
There are times when students just don’t get it, and the best that can be done is to try to understand the situation.
An environment of a well-disciplined classroom gives not only reason for academic success but also provides room for emotional and social growth.
Through respect for one another, it gives students power to claim ownership for their behavior and own it.
To get such a classroom to be productive and thriving, discipline isn’t easy, yet the right strategies and positive approach can help keep things in check.
Discipline is so much more than rules, it’s about having clear expectations and consistent routines, building strong relationships.
It’s about creating a supportive environment where children feel safe, valued, and empowered to succeed both academically and personally.
This blog will endeavor to explain the important techniques and tips that aid in making classroom discipline become something other than just possible, Discipline becomes more than just a possibility — it transforms into something beneficial for everyone involved.
Table of Contents
What is Classroom Discipline?

Facilitating classroom discipline means employing teaching methods which help teachers direct student conduct while establishing orderly learning areas.
Students benefit from structured rules backed by prompt behavior modifications when they occur.
Effective discipline serves as a direction system to help students develop mature choices while they learn to respect others effectively.
However, disciplined students learn self-control and show respect and responsibility, which helps them do well in both school and life.
The Importance of Classroom Discipline
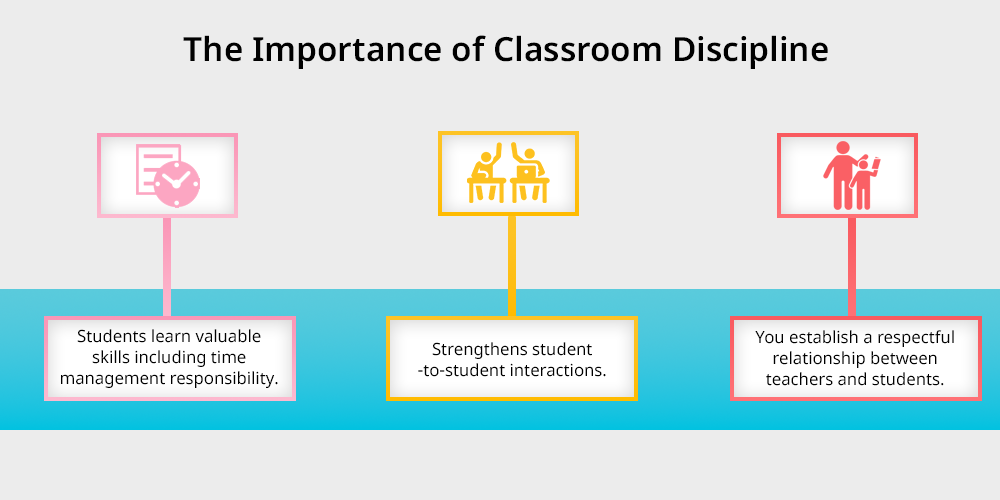
