Do you think learning disabilities and learning difficulties are the same thing?
Learning difficulty and learning disability are both different concepts related to each other. Most people use both terms interchangeably to denote learning challenges faced by individuals.
Learning difficulties and learning disabilities are related to intellectual abilities. People with learning difficulties, such as dyslexia, have difficulties in achieving their full potential, even though they possess the mental ability to understand and work with words or numbers.
On the other hand, intellectual capacity is impacted by learning disabilities. This creates a variety of obstacles which hinder the true potential of individuals to achieve their desired goals.
Students who have learning disabilities need support from others or equipment.
The problem of learning difficulties can be avoided by changing the lifestyle, changing the way the information is shared, adapting learning styles, positive learning environment or even allowing individuals with learning difficulties more time to adjust and finish assignments than those without learning difficulties.
Contents
What is a Learning Disability?

Learning disability is a neurological disorder that hampers students’ learning ability. Due to learning disabilities, individuals find it difficult to learn new things or recall new things quickly.
Due to learning difficulties, students find it difficult to speak, write, read, pay attention, understand new things, etc. People will find it difficult to conclude Mathematical calculations or coordinate movements.
Learning disability is different from intellectual disability and doesn’t affect intelligence.
Children who have learning disabilities find it difficult to learn; however, it doesn’t affect their Intelligence Quotient (IQ), or children mental health and it will remain the same or above.
Learning disability can occur due to various issues such as biological factors, birth complications, malnutrition and so on.
What is Learning Difficulty?
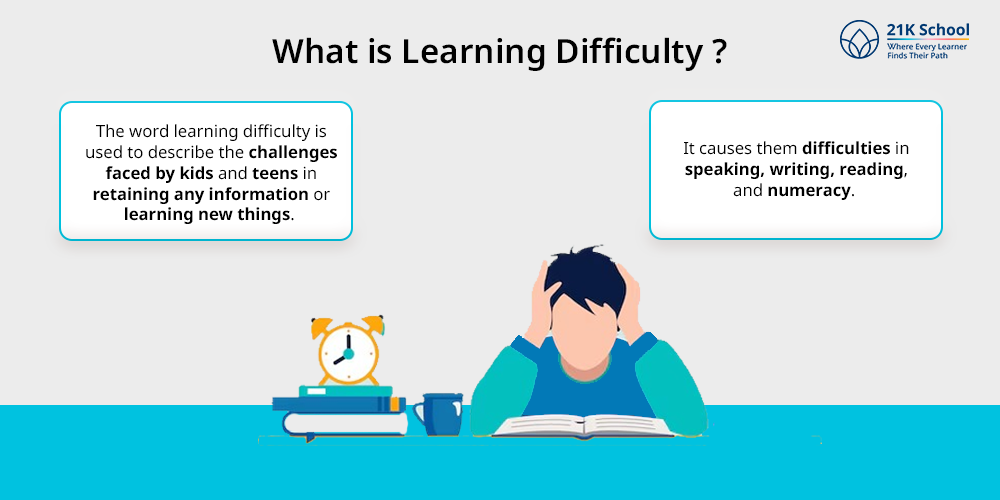
The word learning difficulty is used to describe the challenges faced by kids and teens in retaining any information or learning new things. Due to learning difficulties, students find it challenging to acquire new skills or adjust to existing ones.
It causes them difficulties in speaking, writing, reading, and numeracy. Children who have learning difficulties also face problems with gross motor skills as well as hampers their visual and auditory senses.
Many people consider learning difficult the same as learning disabilities but both are different concepts. Most words are related to each other, but one has an internal factor while the other has an external factor.
Learning difficulty occurs due to various factors such as behaviour changes, sensory impairment, psychological issues and so on. This causes students to process information slower and develop poor knowledge retention.
Distinction Between Learning Difficulty and Learning Disability
Learning difficulties and learning disabilities are related to each other, and many people consider both the same thing.
Both things are considered as problems with difficulties in understanding or analysing new things.
Learning difficulties can occur for a short period of time and can go through proper support or on their own.
Whereas, learning disability is a neurological condition that can occur due to various reasons and can stay for a longer period of time or lifelong.
It is also necessary to know how teachers can help children with learning disabilities
The following are the mentioned differences between learning disabilities and learning difficulties.
| Aspect | Learning Difficulty | Learning Disability |
| Definition | Learning difficulties are obstacles in particular learning domains like math, reading or writing that can be addressed with focused assistance and interventions. | Learning disability is a neurological disorder that hampers students’ learning ability. It affects an individual’s capacity to learn and carry out daily tasks by influencing their adaptive behaviour and intellectual functioning. |
| Impact | Learning difficulty may affect students academic performance and learning ability, However, it doesn’t affect cognitive abilities of students. | Learning disability affects academic performance of students as well as daily activities. It also hampers cognitive function and causes students to hamper their thinking capacity. |
| Characteristics | Learning difficulties affect specific subjects or areas of learning. Due to this students find it difficult to grasp new knowledge. However this can be improved with target intervention and support. | Learning disabilities affects a wide range of learning areas and it can be lifelong. This hampers reading, writing, and math, which also cause difficulties in memory, attention, and organization. |
| Recognition | Both the Disability Discrimination Act and state disability laws do not distinguish learning difficulty as disability. The law does not apply to learning disabilities that result from environmental, emotional or physical factors since they are not an underlying illnesses or malfunctions. | Legally learning disabilities are considered disabilities. State disability laws and the federal Disability Discrimination Act both protect the rights of people with learning disabilities. |
| Example | learning challenges brought on by a stressful home environment, having trouble understanding math concepts because of a lack of practice or having trouble reading because of poor instruction. | This hampers reading, writing and speaking due to various disorders such as Dyslexia (difficulty with reading), dysgraphia (difficulty with writing), and dyscalculia (difficulty with math). |
Wrapping up
Although they are sometimes used interchangeably, learning disabilities and learning difficulties are two different ideas.
Learning difficulties are short-term obstacles to learning new skills or remembering information that are frequently overcome with help and modifications to learning techniques.
On the other hand, learning disabilities are neurological conditions that impair a person’s capacity to receive and process information, even if they are intelligent or above average.
Knowing these distinctions is essential to offering the right kind of assistance and interventions to enable people to realise their greatest potential.