In the 21st century, education is rapidly changing and evolving towards the betterment of everyone.
With globalisation and digitalisation a growth in the education sector is not limited to memorising only the content that appears in syllabus or textbooks.
Traditional learning is limited to rigid structured, memory based and adapt teacher-led approaches. However, in the modern education system the shift is defined as contemporary education.
To explore what contemporary education means, its history and features in India, let’s understand everything in detail.
Table of Contents
What is Contemporary Education?

Contemporary education is a modern approach in which learning is not limited to textbook information and knowledge gaining but also development of skills, creativity and holistic development.
The traditional education system is mainly focused on memorising textbook knowledge and rote learning. It is also based on a teacher-led approach; learners follow exactly what the teacher guides.
But not in contemporary education because it includes critical thinking skills, technology in education and project-based learning to face real world challenges.
History of Contemporary Education in India
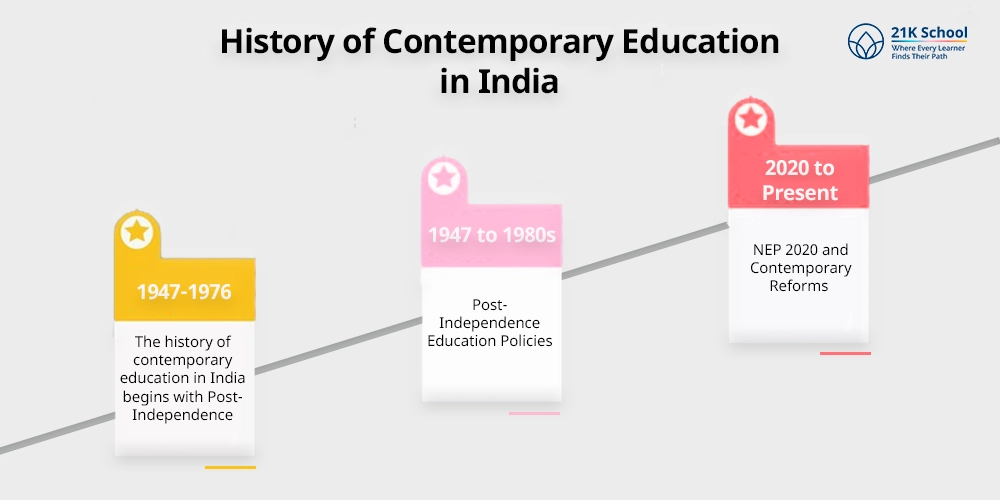
The history of contemporary education in India is long and detailed. Here we will go through point by point to understand easily:
- The history of contemporary education in India begins with Post-Independence (1947-1976). It aimed for widespread literacy and primary education. The Constitution mandated free and compulsory education for children.
- Post-Independence Education Policies (1947 to 1980s): After independence, the country established the National Policy on Education (1968, 1986). It helped in expanding primary education in India.
Later, the National Policy on Education in 1992 modified the 1986 policy to align with an open-door policy, emphasising the creation of skilled labour.
- NEP 2020 and Contemporary Reforms (2020 to Present): The most recent policy focuses on the NEP 2020 including technology, Indian knowledge systems, digitalisation and skill-based learning.
It also prioritises multidisciplinary learning, vocational training, online education, the rise of institutions like IITs and IIMs and incorporates the Indian Knowledge System (IKS) into the curriculum.
Key Features of Contemporary Education in India
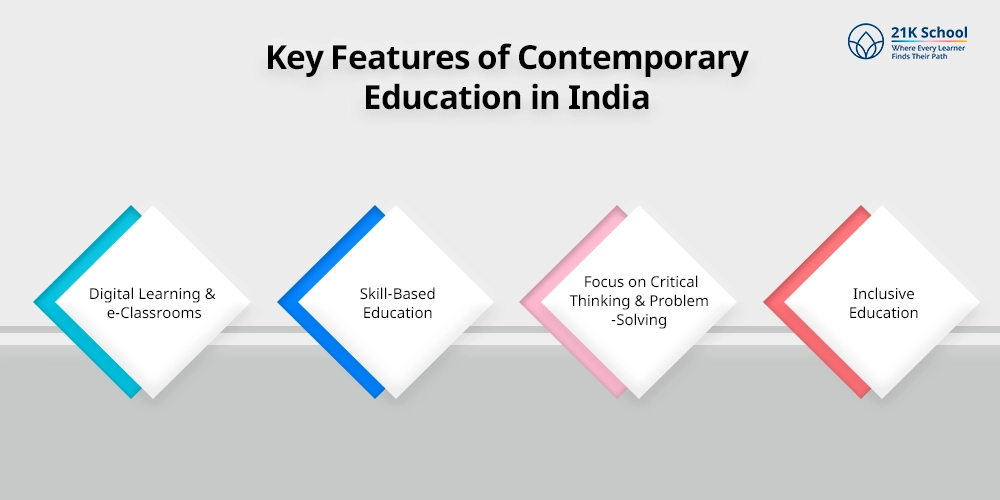
To understand the contemporary education in India one must discover the key features in details:
1. Digital Learning & e-Classrooms

