Think about a classroom where students are not sitting but eagerly listening to a lecture. They are actively sharing their thoughts, collaborating, reasoning, and thinking.
It sounds like an education model of the future? It’s not. It is already the present in the flipped classroom and flipped learning paradigm.
Flipped classrooms are not exactly the same as flipped learning , even though they are frequently interchanged in practice. One is a foolproof process, and the other is an education approach.
The categorical distinction between the two is essential to application and maximization of active learning environments. In this article, we will unpack these terms and look at their advantages, disadvantages.
Read on to see how they are different and similar to each other.
Contents
- What is a Flipped Classroom?
- Key Features of Flipped Classroom
- Advantages of Flipped Classroom
- What is Flipped Learning?
- Key Elements of Flipped Learning
- Advantages of Flipped Learning
- Comparison between Flipped Classroom and Flipped Learning: Key differences
- Concerns to Deal with Flipped Classroom and Flipped Learning
- In Conclusion
What is a Flipped Classroom?

A flipped classroom is a paradigm of teaching that plays the role of reversing the classic method of teaching. It does not present new material in the classroom or gives homework as a study aide.
However, the initial concept is learned outside the classroom via video lectures, readings or other self-paced materials. Interactive learning that involves applications then takes the class time.
The idea simply boils down to learning it at home and doing it at school, which explains the so-called flipped part of the concept.
Key Features of Flipped Classroom
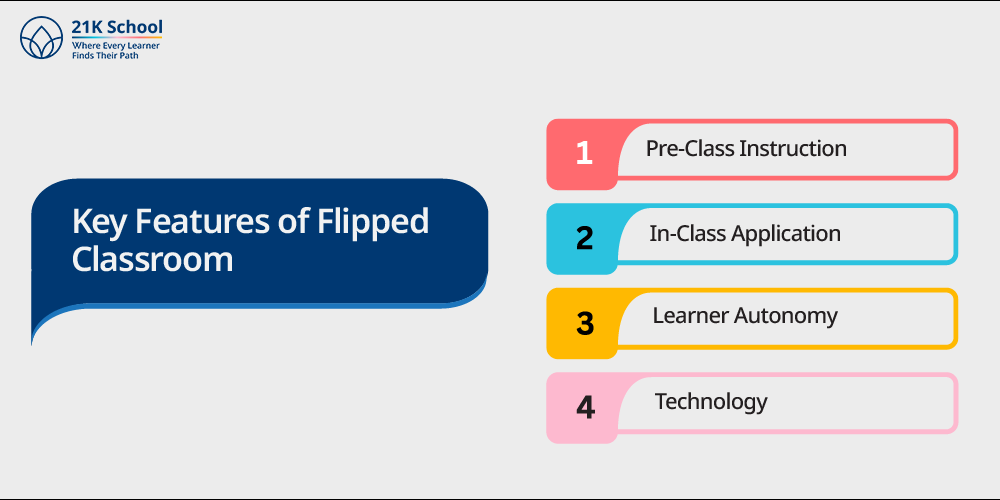
Flipped classrooms seem different from what we understand and learn in traditional schooling . The major characteristics of flipped classrooms can be mentioned as:
- Pre-Class Instruction: There is pre-recorded video, online article, podcast or interactive module with the content.
- In-Class Application: Class time is allocated to group work, directed problem solving, groupwork, and instructor clarification.
- Learner Autonomy: The learners are responsible for defining their learning speed.
- Technology: Digital tools (LMS, video-sharing materials) are important in the delivery of the content.
Advantages of Flipped Classroom
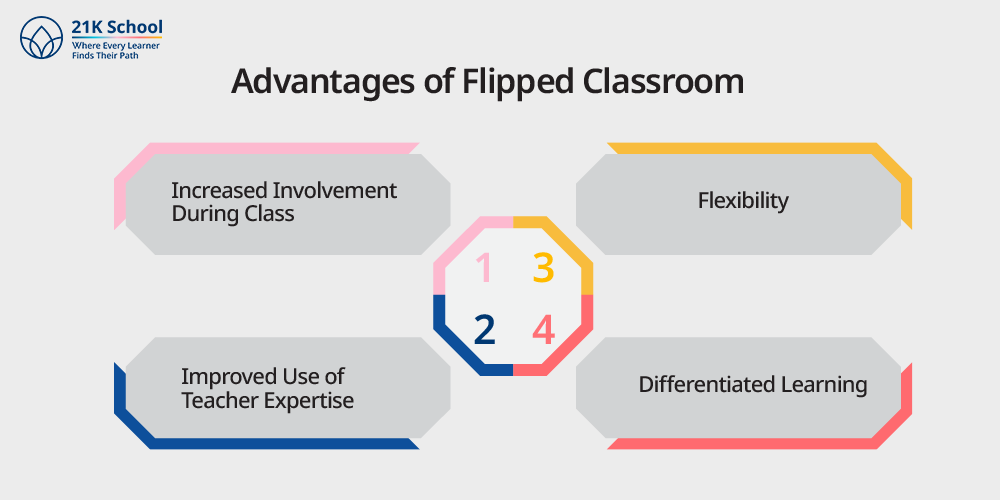
Besides totally reciprocating the concept of general classrooms, flipped ones are in trend due to their other benefits. It has changed how students understand the importance of learning and makes them more engaged in it.
- Increased Involvement During Class: Students no longer passive listeners are engaged in useful activities, under the guidance of peers and teachers.
- Improved Use of Teacher Expertise: Teachers are able to clear up confusion, give explanations and amplify learning during lessons.
- Flexibility: The learner presents the ability to revisit the material at all times and can rewind/replay lectures.
- Differentiated Learning: Teachers will be able to provide support depending on the needs of a child through interactions in the classroom.
What is Flipped Learning?
Flipped learning is an educational institution of higher learning. It comes with a wider foundation on what a flipped classroom model is but takes it one step further.
It is not merely inverted instruction; it is redesigning how the students learn and the role of the teacher to the learning process.
Flipped learning is described as the learning model in which direct instruction takes place in the individual learning space. Rather than where the group learning space and the resultant group space is used as an interactive learning environment.
Key Elements of Flipped Learning
The prominent features of flipped learning demonstrates its multidimensional approach with regards to student development. The approach evolves around student centred learning , while attaining flexibility in the environment.
1. Student-Centered Approach

