
Do you know what is the new education policy? And why is there a need for a new education policy?
In 2020 a new educational policy was announced known by the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
Vocational education and skill development are the main goals of the New Education Policy 2024. The primary goal of India’s new education policy 2020 is to improve the country’s educational system and swap out the outdated curriculum in education for the updated one.
The NEP 2020 has a new curriculum that replaces the old 10+2 system with 5+3+3+4. A new change was implemented in 2020 for the National Education Policy regarding the detention policy.
In the new education policy, the no-detention policy has been eliminated and become mandatory for students to pass classes 5 and 8 who did not pass the year-end exam have to retake it within two months. Failing to pass the examination leads to back in the same grade.
Table of Contents
What is New Education Policy 2025-26?
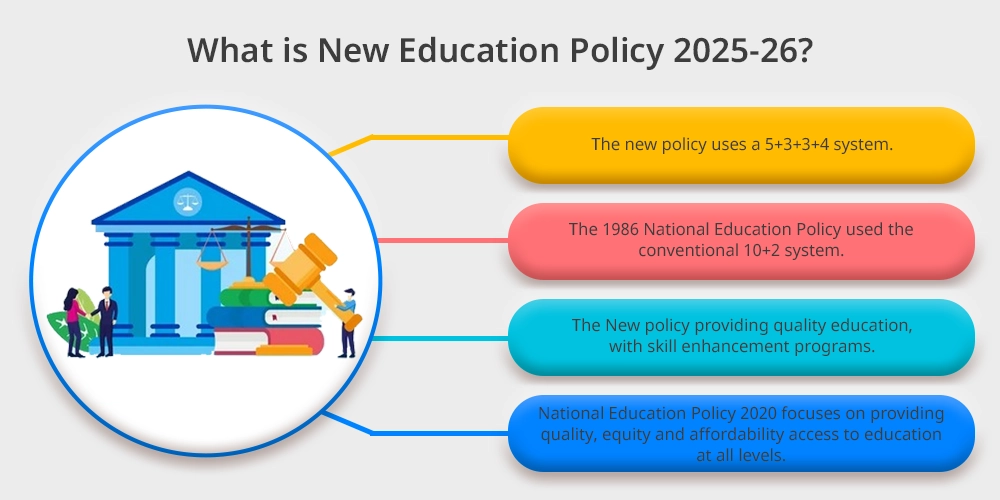
The new policy emphasizes education for the twenty-first century and uses a 5+3+3+4 system that takes into account the developmental stages of children aged three to eighteen.
The 1986 National Education Policy which used the conventional 10+2 system is being replaced by the new one.
The New national education policy has a vision of providing quality education , with skill enhancement programs that will modernize the Indian education system . To meet the educational standards of the 21st century .
Offering high-quality education along with skill-development initiatives is the goal of the new national education policy that will modernize the Indian educational system to fulfill 21st-century educational requirements.
National Education Policy 2020 focuses on providing quality, equity and affordability access to education at all levels.
Features of New Education Policy 2026

The new national education policy has an emphasis on early education that promotes skills development. There are various features of NEP 2020 are mentioned below.
- Early Foundation: The goal of the new education policy is to provide all children with access to education that fosters creativity advances cognitive abilities and aids in the development of emotional intelligence . Developing young brains during their formative years is the main goal of the early Foundation.
- Language as Medium: The New policy implements local language as a medium of instruction for children. This will help in understand the concepts and enhance their confidence.
- Literacy and Numeracy: As part of NEP 2023 one of the main initiatives is to provide basic literacy and numeracy skills by class 3. In addition to improving reading and writing skills this will teach fundamental math and calculation for later study.
- Change in Curriculum: A new curriculum system of 5+3+3+4 has been announced under NEP 2020 replacing the previous 10+2 system. A flexible education system that promotes child development is offered by the new system.
- Higher Education Reforms: There will be no UGC AICTE or NCTE bodies for higher education under the new education policy with the exception of legal and medical studies. All educational boards in india will be governed by the Higher Education Commission of India (HECI) a single umbrella organization.