With time and technology advancement, education is interlinked with the digital world to ensure learners stay connected with education even from home.
Various online platforms focus on digital learning, e-classrooms and apps that engage learners.
Now, learners can access smartboards, video lectures, and online assessments, even in situations like pandemic.
2. Skill-Based Education
This type of education connects learners with real-world skills rather than purely theoretical knowledge.
It improves both personal and professional development and aims for new opportunities in the competitive job market.
3. Focus on Critical Thinking & Problem-Solving
Contemporary education in India promotes critical thinking skills & problem-solving abilities of learners to understand, analyse and resolve real life problems.
4. Inclusive Education

One of the key and popular principles of the modern education system is inclusive education where all kids learn in the same classrooms within the same schools.
No matter which background, students with disabilities, slow learners or speakers of minority languages, everyone get equal education.
Continuous Assessment over Rote Memorisation.
In this kind of education the main focus is shift from year end examination to continuous monitoring or CCE.
This includes different types of assessments, real life projects, presentation and active participation.
Teaching Methods Under Contemporary Education in India
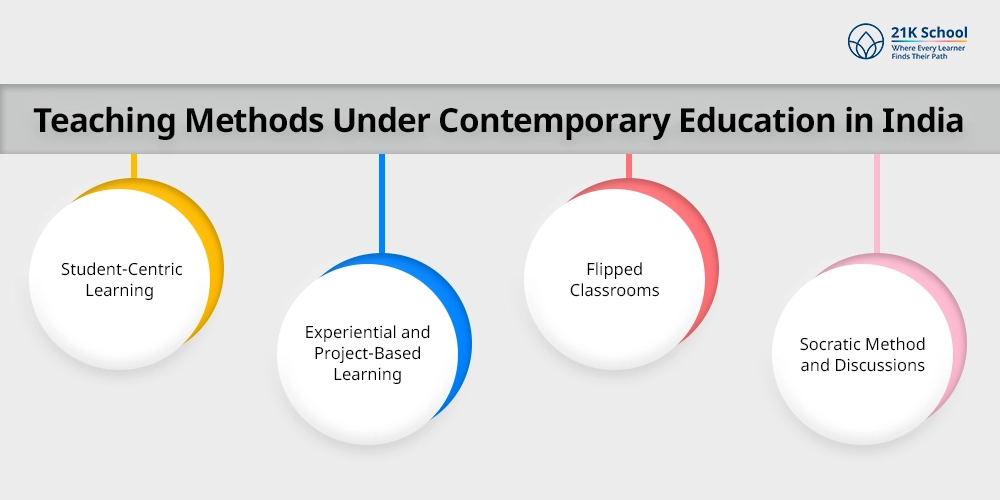
Incorporating effective teaching methods in modern learning helps students to engage and improve learning. Some effective methods includes:
1. Student-Centric Learning
Contemporary education instead of a teacher-led approach uses student-centric learning where students are a core part of the system.
2. Experiential and Project-Based Learning
In traditional learning, teachers command and students learn by memorising the concepts which only work well with theoretical subjects.
However, contemporary education in India is designed according to experiential and project-based learning where kids deal with real-life scenarios.
3. Flipped Classrooms
In this model students learn through various digital tools like videos and reading materials independently in personal time.
And in the classroom they discuss, solve the problem and resolve each other’s questions which increase their problem-solving skills and critical thinking skills.
4. Socratic Method and Discussions

