
Inclusive education has become a very essential philosophy in the modern education system and seeks to give all children. Despite their ability, background, or needs, a level playing field to learn and develop.
Inclusion is such that students have various issues. Such as learning disabilities, behavior problems, or cultural gaps are not isolated or segregated as in the past.
Rather, they are accepted as valuable participants of mainstream classrooms. Teachers are the facilitators in this change process.
They strongly determine the extent to which a classroom can be inclusive through their actions, decisions and beliefs.
The teacher role, thus, is not confined to the sphere of instruction only. It has to deal with advocacy, flexibility, sympathy, creativity, and life-long learning
Table of Contents
- What is Inclusive Education?
- 13 Central Roles of Teachers in Inclusive Education
- 1. Recognizing and Managing Various Needs
- 2. Using Cooperative Learning
- 3. Enhancing Social Inclusion
- 4. Offering Equal Opportunities
- 5. Enforcing Mutual Respect
- 6. Adjusting Assessments and Assignments
- 7. Parental Concerns
- 8. Diverse lesson Types
- 9. Collaborative Approach
- 10. Curriculum Adaptations
- 11. Other Reading Materials
- 12. Discrete Personal Assistance
- 13. Establishing Good Learning Environment
- Challenges Encountered by Teachers When Ensuring Inclusive Education
- Strategies for developing Role of Teacher in Inclusive Education
- How 21K School Facilitate the Inclusive Teacher Qualities Development?
- Concluding Comments
What is Inclusive Education?

Inclusive education is a teaching method that offers admission to all children to normal classrooms. Without regard to their physical, intellectual, social, emotional, linguistic, and other states.
It is founded on the principle that all children deserve quality education and that they learn better when they do it together.
Inclusion is opposed to integration, where students are merely put in the same room.
Instead, inclusion provides active support of participation through differentiated curriculum, instruction and assessment.
It demands systemic reform, it means changing the culture of schools, professional development, instruction, and even the attitude to learners.
Inclusive education is not equal to uniformity.
13 Central Roles of Teachers in Inclusive Education

Without the skilled assistance of teachers, it is quite impossible to include inclusive education in the curriculum.
Defining roles and responsibilities make it way easier when incorporating training while hiring teachers.
Some of them are mentioned below and are very basic as well as crucial to make every student feel included.
1. Recognizing and Managing Various Needs

When there is a student in distress, academically, attentively or emotionally, the teachers usually notice it first. They make informal assessments, write down behaviors, communicate with parents and specialists in order to provide early intervention.
Accommodating varied requirements entails differentiated learning individual attention or even a referral to special educators or therapists.
When these differences are identified and handled at an early stage, student outcomes are better.
2. Using Cooperative Learning
Cooperative learning methods like peer tutoring, group projects or switching roles enable the students with different abilities to develop together.
These groups are deliberately made by teachers to cross skill levels, be inclusive and eliminate social barriers.
In addition to its academic achievement results, cooperative learning promotes empathy, communication and leadership among all students.
3. Enhancing Social Inclusion

Inclusive classroom culture goes beyond academics. These settings encompass activities such as encouraging friendships, participation, and ensuring that each student feels visible and heard.
Teachers can support that by creating activities that involve all children, by valuing cultural and personal diversity. Not just that, they focus on educating their students about tolerance and compassion.
Social inclusion can alleviate isolation, and it averts bullying.
4. Offering Equal Opportunities
Teachers make sure that every learner has access to learning opportunities according to their potential.
This can be by offering audio books to visually impaired students, additional time in tests, or practical assignments to kinesthetics.
Equal opportunity does not entail similar treatment of all people. It provides the learner with what he or she requires to prosper.
5. Enforcing Mutual Respect