- Skill-based Learning: Vocational and skills-based learning are the goals of the New Education Policy 2024. The course material will be condensed as part of this initiative which will emphasize experiential learning over theoretical learning. Vocational education is now required for students in grades 6 through 8 under the NEP 2020.
- Enhancement of Online and Distance Education: Online and distance learning alongside traditional classroom instruction is the main goal of the new educational policy. Students will benefit from receiving high-quality instruction and mentoring as a result.
Read More: Online school beneficial for teachers
Need for New Education Policy?

Have you ever wondered why there is a need for a new education policy?
The new policy prioritizes hands-on experience over classroom instruction. Prior to NEP 2020 the Indian educational system had certain drawbacks.
A new national education policy is required for the following reasons.
- 21st Century Education: In the new education system, the framework was designed by aligning the goal of 21st century education. In 21st century education more focus was laid on practical learnings and technical skills.
- Introduced Single Board: Previously there were separate boards for distinct exams which led to difficulties and problems managing different exams. A single board was created to address this issue.
- Higher Education Commission of India (HECI): To eliminate the multiple boards the Higher Education Commission of India (HECI) established a single board. .
- Vocational and Practical Learnings: NEP 2023 places more emphasis on practical and vocational learning than on theoretical learning whereas the early education policy placed more emphasis on traditional subjects than on vocational skills.
- Focused on Formal Education and Skill Enhancement: The goal of the new educational policy is to close the gap between formal education and skill-development initiatives.
What is the 5+3+3+4 System in the New Education Policy?
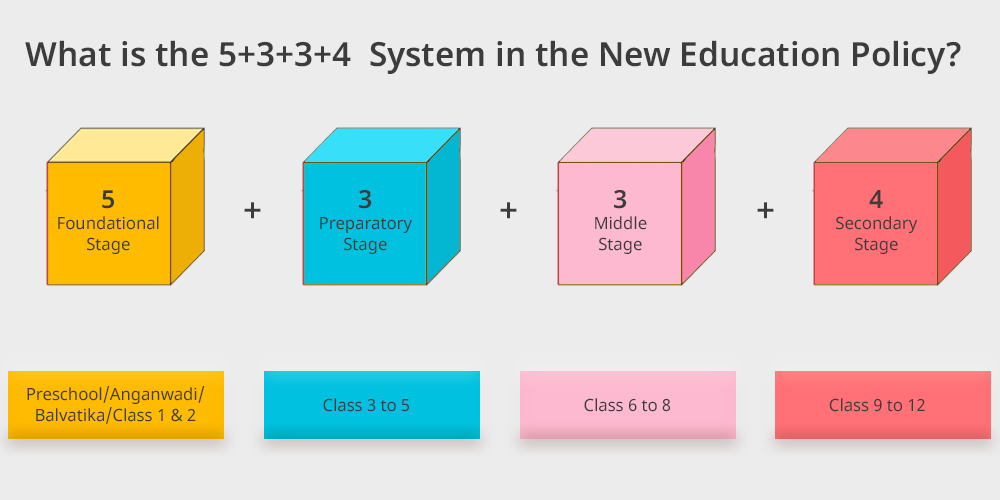
The academic structure of the new national education policy is based on the 5+3+3+4 system which means that students will spend five years in the foundation stage three years in the preparatory stage three years in the middle stage and four years in the secondary stages.
The traditional 10+2 system consists of two stages and is based on exams and a syllabus . The four stages of the new structure on the other hand offer flexible and multilevel learning.
Here is the detailed academic structure of NEP 2020 tabulated below.
| Stages | Class | Ages |
| 5 Foundational Stage | Preschool/Anganwadi/Balvatika/Class 1 & 2 | 3 to 8 |
| 3 Preparatory Stage | Class 3 to 5 | 8 to 11 |
| 3 Middle Stage | Class 6 to 8 | 11 to 14 |
| 4 Secondary Stage | Class 9 to 12 | 14 to 18 |
Objectives of New Education Policy

The new national education policy was developed by incorporating specific goals that alter the Indian educational system and focus on skillful and high-quality instruction.