Socratic method and discussion help learners through dialogue and critical questioning. Learners involved in debates and discussions, developing reasoning and analytical skills.
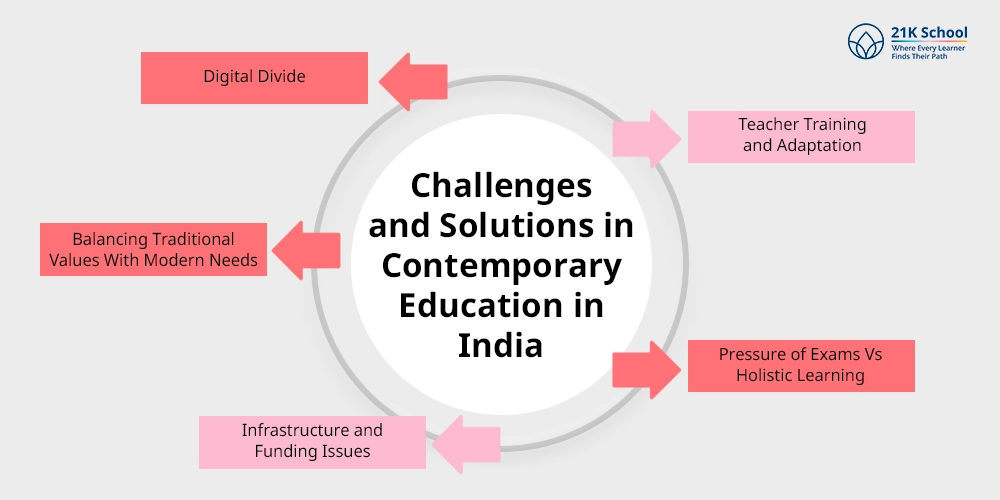
Challenges and Solutions in Contemporary Education in India
Contemporary education has various advantages like lifelong learning and conceptual integration. However, it also comes with some disadvantages or challenges that impact learning.
Some common point includes:
1. Digital Divide
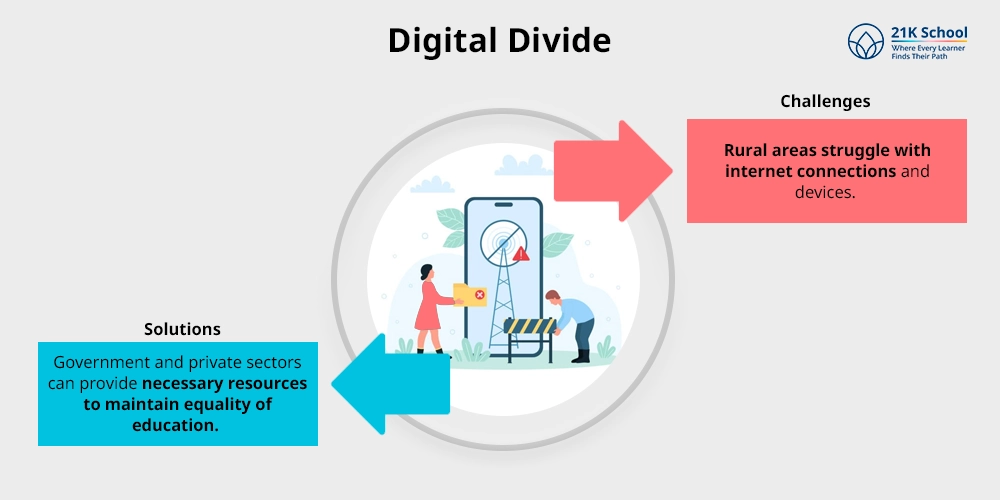
Digital divide means urban and rural students in which urban people enjoy learning digital with virtual classroom and e-learning platforms.
On the other hand, rural areas struggle with internet connections and devices.
To resolve this problem Government and private sectors can provide necessary resources to maintain equality of education.
2. Teacher Training and Adaptation
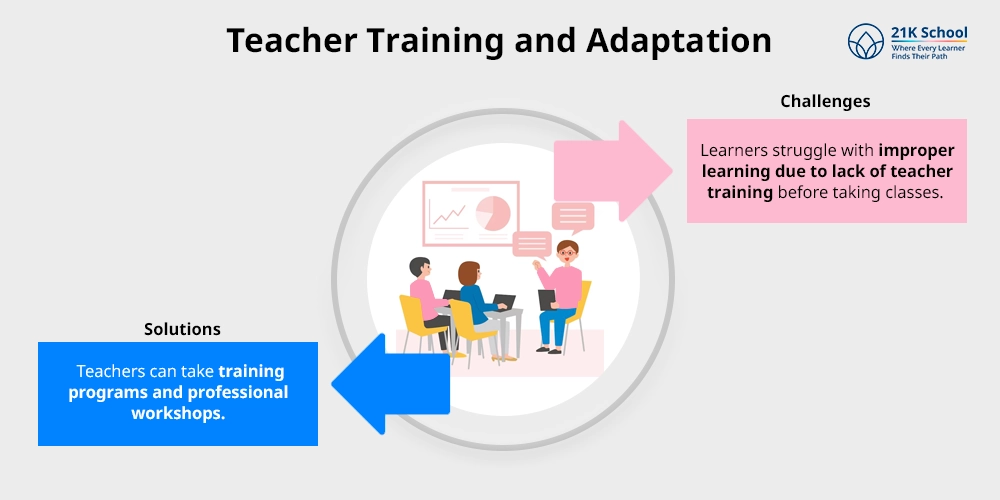
Learners also struggle with improper learning due to lack of teacher training before taking classes.
Teachers can take training programs and professional workshops. This guides them to embrace changes.
3. Pressure of Exams Vs Holistic Learning
Students feel stress and anxiety due to exams which overshadows creative thinking skills and holistic development.
With the help of competency-based testing and alternative assessments stress can be reduced and managed.
4. Infrastructure and Funding Issues
Problems like inadequate infrastructure and funding issues badly affect learning due to the lack of laboratories, libraries and other resources.
Various government shared initiatives and CSR programs can be an ideal choice for learners and schools.
5. Balancing Traditional Values With Modern Needs
In contemporary education in India using modern techniques is important, but it’s crucial to preserve India’s cultural and ethical values.
