Education and Knowledge are more likely to seem to be similar concepts, but in reality, they are completely different concepts. Both combine to shape the future and career development of the budding learners.
Education basically refers to a structured framework, which includes only classroom learning in a step-by-step manner. Knowledge is something in a way of human beings and society can together add significant value with proper understanding.
Therefore, both are the fundamental pillars of human growth and development. They both are completing each other – education helps in gaining knowledge, and knowledge improves the value of education.
Table of Contents
What is Education?
1. Definition and Meaning
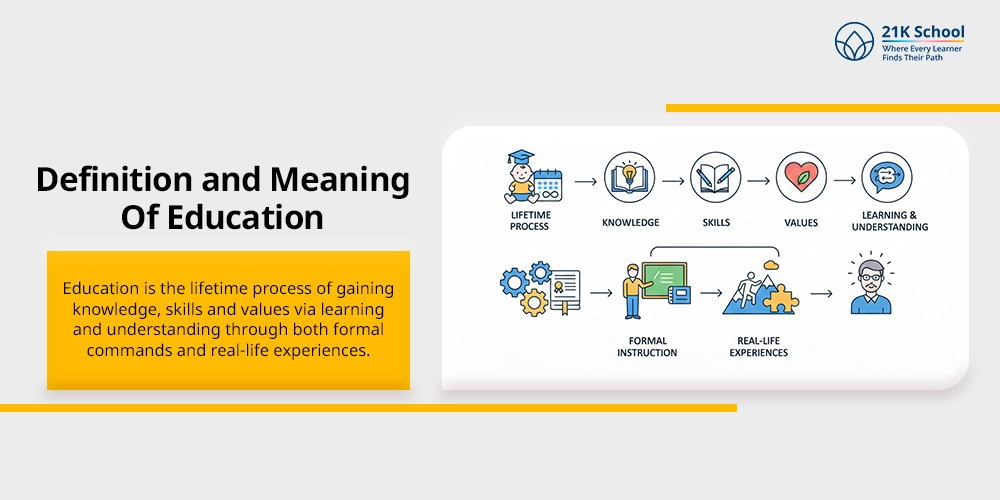
Education is the lifetime process of gaining knowledge, skills and values via learning and understanding through both formal commands and real-life experiences.
It is a continuous learning process to develop strong intellectual skills and maintain a positive attitude towards society and community.
It helps individuals to foster certain intellectual skills, such as critical thinking, analytical skills, and problem-solving skills, in order to build a strong personality.
2. Purpose of Education
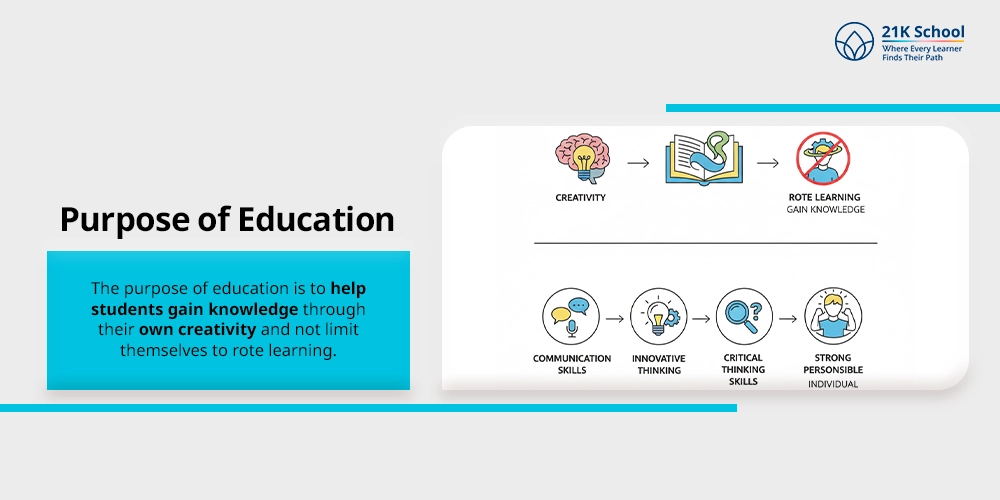
The purpose of education is to help students gain knowledge through their own creativity and not limit themselves to rote learning.
It improves communication skills, innovative thinking and critical thinking skills in order to develop a strong personality in society and act as a responsible individual.
