In education, gaining knowledge is a fundamental part of learning for each student. However with time there are many ways to gain knowledge based on need.
Modern education offers flexibility in learning to conquer success through various approaches.
The two essential types such as declarative and procedural knowledge help learners how to learn, remember and apply in the real world.
Understanding these two types of knowledge is crucial for parents, facilitators and students to implement the best at the right time to achieve success.
Contents
What is Declarative Knowledge?

Declarative knowledge is knowledge of facts, concepts and information that can be consciously recalled and expressed. It is an answer to this question: What do you know?
It is essential in the first levels where the learners have to build a background knowledge on the topic being learned. Declarative knowledge like general knowledge about the world and individual experiences saved in the episodic memory are recorded in semantic memory.
Some other examples of declarative knowledge are understanding the law of inertia or recognising the spring season.
What is Procedural Knowledge?

Procedural knowledge on the other hand depicts knowledge of the way to do something. It is about abilities, tactics, and procedures of working. Procedural knowledge is the answer of: How do you do it?
It mainly focuses on actions, not verbal explanations like declarative knowledge. Learners main focus is to complete the task which develops accuracy and perfection due to practice.
Some examples of procedural knowledge include knowing how to make coffee or exploring computer software.
Difference Between Declarative and Procedural Knowledge
Before using both declarative and procedural knowledge one needs to understand each in depth.
It is worthwhile comparing declaring and procedural knowledge in several aspects to know fully about their functions.
Here’s a comparison table:
| Particulars | Declarative Knowledge | Procedural Knowledge |
| Definition: | Knowledge of facts, concepts, and info | Knowledge of how to perform tasks |
| Alternate Name: | “Knowing what” | “Knowing how” |
| Nature: | Explicit and conscious | Implicit and often unconscious |
| Examples: | Capital of Italy is Rome | How to ride a bicycle |
| Learning Method: | Reading, listening, observing | Practicing, doing, experiencing |
| Memory Type: | Stored in explicit memory | Stored in implicit memory |
| Verbalization: | Easy to explain verbally | Difficult to explain; shown in action |
| Assessment: | Through written tests and quizzes | Through demonstrations and tasks |
| Development: | Comes before procedural in most cases | Often builds on declarative knowledge |
| Application: | Understanding rules, theories | Applying those rules in practice |
1. Nature of knowledge
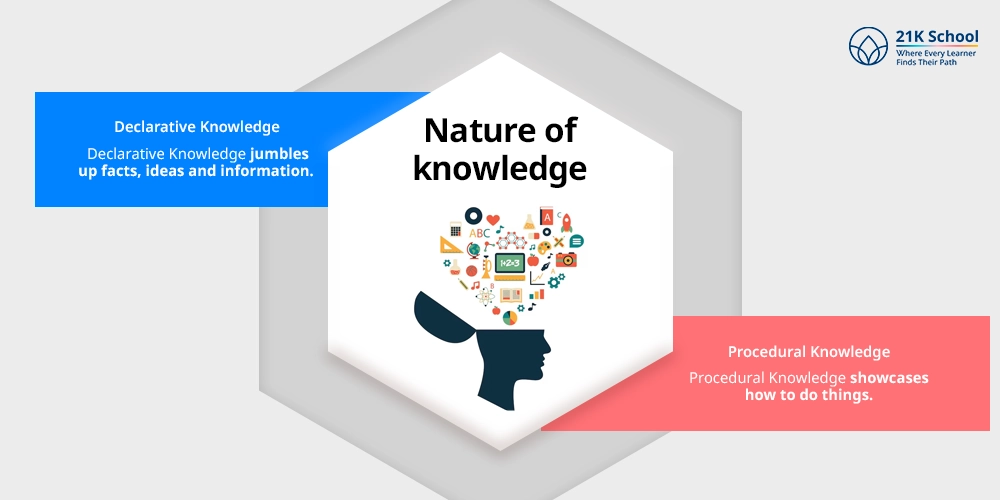
Declarative Knowledge jumbles up facts, ideas and information. It is the knowledge ( e.g. the knowledge that 2+2=4).
Procedural Knowledge showcases how to do things. It is the familiarity with how to go about it, for example how to solve math problems step by step.
2. Question Answered