It puts its focus on active, collaborative learning by placing students in the center of attention.
2. Four Pillars of F-L-I-P:

- Flexible Environment: The learning environment and time periods allow individual needs.
- Learning Culture: Transitions of teacher to learner centered learning.
- Intentional Content: Educators select resources that help them engage their students as much as possible.
- Professional Educator: The teachers participate in the process actively, reflectively and directionally.
3. Continuous Assessment

From time to time formative assessment informs teaching methods and student progress.
Advantages of Flipped Learning
Flipped learning serves many aspects of growth in students, indulging them into deeper understanding of subjects and enhanced collaboration. The other benefits of flipped learning are as follows:
- Deeper Learning Outcomes: Promotes thinking critically, problem-solving and use in practice.
- More Student Responsibility: Students learn to become self directed and take ownership of knowledge.
- Improved Cooperation: In-class time promotes teamwork, communicating and communal inquiry.
- Better Teacher-Student Communication: Teachers are more interactively involved with the students providing input and guidance.
Comparison between Flipped Classroom and Flipped Learning: Key differences
The flipped classroom can be considered rather a structural than a philosophical and methodological change in learning. And the main differences between flipped learning and flipped classrooms are explained in the following table:
| Features | Flipped classroom | Flipped learning |
| Definition | A model of teaching where home is for instruction-giving and classroom for practice | It is a pedagogical approach that uses flipped model to modify the learning experience |
| Aim | Where and when instruction to be given | How learning occurs and by whom it is done |
| Structural Output | Lectures in home through video-conferences and practice at school | Fosters active learning, formative assessments under flexible environments |
| Role of Teachers | Delivering content and act as facilitator in classrooms | More like a guide, mentor, or reflective practitioner |
| Role of Students | Grasping delivered content and participate in classroom activities | Encouraged as active listener,participating in collaborative learning and decision-making |
| Use of Technology | Vital for smooth and faster content-delivery | Used for all content delivery, assessment tools, and collaboration |
| Scope | Restricted to only delivery of instructional content | It has broader scope in curriculum designing and pedagogy |
1. Purpose and Philosophy
- Flipped Classroom: It is concerned with transformation of content delivery. It has to do with efficiency, it is more time in the classroom to interact and less time in lectures.
- Flipped Learning: It is interested in a whole change of learning. It teaches independence, creativity and proactively solving problems.
2. Scope

- Flipped Classroom: An instructional approach that is implemented parts of the time or during a rather particular unit.
- Flipped learning: An educational philosophy encompassing the whole course or curriculum.
3. Teacher’s Role
- Flipped Classroom: Teachers pre-structured the material and help the students in the classroom.
- Flipped Learning: Instructors implement a flexible learning environment and help students research and will always adjust to feedback.
4. Student Engagement

- Flipped Classroom: Students use their homes to consume passively and arrive to the classes to be active.
- Flipped Learning: The students become active learners before, during, and after the lesson- it is they who take charge of their learning results.
5. Technology Use