And, sometimes new and flexible structures lack depth. The solution is to blend modern knowledge.
Future of Contemporary Education in India
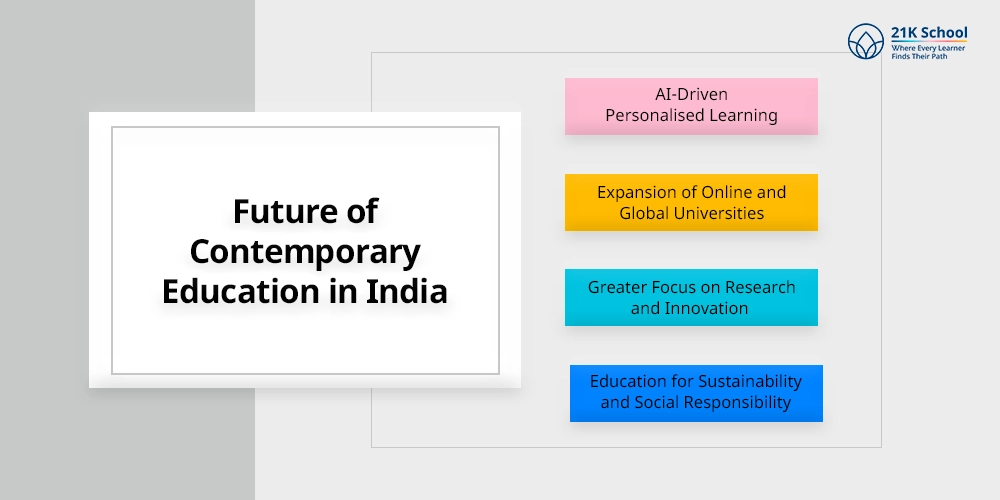
The future of contemporary education in India is a combination of accessibility, adaptability, inclusivity and innovation.
Given below are some major points one must know:
1. AI-Driven Personalised Learning

AI in education transforming the classrooms and connecting with the digital world by incorporating smart classrooms, customised learning, AI tutors and adaptive learning.
2. Expansion of Online and Global Universities

Now learners can connect globally and learn from anywhere anytime.
This can be done by collaborating with worldwide Universities and applying for different courses.
3. Greater Focus on Research and Innovation

Modern education’s objective is to promote and focus on research and innovation.
Schools and universities provide new opportunities in different fields like business, entrepreneurship and innovation.
4. Education for Sustainability and Social Responsibility

It’s important to learn and work towards betterment of society. Contemporary education fulfills the need by providing a positive learning environment to every child.
They can explore and innovate better solutions towards society.
Conclusion
Contemporary education in India includes advanced technology 21st century skills, inclusivity, and critical thinking.
Learners focus on different areas from traditional and cultural information to digital learning. The system is designed from pre-primary to higher education to provide new opportunities.
The future with contemporary education holds many benefits from digital literacy to innovation and social responsibility.
It’s time to balance both modern methods and traditional values to empower every learner from national to global.



