Imagine, every morning when your child enters school they face feelings of apprehension and distress about their safety.
The instances of bullying happening with them is likely concealed underneath their avoidant behavior, screaming through their silence.
The word seems harmless enough yet the statistics tell an altogether darker story. Bullying exceeds basic childhood humor, creating persistent harm which deteriorates student mental health, academic potential, and even causing death.
The occurrence of school bullying has escalated to dangerous levels across the globe in recent years.
Additional digital platform accessibility has transformed bullying into dangerous aggressive behavior.
While there are different factors affecting a child’s mental health, it hides beneath personal virtual spaces.
The rapid rise of bullying concerns needs immediate action from educational institutions, parental support, and aid from entire communities. We need to understand the legal and social aspects of bullying before analyzing its statistical data.
Contents
Is School Bullying Illegal?

To be precise, bullying may or may not be always labeled as a criminal offense. But, it is certainly punishable under the eyes of the government and its policies.
Though there are no direct actions against these crimes, serious bullying leading to the death of a person won’t go off-cards. These types of misdeeds comes under abetment of suicide under Section 306 of Indian Penal Code (IPC), 1860.
Is Bullying a Crime in India?

For present records, there is no specific anti-bullying legislation in India. Yet multiple provisions of the Indian Penal Code (IPC) deal with bullying elements.
Small bullying offenses can be prosecuted by using Section 323 for causing harm through voluntary actions. Other severe cases would be prosecuted under Sections 506 and 509.
Student harassment cases falling under sexual offenses are included in the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences Act (POCSO). Schools must establish anti-bullying committees according to CBSE requirements and RTE (Right to Education).
Both of these organizations work toward establishing secure learning environments. Existing measures prove ineffective at the grassroots level because of insufficient community awareness about their application.
Prevalence of Bullying

Numerous students experience bullying in educational institutions around the world. Each year approximately 246 million students face school violence and bullying according to the reports of UNESCO (2019).
The situation worsens in areas where schools lack awareness about safety rules and where these obligations are not enforced effectively.
The National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR), India, conducted research showing that 42% of school students have experienced bullying.
A higher proportion of cases occur within middle and high school populations. These kids face greater risks due to hormonal transformations and peer group influence.
Facts About Bullying

- The global statistics show that regular bullying targets one-third of total students.
- Female students usually endure relational bullying through social isolation and spread of rumors. But boys usually experience actual physical confrontations.
- A study reveals that bullying targets approx one-fifth of American students who are between 12 to 18 years old.
- After the pandemic-inflicted period, cyberbullying has surged to affect almost one quarter of all teens.
- The risk of suicidal thoughts among bullied students elevates to 2.5 times higher compared to not bullied ones.
These statistics reveal that bullying transcends being a temporary issue since it has become a pressing matter for public health.
Bullying in Schools Statistics
1. Trends

Bullying patterns have undergone significant changes in the last ten years. The evolution in bullying techniques has far gone from pushing, and name-calling.
This is because students now use more insidious methods including social exclusion and cyberbullying.
The doubling of cyberbullying cases in various regions after 2020 directly correlates to the rising screen time and internet usage. Children at age 8 have started showing signs of exercising bullying activities.
Concerning reports indicate that victims do not report bullying incidents. Primarily because they are afraid or experience shame or do not trust the system.
2. Prevalence Among Different Age Groups

- Physical bullying along with exclusion among students begins during primary school ages 6-10 (20-25 percent).
- The majority of bullying occurrences happen to students in middle school between ages 11 and 13. A large proportion of students encounter bullying (40%-45%) or see others bullied.
- Students in High School (Ages 14-18) show continuous bullying through emotional or cyberbullying attacks (30-35%).
- Bullying persists in the college and university (approx20%) in the student population over age 18.
3. Types of Bullying

Proper intervention requires knowledge of different bullying types.
- Verbal Bullying: Target individuals faced put-downs and threats together with name-calling in verbal bullying situations (more than 60 percent) .
- Physical Assault: Purely physical assault along with kicking and striking forms the basis of bullying against abused children (4.9% percent).
- Relational bullying: It includes exclusion, rumor-spreading, manipulation– common among girls.
- Cyberbullying: The practice of cyberbullying and internet harassment is growing rapidly. It now affects 1 out of every 4 teenage victims.
4. Impacts

Bullying has lifelong effects. Victims often deal with:
- Low self-esteem and confidence issues
- Academic decline and absenteeism
- Anxiety, depression, and self-harming behaviors
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- Suicidal thoughts or attempts
Both victims and attackers experience suffering because of bullying. Bullies tend to develop antisocial personality traits together with future legal complications throughout their lives.
5. Elementary School Bullying Statistics

- Bullying occurs once a week to children of age group 5-10 (10%).
- Youngsters most frequently meet bullying through verbal abuse while experiencing social isolation and physical assaults.
- The majority of children at this stage fail to report bullying due to their fear or their limited comprehension of the situation.
6. Middle School Bullying Statistics

- The middle school age group of 11-13 exhibits the greatest vulnerability as they encounter bullying (26% of members).
- Three main factors which lead to conflict include peer pressure, puberty and academic stress.
- Male adolescents tend to conduct physical assaults whereas females prefer relational attacks.
7. High School Bullying Statistics
- The nature of bullying transforms into digital actions.
- Bullying incidents occur to US students while attackers typically use electronic devices (15.7%). Adding to that, US students were bullied in schools (around 19.5%).
- India ranks highest globally in cyberbullying of students aged 10-18 being bullied according to McAfee’s report of 2022 (85%).
- Academic expectations and social competition fuel aggressive behavior.
8. Private School Bullying Statistics

