E-learning is different from classroom learning in education. E-Learning can be conducted on any electronic medium. In e-learning students do not even need to leave home and study with computers.
Classroom learning takes place in a physical room, however. Classroom learning usually involves disciplining and giving orders.
E-Learning has pros and cons so before you pick the best education method think about what the students want.
Table of Contents
What is E-learning?
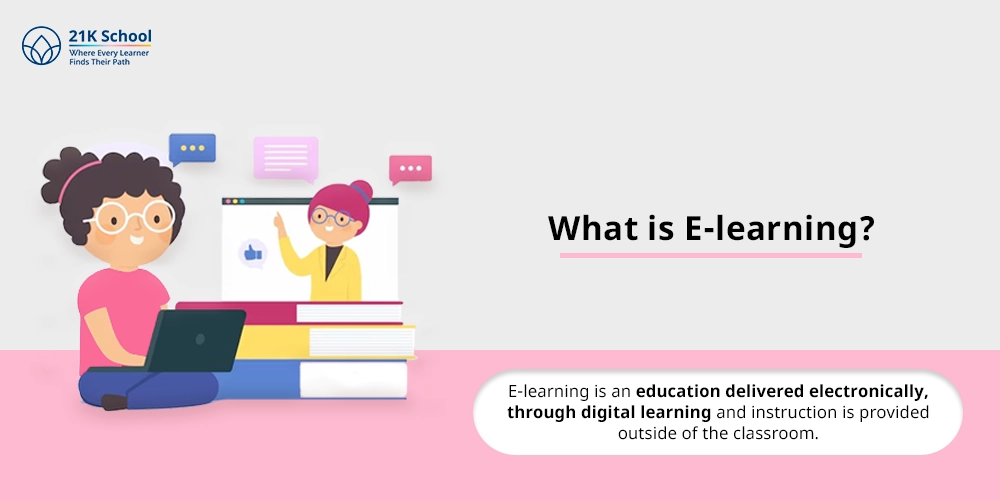
E-learning is an education delivered electronically, through digital learning and instruction is provided outside of the classroom.
E-learning uses online tools such as, internet, computers, mobiles and special software to make education more accessible, flexible and interactive.
Delivery can be synchronous with live online classes or webinars or asynchronous with self-regulated learning where people access material at their own pace via recorded lectures or online modules.
E-learning is flexible and can be used by working professionals/students with disabilities or in remote areas to come to classes without being interrupted.
What is Classroom Learning?

Classroom learning is instruction in a physical classroom where students and teachers do direct work in a set environment – usually at a school, college or university.
That is how educators interact in person lectures, discussions, demonstrations, hands-on activities with textbooks, whiteboards, and laboratory equipment.
At their base are classroom learning classes at fixed times and places, and students of the same age or equivalent academic level find study routine and community to study.
E-learning vs Classroom Learning
Online learning is also called virtual learning. Online studying is possible through an e-learning platform. Instead of classroom learning, students take classes when they come to the school. Differences between e-Learning & classroom learning are listed below.
| Aspect | E-learning | Classroom learning |
| Definition | Electronic media like the internet, displays, mobile devices etc. are used for e-learning. | Classroom learning is learning in classes that students take physically. |
| Personalisation | E-learning offers a personalised learning opportunity that enables students to meet their desired needs. | Classroom learning is more generic because all students are in the same classroom period. |
| Interaction | E-learning is mostly virtual interaction via virtual learning platforms or videoconferencing. | Classroom learning involves physical contact between children and teachers. |
| Flexibility | E-learning is adaptable to student study habits and conveniences. | Classroom learning is more rigid and students have to study a class routine. |
| Accessibility | E-learning is accessible compared to classroom learning and is open to everyone so students can study anywhere even in remote areas. | Classroom education is not for everybody, especially in remote areas. |
| Structure | In e-learning there are synchronous and asynchronous learning methods and flexible education possibilities. | Classroom education is structured with rules, routine and curriculum. |
| Cost | E-learning is cost effective as no student pays for transport, uniforms, meals, accommodation etc. | Classroom learning costs money, students pay for transportation, accommodation, meals, uniforms, I-card fees etc. |
| Assesment | Assessment process of e-learning is automated which, includes online quizzes, simulations, peer reviews, which is conducted after the completion of course work. | Assessment of classroom education is mostly based on class tests, oral exams, project work, participation and so on. |
| Examples | Examples of e-learning are Coursera, Khan Academy’s free video tutorials with interactive exercises. | Examples of classroom education mostly includes face to instructions provided by teachers to students, along with class notes and copies. |
1. Meaning
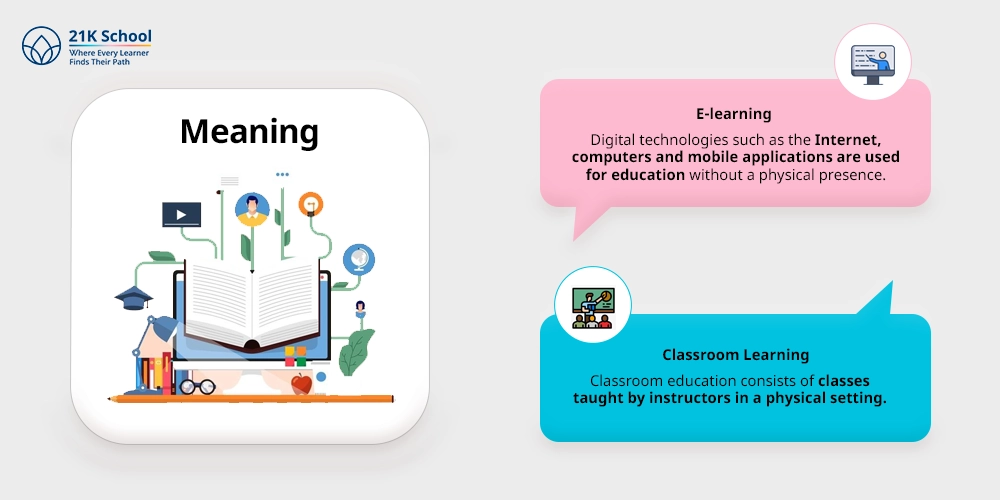
E-learning
Digital technologies such as the Internet, computers and mobile applications are used for education without a physical presence for example, videos, interactive modules and virtual simulations.
Classroom Learning
Classroom education consists of classes taught by instructors in a physical setting, such as schools or universities, lectures, discussions, and hands-on activities based on human contact.
2. Level of Personalisation