Here are the objectives of National Education Policy 2020:
- Improvement of Teaching and Training Quality: The new education policy emphasizes a program for teachers professional development that improves their knowledge and abilities for teaching in the twenty-first century. The National Professional Standards for Teachers (NPST) was established in accordance with this policy to provide professional training for educators.
- Improves Government Regularity: Strengthening the governmental administration of all educational institutions is one of the main goals of the new education policy. At all institutional board levels it establishes an impartial authority to oversee higher education and uphold openness.
- Promotes Lifelong Learning Initiative: The provision of opportunities for lifelong learning is one of NEP 2020s primary goals. Adults will have access to learning opportunities through this initiative which will help them develop their skills.
- Integration of Technology and AI: Using AI and technology in the classroom is another goal of the new education policy. Every person will be able to learn easily conveniently and with flexibility thanks to technology in the classroom. The goal also covers the establishment of online learning AI learning digital infrastructure etc.
Education Policies in India
Various educational policies and reforms were made after independence. The education policies have become an essential tool to unite the country.
Here are the detailed education policies in India:
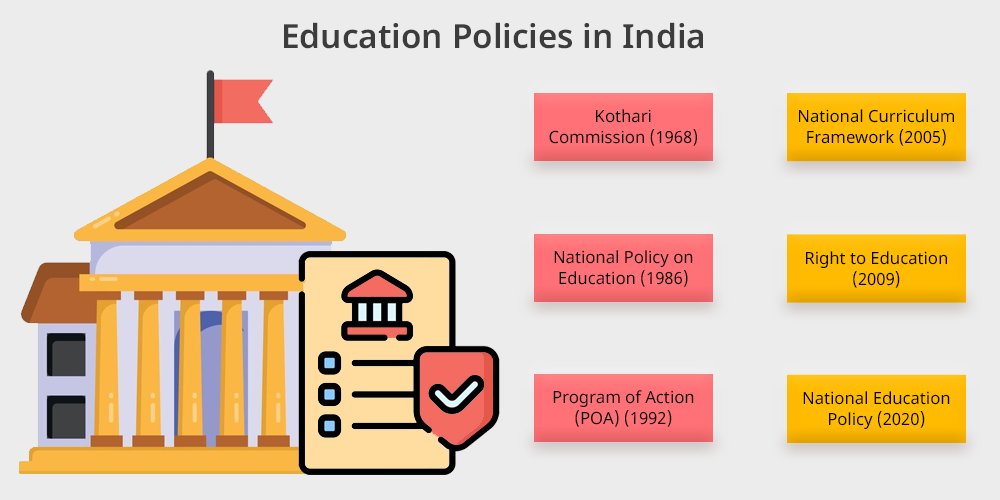
- Kothari Commission (1968): The first education policy was implemented by Kothari Commission in 1968. The main motto of this commission is to provide compulsory education to children up to 14 years of age. This policy also focuses on Mathematics and science rather than social science and arts. One of the major objectives of this policy is to eradicate illiteracy among people.
Do know what are the features of this commission? Here are the key features of the Kothari Commission:
- Strong Foundation: The Kothari Commission has created a foundation and educational structure for the country which has become the pillar of the Indian social system.
- Equal Exam: One of the main aims of this commission is to implement a fair and clean public examination system.
- Division of Exams: This commission has divided public exam system for each class according to the jobs and career prospectus.
- Vocational Studies: Kothari Commission has created an initiative for vocational education. That has changed the future of education.
- National Policy on Education (1986): The National Policy on Education (NPE) was introduced by Rajeev Gandhi in 1986. The main aim of NPE is to prepare the people of India for the 21st Century skills . One of the main mottoes of this policy is to provide education to every rural area of India. Under this policy, every state of India has adopted the common structure of syllabus with maths and science as compulsory subjects.
Do you know that the NPE of 1986 has played a pivotal role in changing the educational society? Here are the key features of NPE 1986:
- Mandatory Education: This policy focuses on creating compulsory education for children between the ages of 6 to 14 and provides them equal rights.