A positive learning environment requires classroom discipline to succeed.
Student discipline keeps learners bound to rules while maintaining conductful actions toward their peers and academic focus.
Educational effectiveness increases as discipline controls classroom activities because it creates optimal student-focus conditions.
Through following smart classroom rules students learn valuable skills including time management responsibility and self-command that become essential life skills both academically and beyond school.
You establish a respectful teacher student relationship, through discipline which produces such a secure environment that each member feels appreciated.
School discipline strengthens student-to-student interactions which creates an environment with enhanced harmony.
Student success and personality development alongside preparedness for future tests entirely depends on classroom discipline.
Types of Classroom Discipline
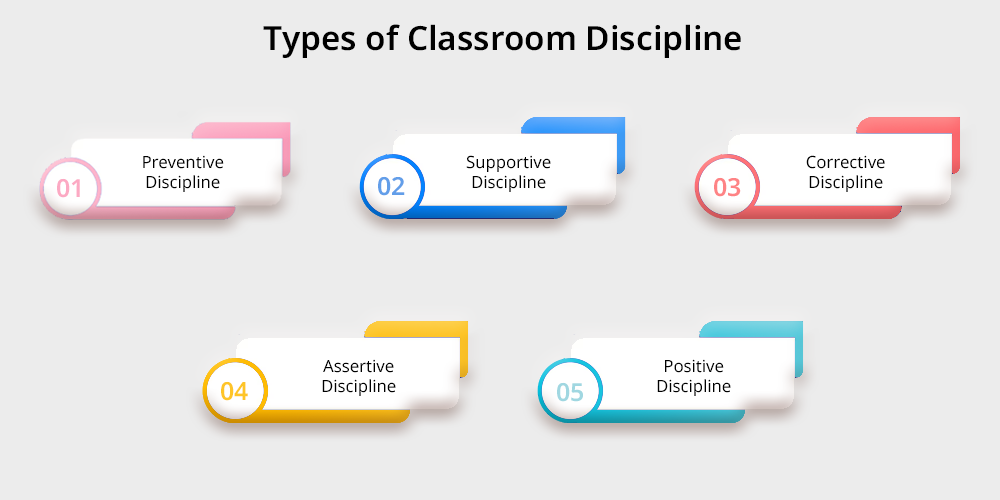
Classroom discipline approaches differ between teachers according to their teaching doctrine and their students’ requirements. The main types of classroom discipline are:
1. Preventive Discipline
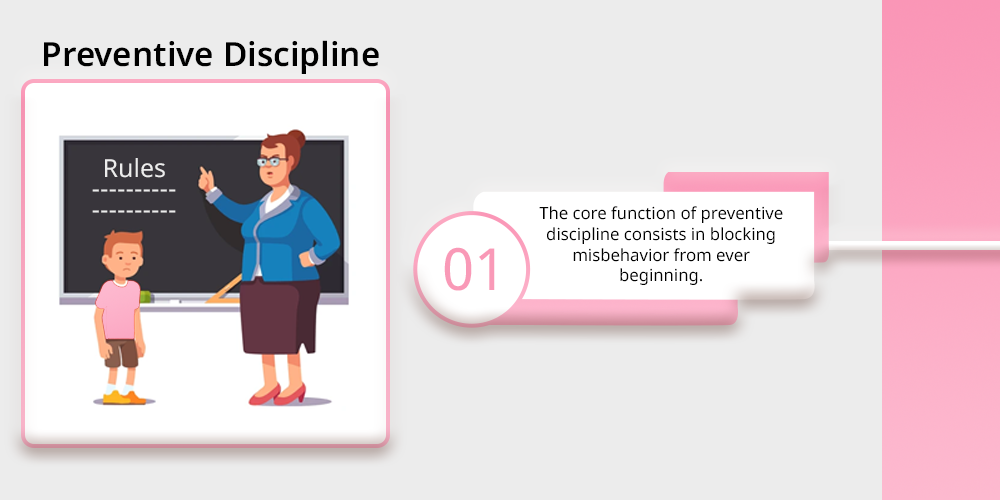
The core function of preventive discipline consists in blocking misbehavior from ever beginning. All teachers begin by establishing clear rules combined with expectations and set routines.
Through clear expectations and structured guidelines students understand classroom norms better while developing positive academic conduct.
A classroom that follows established organization and guidelines teaches students which behaviors are appropriate so they avoid disruptive actions.
2. Supportive Discipline

