People generally interchange two regularly used words: “Education” and “Literacy”. However, both the terms are different from each other.
A lot of people believe that someone who smoothly reads and writes is an educated person. But that’s not true. The meanings are far different.
Understanding the difference between education vs literacy is important to know for both parents and students to implement accurately.
In simple words, literacy is the most basic foundation and education is a wider concept which helps individuals to grow in society.
Let’s explore a detailed comparison between education vs literacy for students and parents’ understanding.
Table of Contents
What is Education?
The term “Education” is popular as the overall development of an individual through gaining knowledge and skills, habits, and values.
Knowledge can be gained in a formal and informal way to understand the world, develop problem-solving skills, make informed decisions, and contribute meaningfully to society.
What is Literacy?

The term “Literacy” means the capability of identifying, reading, writing, understanding, and using the written word to communicate effectively and participate in society.
It is one of the essential parts of students’ learning. For example, a student who is able to read textbooks easily.
13 Key Difference Between Education and Literacy
To understand the difference between education and literacy clearly here’s a quick comparison table:
| S No. | Aspects | Education | Literacy |
| 1. | Meaning | Education is a broad procedure of gaining knowledge, skills, and values for overall growth of learners. | Literacy is the ability to read, write, and understand basic text and numbers without challenges. |
| 2. | Scope | Education covers intellectual, emotional, moral, and social development. | Literacy is limited to reading, writing, and basic comprehension. |
| 3. | Formal vs. Informal | Education san be formal in schools or informal such as life experiences, self-learning. | Literacy is acquired formally through schools or literacy programs. |
| 4. | Duration | Education is a lifelong journey of learning and growth. | It is mostly achieved within early years of schooling. |
| 5. | Goal | The main goal is to nurture wisdom, critical thinking, and responsible citizenship. | To enable basic communication and access to written information. |
| 6. | Assessment | It is measured through exams, projects, practical skills, and life application. | Literacy is measured by ability to read, write, and perform basic numeracy. |
| 7. | Access | Requires resources, teachers, institutions, or experiential learning. | Can be taught with minimal resources such as books, literacy campaigns. |
| 8. | Impact on Society | It builds leaders, innovators, and socially responsible individuals. | It increases literacy rates, reduces illiteracy, and supports basic needs. |
| 9. | Measurement | Sometimes harder to quantify. However, the quality varies by institution and learning environment. | It is easier to measure through literacy rates and reading/writing ability tests. |
| 10. | Examples | Learning different subjects in the classroom for example, science, mathematics and history. | Some common examples like basic maths skills or newspaper reading. |
| 11. | Application | It is applied in decision-making, careers, personal growth, and social change. | It is applied in daily tasks like reading labels, filling forms, or using devices. |
| 12. | Relationship | Education includes literacy as its foundation but expands much further. | Literacy is just the first step toward education. |
| 13. | Outcome | It produces well-rounded, informed, and thoughtful individuals. | It produces functionally literate individuals who can read and write. |
1. Meaning
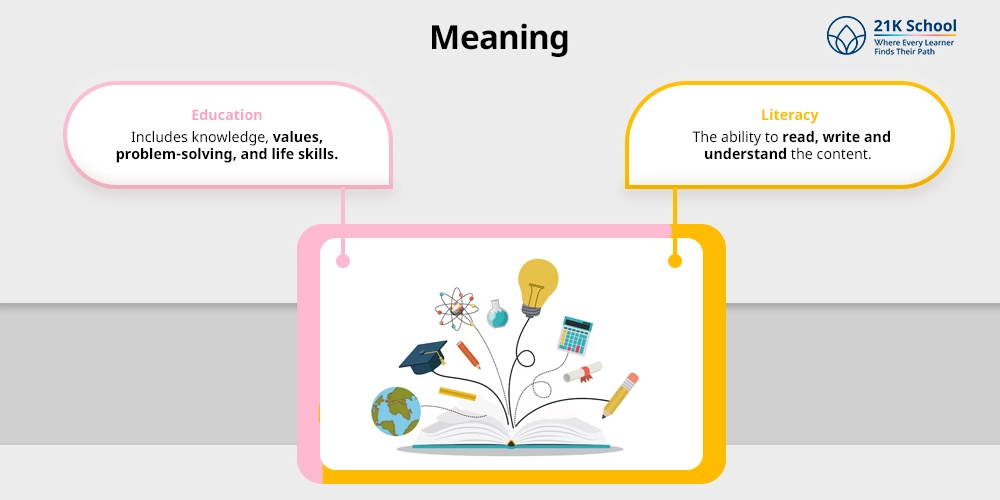
Education: Education is a procedure that includes knowledge, values, problem-solving, and life skills.