E-learning
E-learning generally has high levels of personalised education because it uses technologies of education which adapt content, pace and difficulty according to learner progress, preferences and performance data so that pathways are more personalised even in large courses.
Classroom Learning
Classes offer moderate personalisation in some cases through teacher observation and/or changes during sessions such as one-to-one feedback or modified assignments, but are often constrained by group needs and less tolerant of different learning styles in a one-size-fits-all education.
3. Interaction

E-learning
Interaction is mostly virtual and mediated in e-learning via chat forums, video calls, and discussion boards, which are global but less immediate and personal and thus less social cues/engagement for some learners.
Classroom Learning
Classroom learning is best done in person-to-person contact, allowing for spontaneous discussions, group collaborations, body language reading, immediate clarification by teachers and peers, but not exposure to other points of view outside of the local group.
4. Flexibility
E-learning
E-learning is very flexible; learners can take materials at their own pace from anywhere with internet access on varying times for work, travel or other personal commitments. It is great for lifelong learners or people with irregular routines.
Classroom Learning
Classroom learning is less flexible because it is based on fixed timetables, designated places and synchronised attendance, which enforces discipline and routine but is not always easy for people with mobility problems, full time jobs or distant homes.
5. Accessibility
E-learning
In theory, e-learning is accessible to all people worldwide via online platforms and includes access for those with physical disabilities via subtitles or screen readers when compared to classroom learning. It needs reliable internet, devices and tech skills that not everyone has.
Classroom Learning
For local populations living in close proximity to institutions sharing resources/support staff, it is easier to learn in classrooms – not for those in remote areas with transport difficulties or health-related mobility problems that need extra accommodation.
6. Educational Structure
E-learning
Most often, its educational structure is modular and non-linear with asynchronous learning elements such as self-paced modules and optional synchronous elements such as live webinars that allow learners to move content goal-oriented without hierarchies.
Classroom Learning
Classroom learning is more rigorous hierarchical defined curricula, sequential lessons, teacher-centred progression based on class schedules, attendance policies – covered if non-prescriptive.
7. Assessment

E-learning
Assessment is usually automated and varied and may include online quizzes, simulations, peer reviews, formative assessment tools, data analytics, immediate feedback on completion rates, etc.
Classroom Learning
For classroom learning, there are in-person exams, oral presentations, group projects and teacher observations for assessment of understanding, creativity and participation.
8. Examples

E-learning
Examples of e-learning include programming courses on Coursera, Khan Academy’s free video tutorials with interactive exercises, or corporate training on LinkedIn Learning.
Classroom Learning
Classroom learning examples are school lectures in maths, university seminars with professor debates or vocational education, workshops in labs all in physical places with real group dynamics.
9. Cost

E-learning
E-learning costs little money and students can study at home without going anywhere. In the same way as online learning you do not need uniforms or pay for food, accommodation and transport so it is quicker.
Classroom Learning
Classroom learning generally costs more than tuition because of upkeep costs for buildings, utilities, textbooks and faculty salaries plus indirect costs like commuting or uniforms.
Conclusion
E-learning is flexible, accessible & personalised for modern, diverse lifestyles when compared to classroom learning. Whereas classroom learning is more social, disciplined and hands-on-learning.
Ultimately it is a choice about goals, resources and circumstances so learners can succeed in an ever changing environment of education.