- Flipped Classroom: It is primarily adopted to share the content (e.g. videos, presentations).
- Flipped Learning: Uses technology (discussion forums, self-evaluation, research, collaboration tools, and creative stuff).
Concerns to Deal with Flipped Classroom and Flipped Learning
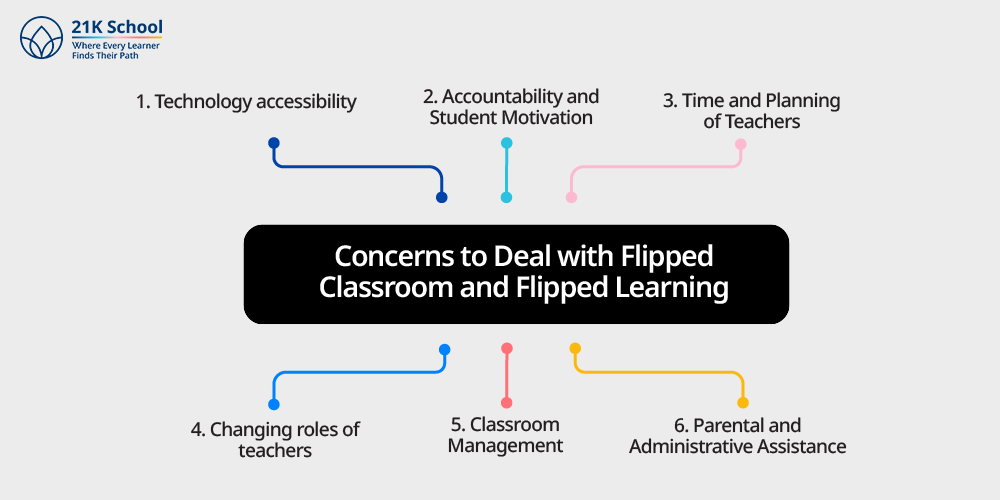
Being rather dynamic and student-oriented, the flipped classroom and flipped learning have some drawbacks, which teachers are advised to know:
1. Technology Accessibility

Every student does not have an equal access to the device or high-speed internet at home. These may cause a barrier to accessing the pre-class material and there is increased digital divide.
Schools might be required to offer different resources, or assistance to free fair access.
Possible Solutions:
- Schools may also provide loaning devices or arrange partnerships with community centers in terms of gaining access to the internet.
- The offline options are available, including materials on USB drives or printouts in packets.
- Achieving accessibility requirements could be assisted using inclusive content creation like subtitle addition or transcripts and screen-reader-friendly formats.
2. Accountability and Student Motivation
Flipped classes focus much on the pre-class work done by the students. Unless students do some preparation work before the lesson, they might not do well during the activities in the classroom. Educators should have some strategies to check students, such as short quizzes or participation checks.
Possible Solutions:
- Include informal quiz or entrance activities at the start of the lesson to determine readiness.
- To enhance the engagement, use the elements of gamification (points, badges, and leaderboards).
- Provide clear feedback and understand how preparations before the classes improve the learning process.
3. Time and Planning of Teachers

Production of video materials and drafting of the interactive activities in classes also needs a lot of time. There might be challenges for the teachers getting stressed with an increased work load.
It can be facilitated by starting small and working with colleagues.
Possible Solutions:
- Begin with the small; do not attempt to flip the whole curriculum but just a unit or topic.
- Share the burden of text-creation with peers or by open educational resources (OERs).
- The schools can assist teachers through training, technologies and sufficient planning time.
4. Changing Roles of Teachers

This transition that entails leaving the position of sage on the stage to guide on the side needs a shift in mindset. Teachers might have difficulties taking a step back and giving more control to students over their education.
Possible Solutions:
- Provide professional development workshops that were based on flipped classrooms and classroom management. Include active learning involving students and student-centered instruction.
- Develop a support system of teachers who can exchange experiences, resources and solutions.
- Support a growth mindset in which teachers perceive challenges as a problem to be innovative and always improve.
5. Classroom Management

Flipped classrooms are active in nature. Keeping track of many groups of people doing various tasks at a go may be complicated. Maintaining focus may be done by setting clear expectations, organizing activities, and using flexible grouping arrangements.
Possible Solutions:
- Organize group roles (e.g. facilitator, time-keeper, note-taker) to conduct group work.
- Use formative assessment tools such as using real-time quizzes or exit tickets to check individual learning.
- Establish rotating learning stations or others offering flexibility in the classroom that cater to different learning requirements.
6. Parental and Administrative Assistance

Flipped approaches can be misinterpreted because parents or school leaders believe that the approach entails less teaching. Teachers have to articulate the merits of this model to get momentum and alignment with the broader school objectives.
Possible Solutions:
- Host parent sessions that contain information about the flipped model, its advantages, and how they can assist their child.
- Because school leadership will be needed, present evidence-based research and pilot results to win their support.
- Facilitate the idea of flipped learning within the school or in grade-level teams and promote mutual success and consistency.
In Conclusion
Both flipped classroom and flipped learning prove to be a major departure to traditional education. But whereas the flipped classroom is the how, the flipped learning is the why.
Classroom flip is one of the starting points of a practical way of rearranging time and resources. However, flipped learning changes the essence of education and its core focus on students.
Instructors who are interested in this method should do more than taping lectures. They should redefine their role, think about students first, and establish situations that promote active learning, critical thinking, and collaboration.
The future of education in India is fluid, adaptable, and student-centered. Realisation that the future starts with defining the difference between a flipped classroom and a flipped learning is highly needed.