Education is no longer limited to textbooks and classrooms. With the rise of digital tools, a more dynamic and flexible approach has emerged, which is blended learning .
This method combines the strengths of both traditional in-person instruction and online education, giving students more control over how they learn while still offering the guidance of a teacher.
Blended learning is not a one-size-fits-all education solution. There are many models, each suited to different learners, subjects, and teaching styles.
This blog explores 17 types of blended learning models, helping you understand how each works and when it’s most effective.
Contents
- 1 What Is Blended Learning?
- 2 17 Types of Blended Learning Models
- 2.1 1. Rotation Model
- 2.2 2. Flex Model
- 2.3 3. A La Carte Model
- 2.4 4. Enriched Virtual Model
- 2.5 5. Face-to-Face Driver Model
- 2.6 6. Flipped Classroom Model
- 2.7 7. Online Driver Model
- 2.8 8. Self-Blend Model
- 2.9 9. Supplemental Blended Learning
- 2.10 10. Mastery-Based Learning
- 2.11 11. Project-Based Learning (PBL)
- 2.12 12. Adaptive Model
- 2.13 13. Hybrid Learning Model
- 2.14 14. Virtual Game-Based Model
- 2.15 15. Station Rotation
- 2.16 16. Lab Rotation
- 2.17 17. Individual Rotation
- 3 Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Blended Learning Model
What Is Blended Learning?
Blended learning is a teaching strategy that mixes face-to-face instruction with digital learning experiences.
It allows students to access content online, engage with multimedia tools, and learn at their own pace, all while benefiting from live interaction with teachers and peers.
Unlike traditional methods, where the teacher delivers the same content to every student at the same pace, blended learning creates a more personalised learning experience.
It encourages self-paced learning, offers immediate feedback through digital platforms, and increases student engagement by incorporating diverse formats.
Learn about the benefits of blended learning .
17 Types of Blended Learning Models
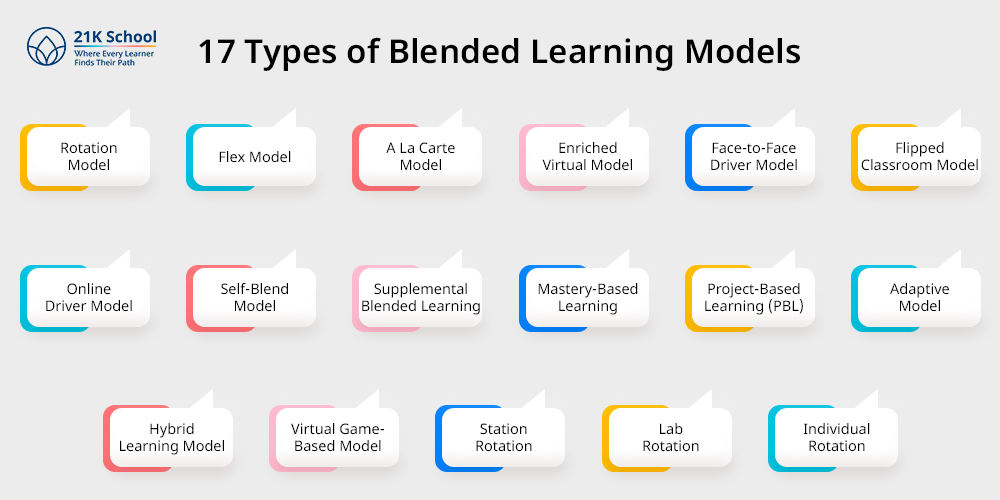
Blended learning models combine online and in-person learning experiences. Each model offers a unique approach to integrating technology and traditional instruction to enhance learning outcomes.
Here are 17 types of blended learning models:
1. Rotation Model
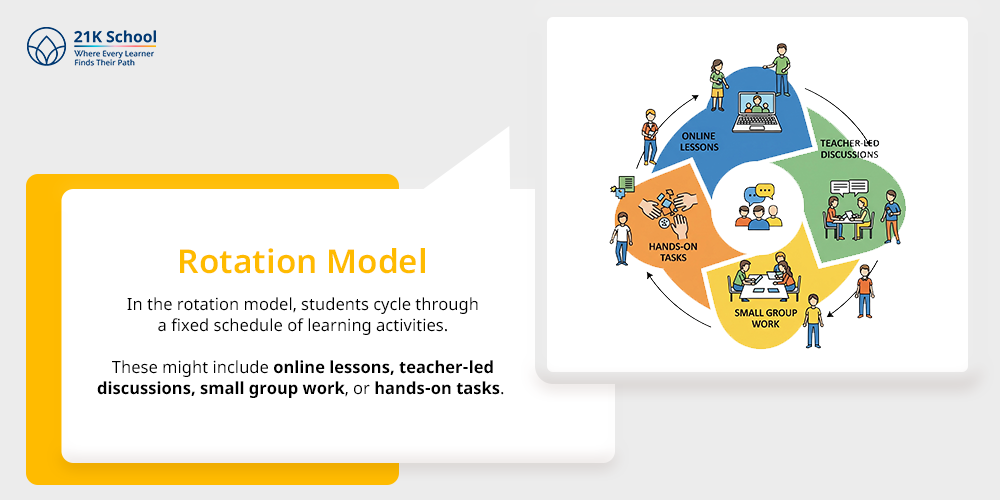
In the rotation model, students cycle through a fixed schedule of learning activities. These might include online lessons, teacher-led discussions, small group work, or hands-on tasks.
