Motivation plays a vital role in every student’s life while learning . It helps the students to maintain a streak in the learning process and academic success.
It behaves as the main factor that empowers the students to gain knowledge , deal with challenges, and achieve the targeted achievement.
Motivation is not only about achieving targets in the exams, but rather it is about developing curiosity, eagerness and interest to learn new things.
A motivated individual can achieve heights in their career easily with their constant efforts, whereas without motivation, even a brilliant student may struggle to perform better.
Let’s find out what motivation is in education , various types of motivation, theories and advantages of motivation in learning in a detailed view.
Contents
What is Motivation in Education?

Motivation in education can be defined as the internal and external elements that can stir interest in the learner to be involved in the learning process.
It may be the personal decision, the extrinsic rewards, or the desire to study and acquire new concepts.
The factors of teachers that can also help in developing a career include providing the student with the appropriate feedback, comfortable learning, and goal-based teaching methods .
Education is based on motivation; it bridges effort to achievement and transforms expertise into output.
Types of Motivation In Education
Motivation is categorised into 2 main categories, i.e., Intrinsic and Extrinsic.
Let’s understand them in detail.
1. Intrinsic Motivation
Intrinsic motivation is driven by the personal interest of the learners.
Students are motivated intrinsically when they are involved in learning because they only find it interesting, fun and interactive.
For Example, if a student who studies literature subjects just because they like to read them and improve their skills in that subject is intrinsically motivated.
This type of motivation helps students to improve a deep understanding of concepts, Creative thinking , and long-term knowledge retention ability in education .
2. Extrinsic Motivation

Extrinsic motivation is driven by external factors instead of personal interests.
These involve appreciations, grades, competitions, or avoiding punishments.
For Example, a student who is working hard to get admission in a recognised institute is extrinsically motivated.
Extrinsic motivation is efficient for short-term goals , and it might not always be ready to handle long-term goals unless it is interconnected with intrinsic motivation.
Theories of Motivation In Education
Let’s find out the motivation theories that are being explained for why the students are motivated, and how teachers are encouraging motivation effectively.
Below are the three main theories of motivation:
1. Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
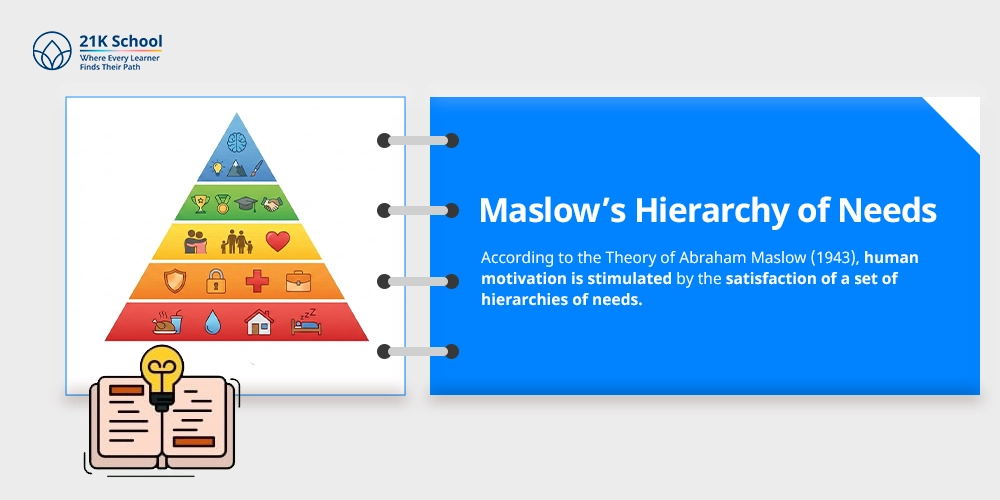
According to the Theory of Abraham Maslow (1943), human motivation is stimulated by the satisfaction of a set of hierarchies of needs.
In the school setup, this theory guarantees that the basics of the students are laid out at the start to allow the learning to be fruitful for them.
Below are the five levels of hierarchy:
- Physiological Needs – Physiological needs are the greatest biological needs that one requires to survive, such as food, shelter, water and sleep.
- Safety Needs – When the physiological needs have been met, the attention shifts to protection and safeguard, which involves being independent of terror and also resources like a good job and a home are needed.
- Love and Belonging Needs – This stage includes social connections and relationships and a sense of togetherness. It helps in creating a friendship and a relationship of intimacy.
- Esteem Needs – After the social engagement is met, the students look for respect and which includes self-respect and appreciation from others. This helps students in building a sense of self-confidence and a sense of suitability.
- Self-Actualisation Needs – This is the top level of hierarchy and includes the interest of achieving the target to become the “best form of identity”.
2. Self-Determination Theory (SDT)