A positive learning environment starts with respect. Educators demonstrate respectful attitudes and implant the rules that prohibit any discrimination or exclusion.
Inclusive language, microaggression solutions, and empathy building can ensure that students appreciate diversity and the dignity of human interaction.
6. Adjusting Assessments and Assignments
Assessment does not only involve marking – it involves gauging comprehension. The teachers adapt tasks to suit learners who might be vulnerable to the traditional approaches.
This can be in the form of provision of oral examination, submission of visual projects or relaxed deadlines.
The idea is to provide all students with an equal opportunity to show their learning and not be limited by their difficulties.
7. Parental Concerns
Parents might feel anxiety regarding the development of their child, fear of stigma, or they might not understand inclusive education.
Teachers can play a key role in reassuring them through open communications and evidence of student growth.
Through this approach, parents will feel engaged in decision-making. They assist in establishing a collaboration in which parents feel encouraged and informed.
8. Diverse lesson Types
Inclusive instruction meant utilizing various ways of explaining a concept, stories, videos, real life examples, interactive games, and tactile materials.
When teachers plan various instructional events, they satisfy visual, auditory, kinesthetic, and linguistic learners.
This makes lessons interactive and helps all students remain engaged and learn in the ways that better suit them.
9. Collaborative Approach
No inclusion is an isolated work of a teacher. Teachers consistently meet with special educators, speech therapists, occupational therapists, counselors and administrators to discuss individual student needs.
Such collaboration leads to more comprehensive education plans and improved problem-solving . Since many eyes are involved in ensuring the child prospers.
10. Curriculum Adaptations
Integrated classrooms usually need the adjustment of the curriculum without watering it down.
Teachers may divide lessons into smaller pieces, use simpler language, give visual displays or come up with enrichment activities.
These modifications make content accessible, meaningful and challenging to everyone.
11. Other Reading Materials
The teachers introduce the students to learning materials that plug the gaps in knowledge and/or accessibility.
It includes larger print storybooks, dual language books, easy to read or audio supported books.
With this kind of diversity in reading materials, no student will be left behind in the enjoyment of literature, and the acquisition of literacy.
12. Discrete Personal Assistance

Sometimes students with additional needs require less than obvious intervention, thus requiring personal support.
Teachers provide personal helpers, repeat instructions in low voice or offer emotional support with no ado.
This will help the student without embarrassing them. And ensures dignity and promotes independence.
13. Establishing Good Learning Environment

Creating a classroom environment where all students are emotionally and physically secure will improve the level of learning.
Teachers can create these environments by using inclusive classroom guidelines, positive reinforcement, culture sensitivity and small win routines.
A caring environment helps children to risk, explore, and develop socially and academically.
Challenges Encountered by Teachers When Ensuring Inclusive Education
There are certain challenges that come across the face of teachers while trying to implement inclusive education in the classroom.
This makes the training more complicated and less applicable in the real classes.
1. Training deficiency

In general education teachers receive little training in special education strategies.
This can cause stress and self-doubt due to their inability to differentiate lessons, manage emotional outbursts, or develop individual learning plans.
2. Limited Resources
Inclusive instruction usually needs assistive technologies, visual supports, therapeutic services or other human resources such as shadow teachers.
Sadly not every school can afford or logistically sustain such resources. And teachers are left to their own devices to lead large and varied classrooms with little to no assistance.
Here are some of the resources for professional development for teachers
3. Time Constraints
Individual consultations, special collaboration, and lesson adaptation require time. Having a versatile curriculum and big classes, a teacher can hardly meet the needs of all students.
Especially, when it’s without sacrificing the speed of the lesson.
4. Resistance to Change
Entrenched beliefs, fears of complexity, and lack of encouragement may lead some educators to be resistant to the adoption of inclusive practices.
Motivation, awareness, and professional development are pillars of changing classroom practices but may not be prioritized all the time.
5. High Workload
Differentiated instructions, ongoing assessments, recording of progress and professional coordination impose an extra workload on the teacher.
This can burn out or frustrate them without scheduling assistance that supports the quality of teaching.
Strategies for developing Role of Teacher in Inclusive Education