The goal is to keep students engaged through variety, while also making sure each mode of learning supports the others. It’s especially effective in schools that want to introduce technology without removing the classroom structure.
2. Flex Model
The flex model places digital learning at the core of the student experience. Most instruction happens online, with teachers offering support and intervention only when needed.
This model is highly flexible, allowing students to progress at their own pace and seek help as necessary. It’s a strong fit for high school learners, adult education programs, or settings where independent learning is encouraged.
3. A La Carte Model
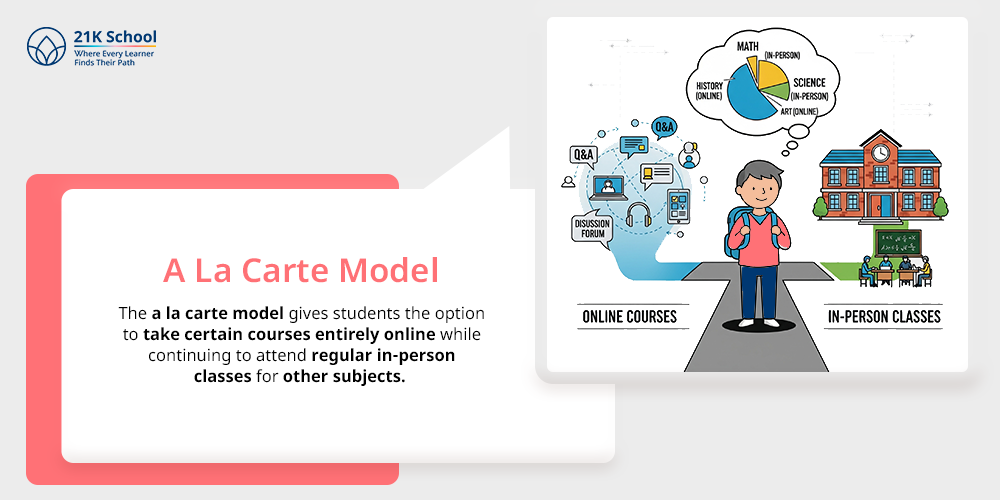
The a la carte model gives students the option to take certain courses entirely online while continuing to attend regular in-person classes for other subjects.
It’s a practical way to offer subjects that may not be available in a school’s curriculum, such as advanced science or niche electives. It also supports students with specific learning interests or scheduling conflicts.
4. Enriched Virtual Model
In the enriched virtual model, students complete the bulk of their coursework online, but still attend scheduled face-to-face sessions with a teacher. These meetings offer support, clarification, or discussion.
The model provides flexibility while still maintaining some classroom connection, making it a good middle ground for students who thrive with both independence and personal interaction.
5. Face-to-Face Driver Model

In the face-to-face driver model, traditional schooling takes the lead, with online tools used to supplement learning. Technology is integrated into the classroom as an enhancement rather than a replacement.
Teachers remain in control of the pace and content, making it ideal for classrooms just beginning to explore digital integration. It allows students to get familiar with online tools in a structured and positive learning environment .
6. Flipped Classroom Model
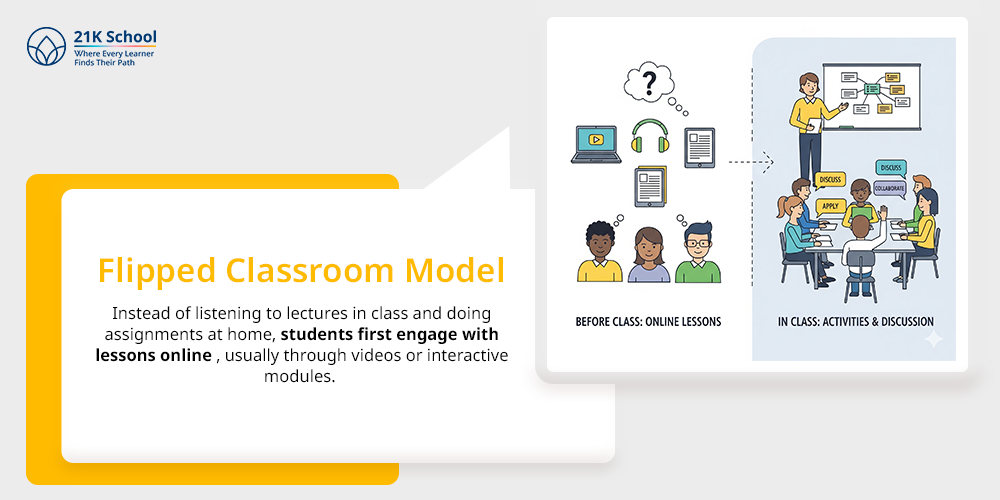
The flipped classroom reverses the traditional learning process. Instead of listening to lectures in class and doing assignments at home, students first engage with lessons online , usually through videos or interactive modules.
