
Computers have seen significant changes and development over time. Each generation of computers brought about significant technological advancements as well as some significant design changes.
In the past, grandchildren had to make long trips to visit their grandparents.
With today’s highly advanced cellphones and laptops, the scenario is different. To better understand the history of computer innovation and development, let’s delve further and learn about the “Five Computer Generations.”
Five Generations of Computer
1. The First Generation, 1940–1956 (Vacuum Tubes)
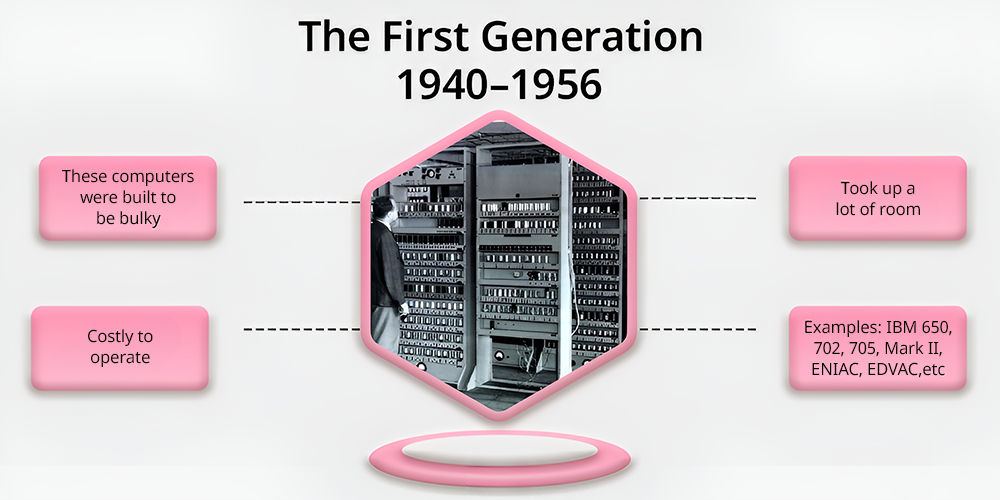
i) Characteristics
- Vacuum Tubes: One of the primary parts for circuitry of vacuum tubes which leads to large size and heat generation in first generation computers.
- Large Size: Computers created in First (Vacuum Tubes) occupy entire rooms due to the bulky vacuum tubes. However, it became difficult to manage.
- Low Speed: These computers are comparatively slower than later generations. It processes a few calculations per second.
- High Power Consumption: Vacuum tubes required a high amount of power or electricity to operate. This contributes to high energy costs and heat output.
- Expensive: The cost is a major problem in this generation. The cost of vacuum tubes and the complexity of building these computers made them expensive. That’s why these computers are accessible only to large organizations in big areas.
ii) Examples
Some common examples of first generation computers are ENIAC, UNIVAC I, IBM 650, and IBM 701.
iii) Advantages
- Complex Calculations: One of the benefits of first generation computers was their ability to perform intricate mathematical calculations. It helps various individuals to perform scientific research, engineering, and other fields requiring complex computations.
- Foundation for Future Development: First-generation computers known for its stepping stone for the evolution of computing technology. It is a big achievement.
- Speed and Efficiency: Earlier people calculated things manually which took a long time. However, with computers manual calculations are replaced.
These computers process data and perform calculations much faster than manual. This makes them valuable for tasks that previously took days or weeks.
iv) Disadvantages
- Large Size and Weight: First-generation computers were physically massive, often requiring entire rooms to house them.
- High Energy Consumption: Vacuum tubes used a substantial amount of electricity, leading to high operating costs and significant heat generation.
- Slow Speed: The vacuum tubes’ operation was slow, making the computers relatively slow compared to later generations.
2. The Second Generation, 1956 – 1963 (Transistors)
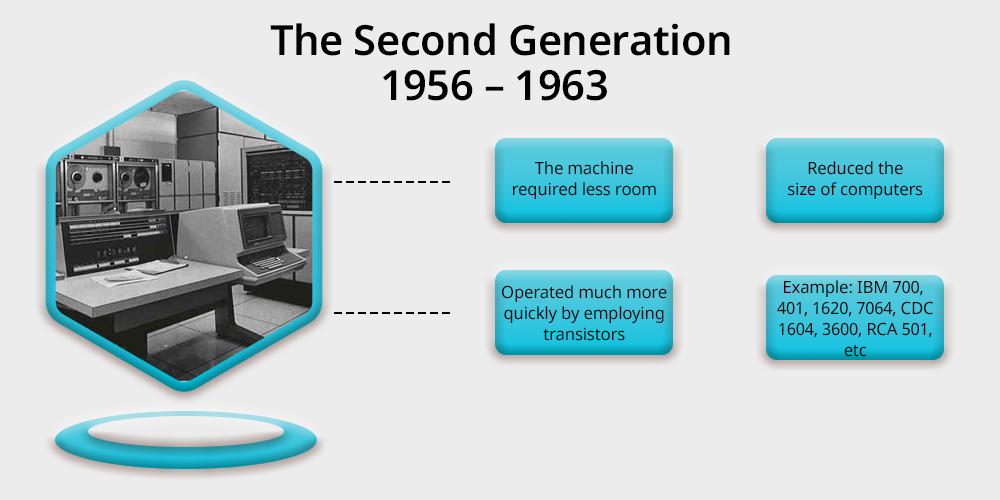
i) Characteristics
- Transistors: In the second generation of computers vacuum tubes are replaced by transistors as the primary electronic component. These are smaller, faster, and more reliable than vacuum tubes.