The question being tested with Declarative Knowledge is What do you know?
The question of the form, How do you do it? is taken care of by Procedural Knowledge.
3. Learning Process
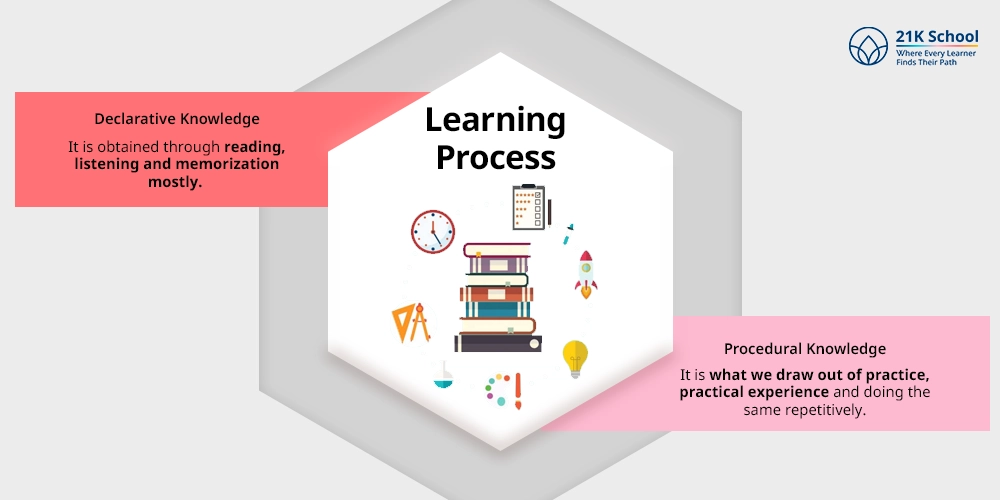
Declarative Knowledge is obtained through reading, listening and memorization mostly. It is the learning acquired in the form of passivity and is taught more usually specifically.
Procedural Knowledge is what we draw out of practice, practical experience and doing the same repetitively. It is a process of active learning which is done and acted upon.
4. Memory Type
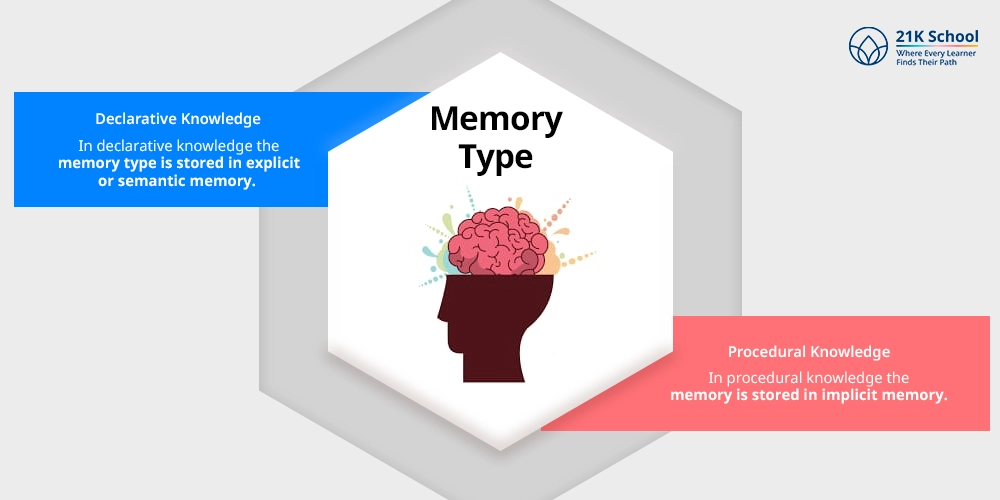
In declarative knowledge the memory type is stored in explicit or semantic memory. It means it provides long-term memory individuals can consciously access.
However, in procedural knowledge the memory is stored in implicit memory. This type of memory is operated unconsciously or automatically by learners.
5. Verbalization
In declarative knowledge one can easily explain and describe through verbal communication. Also explore how to improve communication skills in students .
On the other hand procedural knowledge needs demonstration instead of verbal which is hard or takes much more time and preparation to explain.
6. Application
Declarative Knowledge is used to understand concepts, rules and principles. This does not necessarily have to be applied in doing things but it will help to achieve an effective theoretical knowledge .
Procedural Knowledge is utilized in the bid to carry out processes and knowledge materialized. It helps learners in decision making and problem-solving through practice.
7. Learning Method

The learning method used in declarative knowledge is based on reading instruction observation listening etc. While in the case of procedural knowledge it is different.
Here students learn through practice experience repetitions for better understanding and accuracy.
8. Communication
The communication preferred in declarative knowledge is based on explanation, through diagrams or written content.
However, in the case of procedural knowledge the best way of communication is demonstration or practice in real life.
9. Examples
Knowing that the Earth rotates around the Sun is what we call Declarative Knowledge; it is the facts about grammar of a language, dates, historical facts that have been memorized.
Procedural Knowledge includes things like how to ride a bike, work out a quadratic equation, write an essay or carry out an experiment.
Declarative and Procedural Knowledge Examples
Some common examples of declarative knowledge based on science, history, and general facts includes:
Declarative Knowledge
- Science: Photosynthesis is the process of generating food for plants. Sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid react to form common salt.
- History: Recalling World War II incidents in detail for historical knowledge. Exploring the ancient manuscripts.
- General Facts: Knowing the names of the presidents of the last 5 years. Recognising the full moon day.
Some common examples of procedural knowledge based on skills , tasks and operations includes:
Procedural Knowledge
- Tasks: Learning how to balance objects or playing a violin.
- Skills: Cooking a French toast or preparing a month end report in the office.
- Operations: Science experiments for example, displacement reaction, oxidation reaction. Operating new technology or software.
Conclusion
Learning in a meaningful manner ensures growth and academic progress of learners. Understanding different kinds of knowledge while learning can be beneficial.
Declarative and procedural knowledge are two crucial approaches which help them to explore fundamentals of learning.
In declarative knowledge learners can go through facts and data while procedural knowledge they work on projects, tasks and experiments.
Remember education is a combination of facts, knowledge and real life application which can be balanced by implementing both declarative and procedural knowledge.