The Self-Determination Theory was established by Deci and Ryan (1985).
This theory mainly focuses on how the passion of students is guided by three fundamental psychological needs: autonomy, competence and relatedness.
- Autonomy – This is a feeling where the learner feels being control of their own choices and interests. When the students are offered choices to select on their own, then they feel really motivated in that scenario.
- Competence – Every individual is aware of the fact that hard work and strong efforts lead to a successful career. Therefore, constructive feedback helps them to stay motivated.
- Relatedness – As soon as the students are made to feel that they are connected to the teachers and the other members of the peer it enhances the interaction. A good classroom environment can be used to enhance student motivation.
3. Expectancy-Value Theory

Eccles and Wigfield (1983) introduced Expectancy-Value Theory. Through this theory, one is able to comprehend that there are two key factors of motivation:
- Expectancy – In this case, a person is convinced that he or she can go very easy in accomplish any given task very easily.
- Value – This indicates the value of the person to whom the task was provided.
Also explore the self motivation activities for elementary students .
Importance of Motivation in Education
Motivation is not just an emotional factor; it is a psychological driving force that creates a foundation for a productive learning and teaching process. The major importance of motivation in the education system is motivated by the following reasons:
1. Enhances Learning Environment

An engaged classroom is a positive learning environment where the students are eager to learn and communicate with their peers.
Motivation assists in the formation of a practical learning process, enthusiasm and facilitates active involvement.
2. Increases Learner Engagement

Motivated students promote a sense of responsiveness and curiosity towards learning, and this makes them career-oriented.
They maintain their activity and get engaged in all sorts of discussions, are honest and disciplined in their studies and help in collaborative learning .
3. Deepens Understanding

Once the students are motivated, they do not limit their learning to rote but rather give primary attention to knowing the concept.
Through this attitude, they begin to make new thoughts informed by the right knowledge and critical thinking skills on what they have learned.
4. Improves Attention and Focus

Student motivation would assist in ensuring that students are attentive during lessons and classes.
They are largely interested in managing the inner drive to learn and meet the goals instead of the outer force.
5. Drives Goal-Oriented Learning

Motivation is providing the students with the avenue to pursue a specific course towards goals.
They assist in strengthening self-discipline and discipline in the long run. Students continue to make goals and plan their ideas until they achieve their goals.
6. Improves Academic Performance

Students work harder and consult the teachers, thereby finding it easy to encounter challenges and problems.
Those students who are on top of their academic performance are always internally motivated.
Learn how to improve a childs academic performance .
7. Builds Confidence and Positive Behaviour

Motivation develops self-respect and boosts confidence in the individual.
When the students are starting their experience of achievements with the help of their hard work, willpower and confidence, they foster a sense of positive attitude towards learning.
8. Promotes Critical Thinking

Motivation encourages students to improve their critical thinking skills by exploring various research papers.
By exploring like this, the students can relate the problem-solving skills to real-life scenarios.
Conclusion
This assists in transforming traditional schooling into experiential learning by transferring the learners into rational and driven performers.
Motivation is encouraging all aspects of learning, including the intrinsic pleasure of discovery, and extrinsic prizes and recognition.
It assists in acquiring wisdom on inspirational theories such as the Hierarchy according to Maslow, self-determination and the Expectancy-Value concept. Teachers can create a classroom where every individual feels motivated, capable and encouraged.
Finally, motivation is connecting the gap between the capability and accomplishment because it is the only thing that energises a lifelong learning environment.