Class time is then used for deeper discussions, problem-solving , or collaborative work. This model encourages active participation and helps students arrive in class ready to explore topics more thoroughly.
Also read: Traditional Classroom vs Flipped Classroom .
7. Online Driver Model

The online driver model shifts all instruction online, with minimal in-person interaction. Teachers offer guidance remotely, often through emails, discussion boards, or video calls.
This model is commonly used in virtual schools or distance learning programs, where students need flexibility due to location, health, or personal reasons. It requires a high level of discipline and self-motivation from learners.
8. Self-Blend Model

In the self-blend model, students voluntarily take online courses alongside their regular school curriculum. These extra courses might be for academic enrichment, test preparation, or personal interest.
This model empowers students to expand their learning independently and explore subjects beyond what their school offers.
9. Supplemental Blended Learning
Supplemental blended learning uses online learning as a support system outside regular class hours. Students might use virtual learning platforms for revision, extra practice, or exploring topics further.
The core classroom experience remains unchanged, but the online component helps reinforce learning. It’s a great option for homework help, exam prep, or individualised support.
10. Mastery-Based Learning
In the mastery-based model, students move on only after they’ve mastered a topic. They work through online lessons and assessments at their own pace, repeating or advancing as needed.
Teachers act as facilitators, ensuring students reach a certain level of understanding before progressing. It’s a personalised and results-driven approach, ideal for ensuring strong foundational knowledge.
11. Project-Based Learning (PBL)

Project-based learning focuses on solving real-world problems through extended projects.
In a blended format, students might conduct research online, use collaboration tools to plan and present, and receive guidance from teachers during in-person sessions.
This method fosters creativity, collaboration, and critical thinking while also making learning more engaging and practical.
12. Adaptive Model
The adaptive model uses technology to tailor learning experiences based on each student’s performance. Online platforms track progress and adjust content in real-time.
Students receive material that matches their level of understanding, while teachers use data to offer targeted support. It’s an effective way to manage classrooms with varied learning speeds and abilities.
13. Hybrid Learning Model

Hybrid learning blends online and offline experiences, but with more emphasis on digital delivery.
Unlike traditional blended learning, hybrid models often involve students learning from home with scheduled in-person meetings.
It’s commonly used in higher education, especially in universities offering part-time or remote programs.
Check out: Traditional Learning vs Hybrid Learning
14. Virtual Game-Based Model
A virtual game-based model uses interactive digital games to make learning fun and memorable. Students play educational games that teach concepts while tracking progress.
Game-based learning is especially effective for younger learners who benefit from visual and interactive experiences. These games can be used both in the classroom and at home to reinforce skills.
Discover: 7 Best Educational Online Games for Kids .
15. Station Rotation
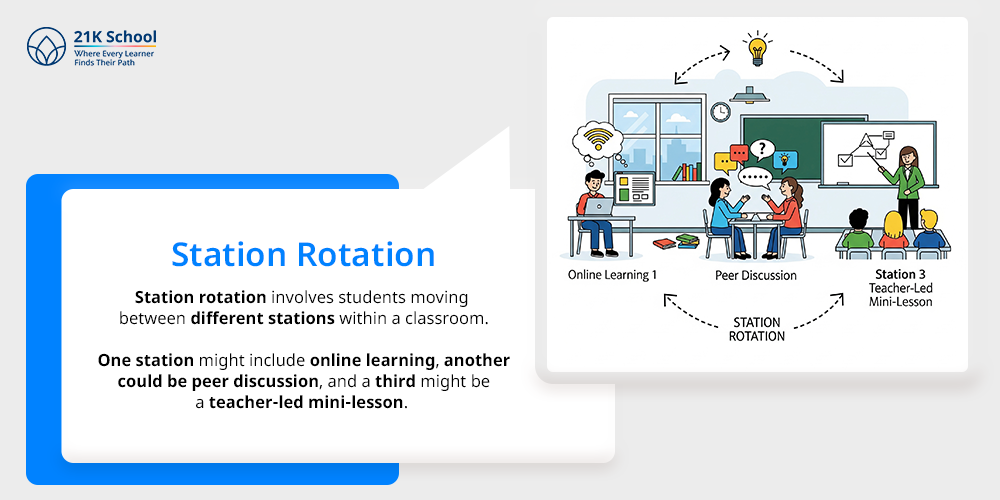
A variation of the rotation model, station rotation involves students moving between different stations within a classroom. One station might include online learning, another could be peer discussion, and a third might be a teacher-led mini-lesson.