It is the ideal replacement which controls heat. This helps to make computers more efficient and durable.
- Memory: Magnetic core memory was used as the primary memory of second generation computers.
For secondary storage devices Magnetic tapes and disks are used. This helps in more effective storage and faster data access.
- Assembly Language and Early High-Level Languages: Assembly language has become crucial for this generation. The use of high-level programming languages were introduced.
Languages like COBOL/Common Business Oriented Language and FORTRAN/Formula Translation.
- Speed and Reliability: Speed plays a major role and use of transistors enabled faster data processing times.
It measured in microseconds as compared to the milliseconds of first-generation computers. It directly impacts the long process and end result.
- Size and Cost: Computers in second-generation are smaller in size and less costly than first-generation. However, still everyone can’t afford it.
ii) Examples
IBM 1401, Honeywell 400, IBM 7094, UNIVAC 1108 and CDC 1604 (Control Data Corporation) are some most used second generation computers that are widely used in business, government, and scientific institutions.
iii) Advantages
- Smaller Size: Transistors help to get smaller size computers compared to the first generation’s bulky vacuum tube-based machines. It is a big achievement.
- Improved Reliability: With transistors computers become more reliable and less prone to failure than vacuum tubes. That’s why second generation computers require less maintenance and service cost.
- Faster Processing: Faster Processing is one of the key advantages of second generation computers. And this happened because transistors help computers to process data much faster. The calculations performed here are in microseconds.
iv) Disadvantages
- Maintenance: Transistors are one of the prime advantages but still these generation computers need regular maintenance due to their specific purposes.
- Cooling: Same as the first generation, these computers need air conditioning to manage heat. However, these are less problematic than with first-generation vacuum tubes.
- Manual Production: Second generation required manual production which needed trained technicians and operators. It was difficult to automate, that’s why requiring a manual element in production.
3. The Third Generation, 1964 – 1971 (Integrated Circuits)
i) Characteristics
- Integrated Circuits (ICs): In this generation ICs replaced transistors. It is now a primary electronic component. It provides smaller, more efficient, and less costly devices.
- High-Level Languages: Due to complex programming previous generations had a lot of difficulties. Third generation is easier with the adoption of high-level languages.
Languages such as FORTRAN, BASIC, and COBOL. These languages help developers to maintain more human-readable code.
- Operating Systems: The development of operating systems Such as IBM’s OS/360 and Honeywell’s OS/8 in third generation computers. It helps computers to manage multiple tasks and applications concurrently which improves efficiency.
- Increased Speed and Reliability: Increased speed and reliability is possible in this generation due to ICs contributing to faster processing as compared to previous generations.
- Reduced Power Consumption and Heat: Reduced Power Consumption and Heat is only happening due to IC technology. And the results are impressive, making computers more energy-efficient.
ii) Examples
Examples of third-generation computers include IBM 360, IBM 370, PDP-11, UNIVAC 1108.
iii) Advantages
- Smaller Size: Some size computers are one of the prime advantages. This is done through Integrated circuits.
- Faster Speed: Calculations in nanoseconds is one of the best features of third-generation computers. Now it could perform in a significant speed improvement over earlier generations.
- Lower Maintenance Costs: Less hardware failures meant lower maintenance costs in the third generation.
iv) Disadvantages
- Costly and Complex Manufacturing: Integrated circuits (ICs) are costly to produce. This requires advanced manufacturing techniques and specialized expertise.
- Maintenance challenges: ICs were difficult to repair and it is one of the most common problems that arise. It also needs specialized technicians for frequent maintenance.
- Need for air conditioning: Third-generation systems are still in need of air conditioning to regulate temperatures.
4. The Fourth Generation, 1971 – 1980 (Microprocessors)
i) Characteristics
- Microprocessor-based: Fourth generation depends on the microprocessors. Some crucial features are small, powerful chips containing millions of transistors. This makes them faster, more reliable, and smaller than previous generations.
- VLSI Technology: Very Large Scale Integration helps complex circuits on tiny silicon chips. It directly improved speed, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
- Personal Computer (PC) Revolution: The rise of personal computers took place in the fourth generation. This makes computing more accessible and leads to a societal shift in the way people use these computers.
- Advancements in Programming Languages: Integration of high-level languages such as C, C++ etc became crucial. It is the start of development of some powerful and complex software.
