
Some of the institutions that follow CBE -Southern New Hampshire University (SNHU), Finland’s Education System, Purdue Polytechnic High School (USA).
Benefits of Competency-Based Education
1. Enhanced Student Engagement and Motivation
CBE captivates students because they can draw correlation between what is being taught to them in the classroom and using it in the real world, hence making them more motivated than situating with models of traditional education.
2. Development of Practical Skills and Knowledge
Central to CBE is the practical, vocational, tangible, and post-industrial skill which equip the students to solve problems at the workplace, contributing to their skill development.
3. Personalized Learning Journeys

Students can learn according to their own pace, and develop their individual skills at their own pace, according to their aptitudes and the problems they meet.
4. Preparation for Real-World Challenges

CBE prepares students for success by fostering such competence as tenacity, complexity-solving, and flexibility, all of which are core competencies when one is out in the job market.
Challenges and Solutions in Competency-Based Education

1. Overcoming Resistance to Change

Changing to CBE can encounter some opposition from teachers, parents, and colleges or school officials. These apprehensions can be eased by proper training and clear communication with the staff and consumers.
2. Addressing Assessment and Evaluation Challenges

We understand that designing good quality meaningful assessments to have a clear reflection of brilliance is important. Using feedback and diverse formats of performance assessment may help implement fair assessment.
3. Ensuring Equity and Accessibility

Premises for equity would require schools to optimise on the quality of technology and support the students need in order to make a success in their endeavours. Technology can highly contribute to students’ success.
Implementing Competency-Based Education
1. Role of Parents and Students

There are different ways parents and students engage in goal setting and in tracking learning progress to solidify the CBE model beyond the learning-teaching process.
What is the real meaning of quality education when it comes to students?
2. Technological Support and Tools

Technology is vital in augmentation of CBE as it monitors, estimates and disseminates data and resources in real time.
3. Policy and Structural Requirements

In this model of CBE, there is the need for the following six forms of policy support: flexible academic structures and organisation, flexible curriculum format and structure, acceptable modes of assessment, technically sound and tangible reward systems, recognition and approval of prior learning, and funding of curriculum development.
Future of Competency-Based Education
1. Trends and Innovations in CBE

Continued growth of the concept of CBE will generate further advancements in technologies and learning tools that make it more practical and adaptive.
2. Impact on Workforce Development

This type of model is suitable in the preparation of future workforce as CBE ensures that graduates produce on the job training skills sufficient for demand of today’s employer.
Conclusion
Competency Based Education stands out as a liberal approach to learning to mastery, relevance, and individualism as compared to traditional offerings.
Most CBE initiatives place practical skills and student centred learning at the core, which not only improves the learning experience but also gets the student ready for the tough environment in the workplace.
With this model in its developmental stage, the education sector can hope to become an experience where the goals are far more than obtaining good grades and passing a test; where learners can progress through their education journey in a path best suited for them.