To dismantle these limitations on the behalf of teachers when practicing inclusive teaching, a certain pathway needs to be followed.
The following section gives you that blueprint.
1. Differentiated Instruction
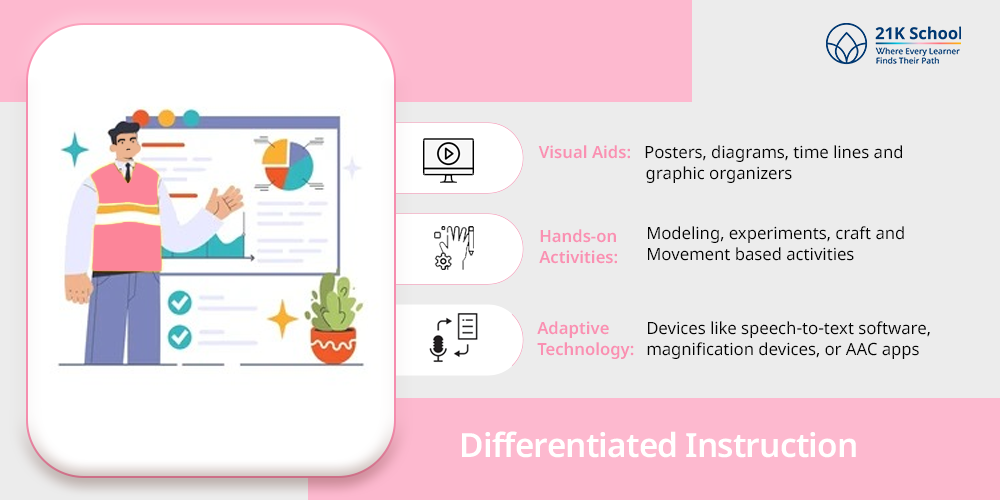
The teachers differentiate the content, process or product depending on the students level of readiness, interest and learning profile.
This approach will allow each learner to work with the content that challenges them sufficiently and takes their individuality into account.
- Visual Aids: Posters, diagrams, time lines and graphic organizers assist memory and comprehension particularly with visual learners or students with reading problems.
- Hands-on Activities: Modeling, experiments, craft and movement based activities enable students to learn by doing. And therefore, abstract concepts become more concrete and interesting.
- Adaptive Technology: Devices like speech-to-text software, magnification devices, or AAC (Augmentative and Alternative Communication) apps allow students with disabilities to follow the curriculum and communicate successfully.
2. Cooperative Teaching Models
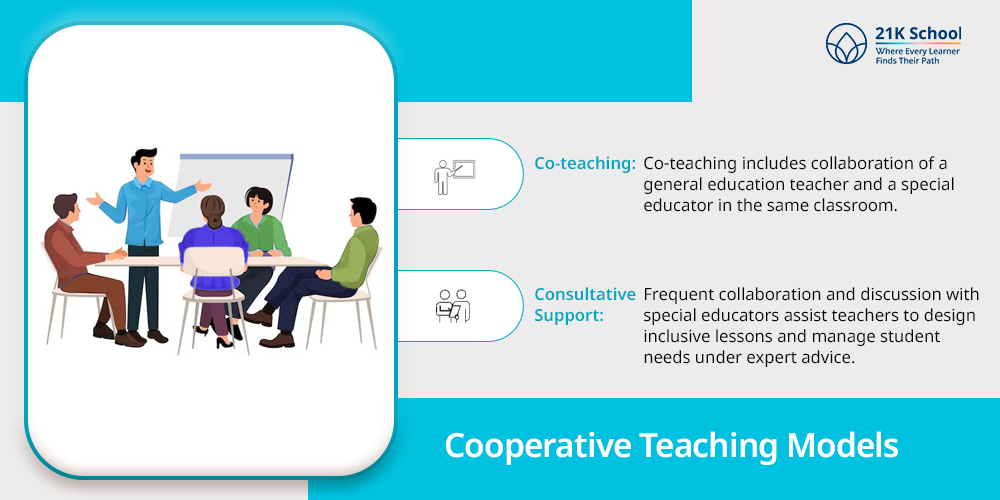
Teaching as a sole responsibility on teachers would create tension. Distributing these responsibilities among other facilitators and administrators makes it way easier and manageable.
- Co-teaching: Co-teaching includes collaboration of a general education teacher and a special educator in the same classroom. They divide planning, teaching and assessing roles, and students get content instruction and special services at the same time.
- Consultative Support: Frequent collaboration and discussion with special educators assist teachers to design inclusive lessons and manage student needs under expert advice. This makes the learning process for students smoother and less chaotic.
How 21K School Facilitate the Inclusive Teacher Qualities Development?

21K School provide teachers with instruments and preparation to use in inclusive classrooms. Their teacher development programs encompass the training on differentiated instructions, emotional intelligence, inclusive assessment, and digital tools in special education.
Teachers are provided practical experience on adaptive technologies and mentored constantly. No student is left behind as it promotes collaboration of general educator, special educator, and counselor using virtual learning platforms
They have a flexible and customized curriculum that enables teachers to address diverse learners without challenges.
Concluding Comments
The moderators of inclusive education are the torchbearers of inclusive education. The experiences of students with diverse needs are determined by their attitude, knowledge, and daily practices.
The path to the fully inclusive classrooms is at best pocked with difficulties. Yet the end result student confidence, peer acceptance, and academic growth are more than rewarding.
Teachers can make every child feel celebrated and supported with the help of institutional aid, collaboration, and learning.
And, finally, inclusive education is not only a policy, but also a promise, and teachers are those who fulfill it.