- Networking: In the fourth-generation one of the good features is connecting with the multiple systems. This is laying the groundwork for the internet era.
ii) Examples
IBM PC (1981), Apple Macintosh (1984), Dell, HP, Lenovo desktops and laptops, Intel Pentium series processors, AMD Ryzen processors, Smartphones and tablets (modern examples of microprocessor-based devices).
These are some common examples of fourth generation computers.
iii) Advantages
- Reduced Energy Consumption: As compared to previous generations, the fourth generation reduced energy consumption.
- Microprocessors: The introduction of microprocessors is beneficial which gives benefits by making computers into smaller, faster, and more powerful devices.
- User-Friendly Interfaces: The development of graphical user interfaces or GUIs made computers easier to use for a wider audience.
iv) Disadvantages
- Advanced Technology Required: The production of Very Large-Scale Integration chips in this generation of computers demanded cutting-edge manufacturing technology.
- Complex Maintenance: The complexity of integrated circuits (ICs) and microprocessors is a disadvantage of this generation of computers. This makes it difficult to repair and maintain and also requires specialized expertise.
- Cooling Requirements: These computers also generated substantial heat which was necessary to cool down the process. The use of fans and even air conditioning to prevent overheating is the only way.
5. The Fifth Generation, 1980 & Above (Artificial Intelligence)
i) Characteristics
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Fifth generation computers are good at mimicking human intelligence. This includes speech recognition, image recognition, and natural language processing.
- Parallel Processing: To execute tasks properly this generation computers use multiple processors. This increases processing speed and efficiency.
- Advanced Graphics: Fifth generation computers can handle complex 3D graphics, rendering realistic and interactive visual experiences.
- Natural User Interfaces (NUI): The interface of the fifth generation offers users to interact with computers more intuitively. This can be done by using voice commands, gestures, and other natural forms of input.
ii) Examples
Watson, Google DeepMind (AlphaGo), Siri, Alexa, Google Assistant, ChatGPT and other AI models, Quantum computers (IBM Quantum, D-Wave are some examples of fifth generation computers.
iii) Advantages
- Faster Processing Speed: As compared to previous generations, the fifth generation offers faster processing speeds. This makes it ideal for complex tasks.
- Enhanced Capabilities: One of the most effective and powerful computers created in this generation. Due to the use of Ultra Large Scale Integration (ULSI) chips and the incorporation of artificial intelligence it has become ideal.
- User-Friendly Interfaces: The use of natural language processing and graphical user interfaces makes these computers more intuitive and easier for users to interact with.
iv) Disadvantages
- Job Displacement: AI and automation play a major role in fifth-generation computers. This can lead to job losses in various sectors especially for technicians and people who provide maintenance. These tasks are now increasingly performed by highly specialized machines.
- Surveillance and Privacy Concerns: Various organizations and governments can use advanced AI-powered systems for surveillance. This can raise issues about privacy and the risk of misuse anytime.
- Complexity and Challenges in AI Development: Developing AI systems that match human intelligence is a difficult and lengthy process. This includes significant problems in comprehending and mimicking human cognitive functions.
Comparison of Five Generations of Computer
A quick comparison table of all five generations of computer:
| Generation | Period | Technology Used | Main Components | Programming Languages | Speed & Size | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| First Generation | 1940 to 1956 | Vacuum Tubes | Vacuum tubes, Magnetic drums, Punch cards | Machine language (binary code) | Very slow, very large (room-sized). | First electronic digital computers, faster than mechanical devices. | Large size, high heat, frequent failures, very costly. |
| Second Generation | 1956 to 1963 | Transistors | Transistors, Magnetic cores, Magnetic tape | Assembly language, early high-level languages (COBOL, FORTRAN) | Faster than 1st Gen, smaller size. | Smaller, faster, more reliable, less heat. | Still expensive, limited applications, cooling required |
| Third Generation | 1964 to 1971 | Integrated Circuits (IC) | ICs, Magnetic storage devices | High-level languages (C, BASIC, Pascal) | Much faster, more compact | Increased reliability, lower cost, easier maintenance | Complex manufacturing of ICs |
| Fourth Generation | 1971 to Present (some classify up to early 2000s) | Microprocessors (VLSI) | Microprocessors, Semiconductor memory | Advanced high-level languages (C++, Java, Python) | Very fast; very small (desktop, laptops) | Affordable, portable, user-friendly, widespread use | Dependence on electricity, software complexity |
| Fifth Generation | Present and Beyond | Artificial Intelligence, Quantum Computing (emerging) and ULSI (Ultra Large Scale Integration) | AI hardware, Robotics, Cloud computing, Quantum processors (experimental) | AI languages (Prolog, LISP), Machine learning algorithms | Extremely fast; very small (wearables, embedded devices) | Natural language processing, AI capabilities, autonomous systems | High development cost; ethical and security concerns, still evolving |
Conclusion
Children should perform better in talent development and learning activities and be more beneficial or successful in numerous sectors when they understand how computers work the more advanced the computer technology.
Children involved in utilizing computers to develop technological projects become more accustomed to the technology and are, therefore, more likely to acquire new technologies more quickly.