- Girl Education: This policy focuses on girls education an important initiative to change the old thinking of society.
- Free Education: NPE focuses on providing free and compulsory education to all. This initiative was taken to enhance the literacy rate and employment in India.
- Common Style: One of the major policies of NPE is to adopt a common structure of syllabus and compulsory subjects. Under this policy, no outside curriculum will be followed and every school should follow equal educational rights.
- Program of Action (POA) (1992): The Program of Action (POA) is a significant step of NPE 1986. Under this policy, some education systems were recanted and re-prepared about adult and elementary education. This policy focuses on providing quality education to minorities and women and converting non-formal education to formal education.
Have you ever wondered why there was a need for POA 1992? The features that hit this policy are:
- Adult Literacy: Adult literacy was very low at that time to tackle this POA is implemented in NEP. That focused on adult literacy and elementary education.
- Formal Schooling: At that time formal schooling is a major topic. Converting non-formal schooling to formal schooling is a top priority at that time.
- Women’s Education: This policy created an initiative to provide education to minorities and women.
- Setup of New School: Under POA new schools called Navodyalaya were set up to enhance the quality of secondary education. This will allow to follow a common structure of syllabus and compulsory subjects.
- National Curriculum Framework (2005): The National Curriculum Framework (NCF) has changed the education system a lot by introducing a student-centric education program. The NCF focuses on new age curriculum, pedagogies, critical thinking and child skills. This helps in bringing more children to schools.
Do you know why NCF 2005 was implemented? Here are the key features of NCF 2005:
- Common Curriculum: The National Curriculum Framework (NCF) created a common curriculum system for all boards and institutions.
- Overall Development: This policy focuses on creating holistic development for children. This allows them to become independent and develop queries.
- Stress-Free: One of the major aims of NCF is to implement burden-free initiatives for all children. Stress-free assessments allow students to live freely and produce favourable outcomes.
- Flexibility: NCF provides flexibility in choosing desired subjects for students.This gives a flexible outcomes for students and allows them to be more productive.
- Right to Education (2009): Right to Education (RTE) 2009 has made education a fundamental right for all. Under this initiative, education has become compulsory for all. Under the RTE Act, 25% of seats were reserved for weaker sections of society.
Do you know that RTE plays a major role in the education sector? Key features of RTE are:
- Compulsory Education: This policy has made elementary education compulsory rights for all students.
- Reservation: Under this policy, 25% of seats were reserved for weaker sections. This allows weaker students to complete their education without any social constraints.
- Easy Access: This policy has improved the accessibility of education to rural areas. Various schools were implemented in rural areas to enhance child enrollment.
- No Detention Policy: RTE also implemented a no-detention policy for students, under which no students will fail until they reach elementary education.
- National Education Policy (2020): This is the current and new education policy introduced in December 2020. The new system focuses on providing quality education and skill development initiatives. The new policy follows a 5+3+3+4 structure, which helps to make education more effective and easy for all.
NEP is a current education policy that focuses on an advanced system Key features of NEP 2020 are:
- Practical Learning: NEP focuses on vocational and skilful learning that allows one to gain practical exposure and enhance technical knowledge.
- New Budget: Expenditure on education has been raised to 6% of India’s GDP. This allows to increase the India’s literacy rate and development of the country.
- Redesigning of Education: New NEP redesigned the education system by implementing extra-curricular activities and modern-day technologies.
- New Structure: NEP introduced 5+3+3+4 structure to all levels. Under new structure children will spend their 5 years foundation stage, 3 years in the preparatory stage, 3 years in the middle stage and 4 years in the secondary stages.
Conclusion
All students will benefit from improved quality accessibility and relevance of education thanks to the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 which offers a substantial overhaul of the Indian educational system.
The NEP focuses on early childhood education skill development and vocational training by substituting the 5+3+3+4 structure for the conventional 10+2 system which is in line with 21st-century demands.
The policy also seeks to promote lifelong learning and integrate technology.
The NEP intends to close the knowledge and skill gap between formal education and practical skills by enhancing teaching standards and regulatory frameworks ultimately creating a workforce that is better prepared for the future.