This model promotes active learning and ensures students stay engaged with multiple forms of instruction.
16. Lab Rotation
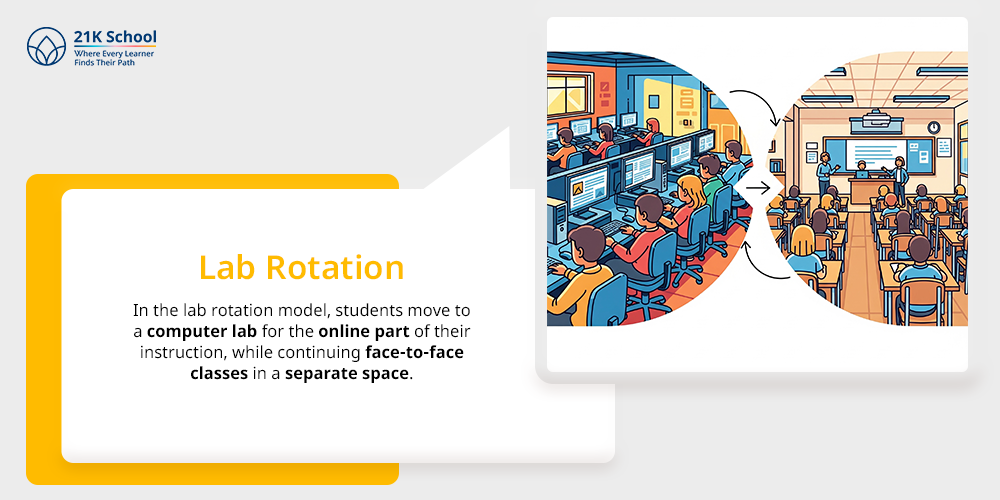
In the lab rotation model, students move to a computer lab for the online part of their instruction, while continuing face-to-face classes in a separate space. It works well in schools with limited classroom technology but access to shared labs.
Teachers remain involved by coordinating with the lab-based sessions and monitoring progress.
17. Individual Rotation
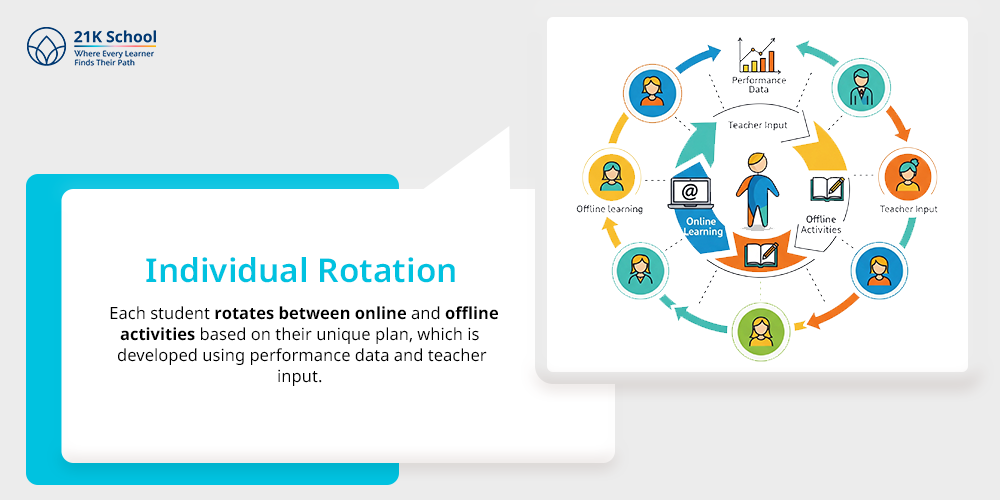
Individual rotation offers customised learning paths. Each student rotates between online and offline activities based on their unique plan, which is developed using performance data and teacher input.
This high level of personalisation helps address individual strengths and challenges more effectively.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Blended Learning Model
Choosing the right blended learning model is not about picking the most advanced or popular option. It’s about understanding what works best for your learners, teachers, and school environment.
Ultimately, the goal is to create a more engaging, inclusive, and effective learning experience.
Blended learning is not just a trend; it’s a thoughtful response to the diverse and changing needs of today’s learners.
With the right model in place, educators can empower students to take charge of their learning journey, encourage deeper understanding, and prepare them for a future where adaptability is key.