Literacy: Literacy simply means the ability to read, write and understand the content.
2. Scope
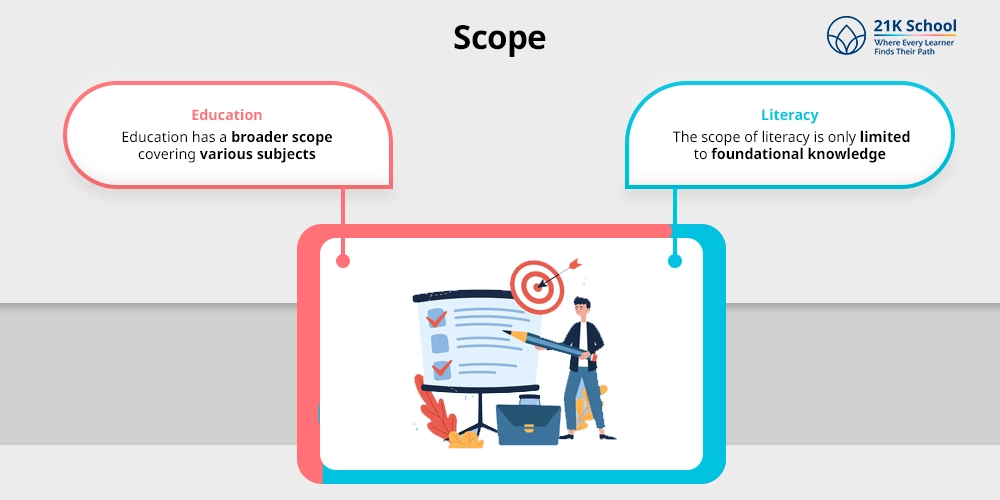
Education: Education has a broader scope covering various subjects, practical experience, social skills, ethics and emotional intelligence.
Literacy: The scope of literacy is only limited to foundational knowledge for example basic numericals and reading paragraphs.
3. Formal vs. Informal
Education: Education can be taken both formal, non-formal and informal ways. For example, learning in the classroom is formal education and tutoring at home is informal education.
Literacy: It is mainly achieved through formal instruction.
4. Duration
Education: Education is a continuous learning in which individuals explore different areas from School two University and so on.
Literacy: Literacy can be achieved in a short span of time by understanding the foundation of learning like writing and reading.
5. Goal
Education: The main goal of education is individual overall development to stay strong in the society.
Literacy: The goal or objective of literacy includes basic comprehension and communication.
6. Assessment
Education: in education assessment is designed by the authority. It includes semester or yearly examination practical exams, classroom tests, projects, internal assessment etc.
Literacy: In literacy the assessment is mainly checked by writing and reading skills.
7. Access
Education: education is easily accessible especially at different levels from primary to higher and vocational education. However, it requires resources, teachers, institutions, or experiential learning.
Literacy: Literacy mainly requires basic things like stationery and stationery. Individuals who lack these basic skills are from rural or underprivileged areas.
8. Impact on Society
Education: It helps in creating strong, independent innovators, leaders, professionals who shape the future well.
Literacy: It helps in reducing the rate of illiteracy and provides all the basic knowledge.
9. Measurement
Education: Education is measured through exams and performance.
Literacy: Literacy rate is calculated by the government whether individuals are able to read and write or not.
10. Examples
Education: Examples such as scientific research or measuring business profit.
Literacy: Reading a letter, study timetable, or advertisement headline are some common examples.
11. Application
Education: Education is applied in various areas like business, professional life, problem-solving, career growth, decision making etc.
Literacy: Literacy applied in basic survival and communication with others.
12. Relationship
Education: Education has more deeper values than literacy.
Literacy: It is an initial step of education that holds many benefits.
13. Outcome
Education: Education provides personal and professional growth, digital literacy, and an environment to adapt to different situations.
Literacy: The result or outcome of literacy is better communication skills and independence.
Final Thoughts!
For learners both education and literacy is important and by understanding the difference the implementation becomes smooth and easy.
Literacy is an initial phase required to continue education. While education is a lifelong learning process helps learners in overall development.
Both literacy and education work together but are not synonymous. Literacy opens the door to a continuing learning journey. Remember, a balance in both ensures future success and growth.