- Private institutions commonly do not report bullying cases because of their reputation-conscious environment.
- Better technological access enables private school students to face cyberbullying. (15% prevalence range)
- Private schools maintain specific social groupings which produce circumstances that lead to relational bullying of students.
Signs That Show Bullying In Children
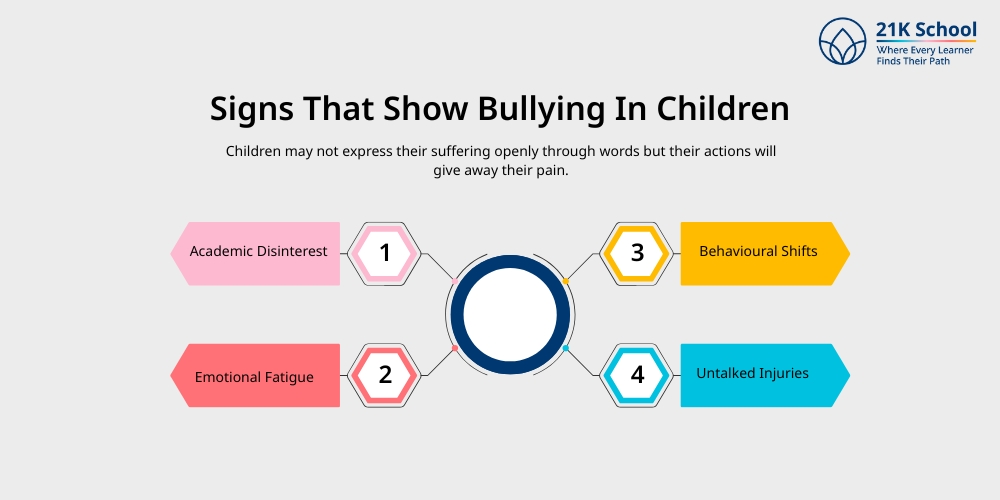
Children may not express their suffering openly through words but their actions will give away their pain.
- Academic Disinterest: School avoidance and declining academic grades should raise suspicions of school being associated with traumatic memories for a child.
- Emotional Fatigue: Notice when your child distances emotionally while also looking for ongoing sadness together with crying spells or increased moodiness. Chronic stress together with anxiety from bullying might manifest through these symptoms. Learn more on causes of stress in students.
- Behavioural Shifts: Changes which include aggression, secretiveness, and avoidances of certain events or classmates point to possible bullying.
- Untalked Injuries: Children having suspicious injuries or physical harm that they are unable to explain might be subject to school-based bullying. Early detection of such warning signs allows you to protect your child from ongoing danger.
Concerns Of Parents: How To Manage
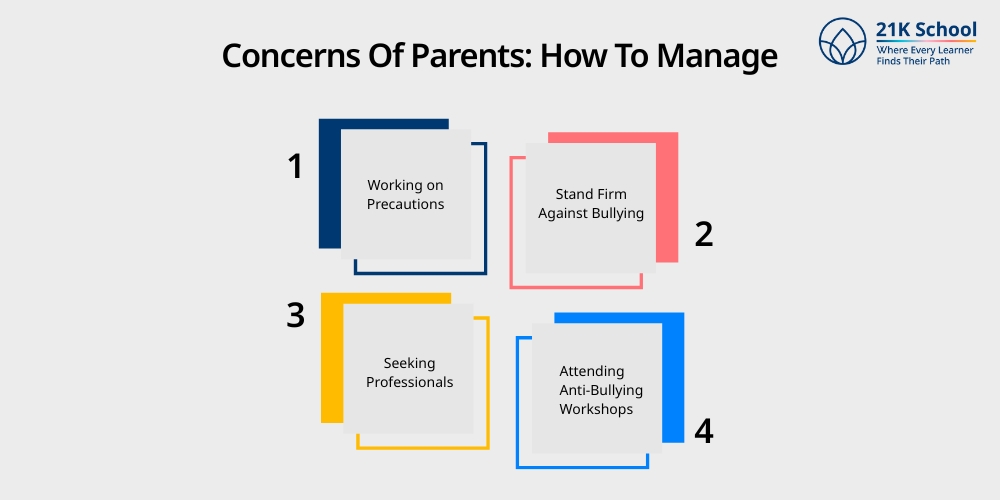
1. Working on Precautions

- Always provide your child with a safe environment for discussing any matters freely.
- Familial digital protection involves watching their electronic communication without invading personal spaces.
- Teach children what bullying means, plus assuring them that it does not stem from their actions.
2. Stand Firm Against Bullying

Take your child’s experiences seriously. The documentation of every incident and contacting school authorities and filing reports must be your first priority.
Report the situation to child protection agencies when school administrators do not resolve it.
3. Seeking Professionals

Ship your child to a counselor or child psychologist when they display emotional trauma symptoms. Early intervention helps in:
- Trauma recovery
- Building resilience
- Developing coping skills
4. Attending Anti-Bullying Workshops

These workshops provide important learning opportunities to parents as well as their children. They offer:
- Conflict resolution techniques
- Awareness about online safety
- Peer-led support systems
Schools need to initiate frequent anti-bullying programs which build both empathy among students while promoting inclusion. Learn more on how to develop empathy in a child.
Winding Up
Bullying exists as a harsh truth which children silently experience in overwhelming numbers. These statistics illustrate the devastating impact. But above all they translate into broken families and ruined dreams as well as permanent injuries to victims.
Every bullying incident including verbal humiliation, physical attacks, and social media abuse reduces a child’s self-assurance and security levels. It hampers the social emotional learning of students.
The problem transcends beyond schools into becoming a major social issue. Parents, teachers, and policymakers need to work toward establishing protective and positive learning environments for each student.
Act immediately by recognizing warning signs because the bullying situation can become too dangerous to save.