Supportive discipline functions by providing direction in combination with continuous positive encouragement.
Given this approach teachers provide students with reminders and positive feedback to assist students in understanding proper behaviors.
Educational systems reward students for conforming to rules thus stimulating their motivation to act responsibly.
Through this method students experience an environment that promotes encouragement alongside their sense of importance.
3. Corrective Discipline

School rules require students to face corrective discipline for noncompliance. This approach defines consequences for misbehavior and incorporates them in student learning about making mistakes.
Also Read: Importance Of Discipline In Student’s Life
School authorities will administer either serious verbal reprimands or hand out additional homework or enact situational-specific disciplinary measures.
Educators strive to show students the cost of their decisions while implementing methods which lead them towards better conduct.
4. Assertive Discipline

Under assertive discipline educators establish concrete rules accompanied by steady enforcement practices.
Under this approach students become fully aware of all resulting outcomes from their behaviors while getting proper consequences for their actions.
Teachers keep complete control over classroom behavior to confirm all students understand expectations.
Teachers experience success by using this approach in educational environments which require defined limits combined with strict rule enforcement.
5. Positive Discipline

Positive disciplinary techniques work to help students develop from their mistakes by making them take ownership of their actions.
Student discipline moves beyond punishment because this method teaches students to solve problems independently along with developing self-control abilities.
The teaching covers how student conduct impacts others plus provides methods to achieve improvement. It builds students’ character and encourages improved choices throughout their future lives.
Strategies for Implementing Classroom Discipline
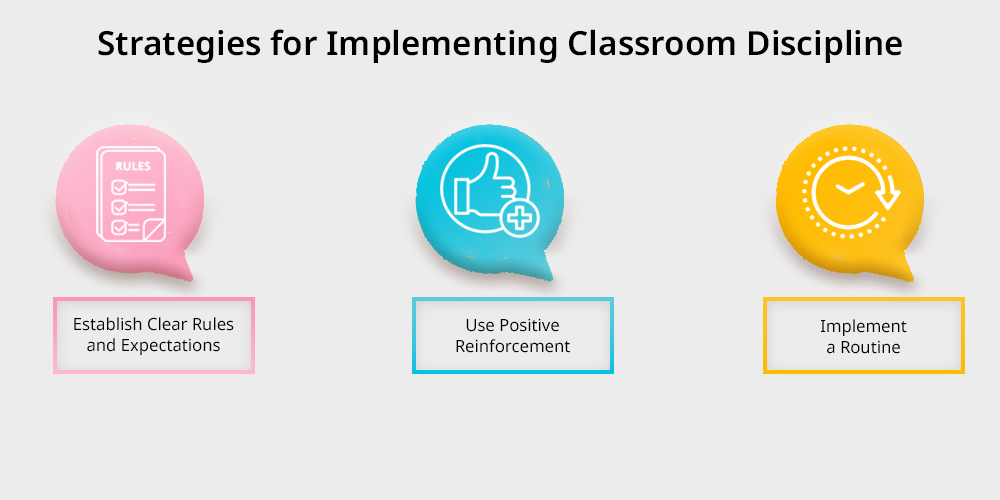
- Establish Clear Rules and Expectations: Students need to hear school rules at the beginning of the year followed by direct rule communication. Students should understand rule expectations through easy to grasp language which teachers can display in prominent classroom areas/ discuss it at the beginning of the year
- Use Positive Reinforcement: Schools should identify students whose behavior meets positive standards so they can receive recognition with rewards. Students respond to praise along with privileges and minor recognition factors in order to follow school rules while establishing a constructive learning environment.
- Implement a Routine: A formal daily schedule enables students to predict what will happen helping them avoid feelings of panic or disruptive conduct. Students stay involved in educational activities when classroom assignments give them responsibility.
- Address Misbehavior Calmly and Firmly: Use a proved tone with steady conviction when you need to correct student misbehavior. Avoid raising your voice because it causes the problem to escalate. Students focus on examining their conduct when taught through a calm manner.
- Encourage Open Communication: Support your students through a caring atmosphere which allows them to freely share emotional responses and worries. The habit of really hearing students enables teachers to earn their trust and earn their respect.
- Lead by Example: Teachers must show desirable traits such as respect and punctuality as well as kindness for students to learn them.
Challenges in Maintaining Classroom Discipline
Students respond differently to numerous school environmental factors proper flexibility combined with strategy enables effective management.
- Lack of Student Engagement: The lack of student engagement that results when lessons fall flat often creates a pattern of both boredom and behavioral disruptions. Sustained student engagement along with digital classroom motivation stands as the vital foundation for keeping order.
- Diverse Learning Needs: Each learning environment contains diverse students because they belong to various backgrounds with different ability levels and ways of absorbing information. Student needs require individualized treatment but a generic discipline system limits fairness in schoolwide disciplinary approaches.
- External Influences: Students’ classroom behaviors and attitudes undergo substantial influences from events or challenges which exist beyond the school environment including family distress and peer group influence and personal crisis situations.
- Technology Distractions: Tech devices like smartphones together with social media platforms join a growing list of digital diversions found in learning spaces. Students need to manage technological distractions effectively to achieve learning goals while using educational technology.
- Inconsistent Discipline: Consistent rule enforcement maintains student clarity and stops them from taking advantage of missing disciplinary practices leading to diminished authority respect.
The Role of Technology in Classroom Discipline
Technology can be used in multiple ways to address classroom discipline, serving both as a potential benefit as well as a potential challenge:
- Enhanced Communication: Parent teacher communication platforms can notify families of their student’s behavior so the parents could be part of the team in handling discipline.
- Behavior Tracking Systems: Digital tools help teachers keep more up to date track of behavior patterns and triggers for misbehavior. Such data can be used in targeted interventions.
- Positive Reinforcement: Gamified learning platforms and reward systems can positively attract and engage positive behavior and create a positive classroom climate.
- Distraction Management: There are tools to help control access to distracting websites or apps while in class time in order to keep the student focused on learning.
- Personalized Learning: Technology can also personalise learning when it becomes tailored to the individual student’s needs, which is far removed from the frustration that draws students into unnecessary misbehaviors in the classroom.
- Cyberbullying and Online Misconduct: Cyberbullying and other forms of online misbehavior are possible by employing technology and schools need to establish clear guidelines on how these are dealt with.
Also Read: Technology in Education
Conclusion
A structured respectful learning environment requires classroom discipline to function effectively.
When teachers combine clear rules with positive reinforcement and effective challenge management they build discipline systems that encourage love for learning.
The correct disciplinary approaches in combination with distribution skills create conditions that lead students toward improved educational success and self-improvement.