In the current generation, education is empowering unity and creativity among the people by allowing them to adapt themselves to the changing environments.
What is Knowledge?
1. Definition and Meaning
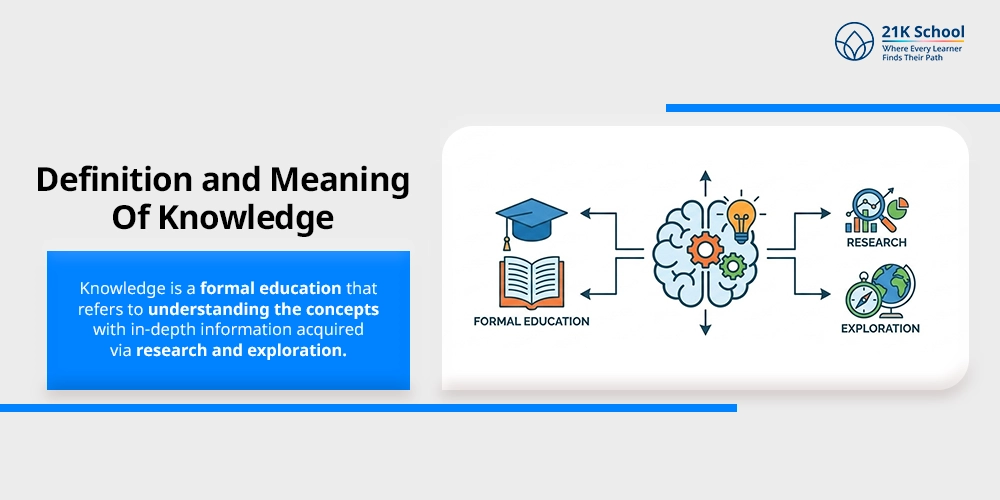
Knowledge is a formal education that refers to understanding the concepts with in-depth information acquired via research and exploration.
It is known for the collective facts and information that help an individual to take proper decisions.
Knowledge can be acquired through any source, be it formal or informal, so it converts the facts to meaningful ideas and helps the individual in solving problem analytically and critically.
A simple example includes: A student understands that avoiding studies may lead to failure in exams.
2. Types of Knowledge

Knowledge is of three types:
1. Theoretical Knowledge:
Theoretical knowledge is defined as the perception of principles, core ideas and concepts learned with the help of studying, reading, or hands-on experience.
2. Practical Knowledge:
Practical Knowledge is defined as implementing the theoretical concepts into real-life scenarios or experiments and is acquired by hands-on learning or by performing real-life experiments.
3. Experiential Knowledge
Experiential knowledge is defined as the knowledge that is learned or acquired through personal experiences, and observations.
Therefore, these types of knowledge are complementing the education, and are making learning more engaging and interactive.
Key Differences Between Education and Knowledge
Let’s explore how both are different from each other and why the involvement of both the pillars is required in order to achieve a well-established future.
Below mentioned is a tabular representation of their key features and differences.
| Aspect | Education | Knowledge |
| Definition | Education, a structured process of learning concepts. | Knowledge, a collection of facts and data. |
| Acquisition | Education is acquired through organised teaching methods or by vocational training. | Knowledge is acquired by overall personal experience and by self-exploration. |
| Nature | The nature of education is theoretical and factual. | The nature of knowledge is practical and experimental. |
| Structure | Education has a structured framework. | Knowledge has a flexible framework. |
| Scope | Education offers a foundation for base career. | Knowledge offers to go beyond the classroom learning. |
| Example | Attending a college to earn a degree certificate. | Implementing ideas to solve real-life challenges. |
1. Definition
Education refers to the method of gaining knowledge from teachers by students, such as ideas, skills and values, which are mostly required in every individual to build a good personality and become successful in their career and future.
Knowledge refers to recognising and grasping the ideas and experiments fast by understanding the depth of the concept and applying them when required.
2. Acquisition
Education is acquired from classroom learning with the help of lectures, group discussions, and interactive activities, which are done in schools, colleges, and institutions.
Knowledge is acquired by understanding the concepts thoroughly and implementing creative ideas over the same in an experimental way to get practical experience.
3. Nature
Education has a structured framework within which teaching methods, syllabi are included.
Knowledge is limitless; it allows individuals to go beyond the academic and think creatively and gain life experiences.
4. Structure
Education has a well-organised structure. It mainly includes stages like primary, secondary and higher secondary with different curricula for each stage.
Knowledge has no fixed structure. It keeps on increasing simultaneously with time and experiences.
5. Scope
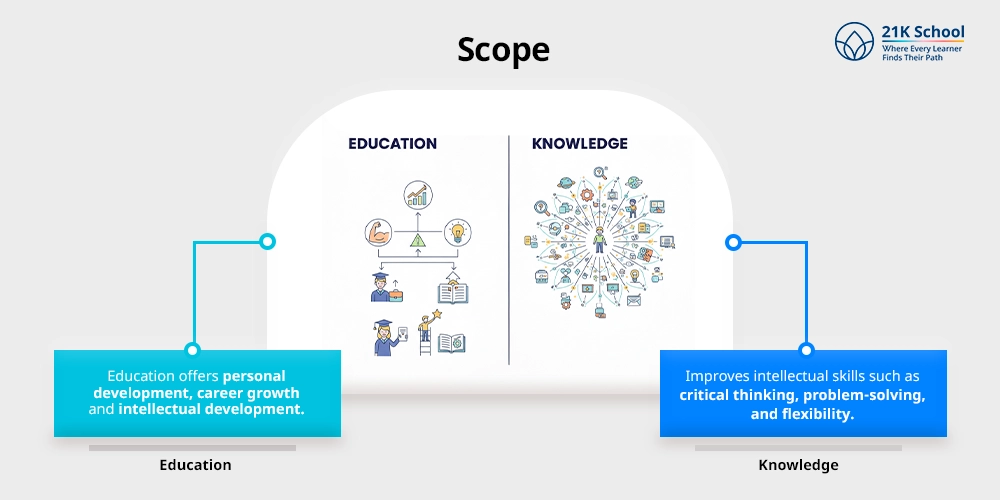
Education offers personal development, career growth and intellectual development of the individuals.
Knowledge offers wider opportunities for individuals in terms of improving intellectual skills such as critical thinking, problem-solving, and flexibility.
6. Example
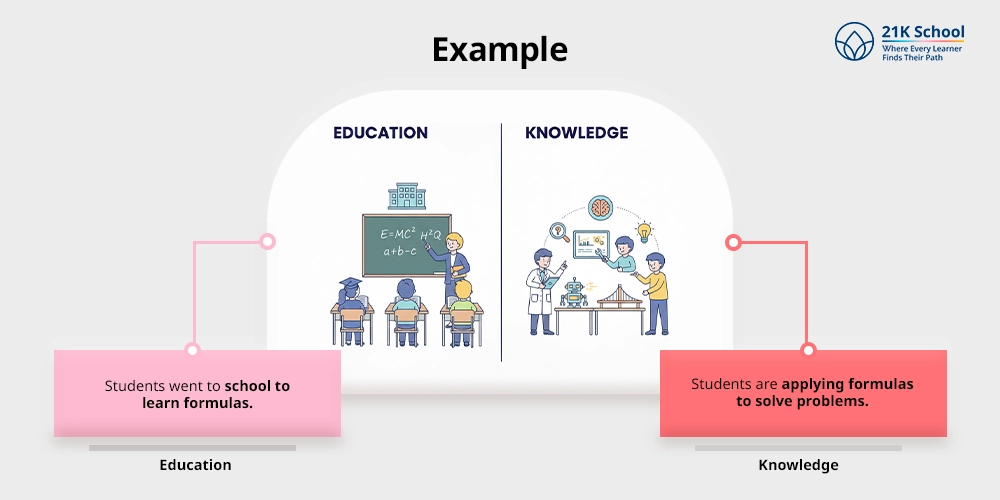
Education – Students went to school to learn formulas.
Knowledge – Students are applying formulas to solve problems.
Conclusion
Education and Knowledge are interlinked with each other, but are different in features. Education offers a structural guide for learning, gaining ideas, earning degrees and certificates.
Knowledge relates to the depth of the concept, which comes from both exploring and experience.
Education now offers the opportunity for every individual, but knowledge makes their concepts and understanding clear and precise.
Education builds the basic foundation of all subjects, which will be beneficial for the students to grasp the concept more easily and smoothly, whereas knowledge helps in utilizing the ideas practically in real-world cases.
In current scenarios, coordination between the classroom learning and experiential knowledge is important. The educated individual gets the credentials, but the knowledgeable individual becomes wise and smart.