Education is the building block of personal and societal development in education and at the heart of which is always curriculum as it acts as a disciplined blueprint for what students are expected to learn out of in an academic year.
The curriculum and education help students analyse how they will learn what they will learn and what are these assessment standards for the knowledge that they gain in the classroom.
The article further tells us about the concept of curriculum in education talking about all the possible aspects like significance types, components development process and even the role of teaching in the process of learning.
Table of Contents
- What is Curriculum in Education?
- What is the Importance of Curriculum?
- Types of Curriculum in Education
- 1. Formal Curriculum
- 2. Informal Curriculum
- 3. Hidden Curriculum
- 4. Spiral Curriculum
- 5. Integrated Curriculum
- 6. Core Curriculum
- 7. Subject-Centered Curriculum
- 8. Learner-Centered Curriculum
- 9. Teacher-Centered Curriculum
- 10. Activity-Based Curriculum
- 11. National Curriculum
- 12. Competency-Based Curriculum
- 13. Montessori Curriculum
- 14. International Curriculum
- 15. Vocational Curriculum
- What is the Difference Between Curriculum and Syllabus?
- Components of a Curriculum
- Curriculum Development
- Challenges in Curriculum Implementation
- Tips for Effective Curriculum Planning
- Examples of Curriculum Models
- Conclusion
What is Curriculum in Education?
Basically the curriculum is referred to as a structured set of learning experiences or activities that guides the education process in an academic year in schools, colleges and other institutions.
This curriculum has everything from lesson plans to instruction, reading materials to assessment strategies and even the learning outcomes that are the set standard which a student is supposed to meet.
A curriculum is not just about academic subjects but rather it also takes in concern the extra curricular or co curricular activities, skill based learning, lifelong learning, reading habits and other development programs.
What is the Importance of Curriculum?
Curriculum is a very essential part of the education system which is vital to the individual and societal goals in many ways.
The core essential framework is very systematic, consistent and aligned with the overall persona of growth defined for students with a predefined standard set uniformly.
The framework is for both educators and for students where educators design lessons and SS progress to achieve the educational objectives whereas students follow the curriculum to ensure their holistic development.
It helps students with knowledge skills and attitude necessary for success in both personal and professional life acting as a bridge between the educational theory and the practice sessions providing students a real world experience with learning challenges and preparation for the future.
Types of Curriculum in Education
There are many types of curriculum that can be discussed but as far as educational philosophies and purposes are concerned there are 15 major distinct types of curriculum.
1. Formal Curriculum
Formal curriculum is a planned organised and structured set of instruction designed to provide educational experience to students in schools and institutions.
Here, in this form of curriculum students are offered with structured learning that takes place in a traditional classroom set-up.
There are four major dimensions of curriculum in a traditional education system:
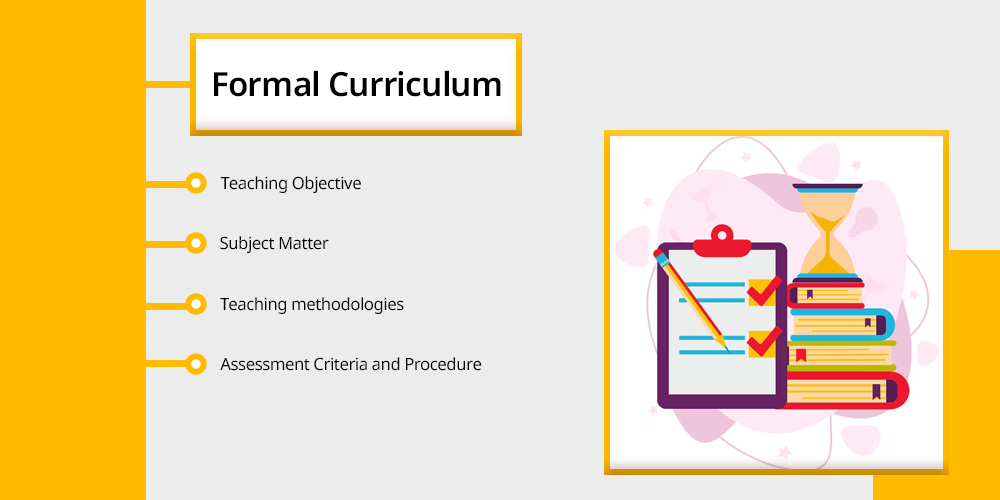
- Teaching Objective – This curriculum defines what is to be taught and how it is to be taught to students in order to ensure a standardised value of teaching, and it also helps in maintaining the standard of education existing in the country.
- Subject Matter – The matter involved in the syllabus for the academic year is often decided by the decision makers who design the curriculum — for example a student in class 10th from CBSE board will have a syllabus designed by the central board of secondary education. The subject matter even changes when shifting from state board to CBSE, and we all are well aware of the Benefits of State Boards Shifting to CBSE.
- Teaching methodologies – The theoretical basis of methods and approaches that can be taken in concern while teaching is a major part of the curriculum, to ensure accessibility. It can consider the age, interests, and instructional strategies of students.
- Assessment Criteria and Procedure – The assessment strategies that are embedded into classroom practice, and the standard for assessment is decided by the authorities involved in the curriculum designing and is strategically designed to consider students regardless of their strength and weakness.
Examples to this standard curriculum offered to students could be:
- Traditional classroom teaching – a method of learning that takes place in a physical classroom — students here attend in-person lectures.
- University courses
- Workshops
- Seminars
- Practical training.
It is often documented as syllabi lesson plan and textbooks which is considered as a standardised method of learning and reading.
It also comes with her standardized assessment plan for students; it is documented for almost one academic year at a time.
2. Informal Curriculum
Informal curriculum is the education or learning that takes place outside the formal classroom environment and can include all co-curricular and peer interaction activities that contribute to skill development or overall development of a student.
This also includes community services and involvement.
All these elements that are covered under informal curriculum are not really listed in the syllabus offered by the traditional schools but they are compulsory.
Some of the basic features to the curriculum is that:
- No specific structure – The course is not designed in a way that students can read it offers versatility in learning and students can choose any from the wide range of the things being offered in the learning journey.
- No specific goal – This curriculum does not promote assessment and evaluation; rather it supports participation and engagement, it’s embedded in the curriculum in a way that students may not even realise that they’re learning.
- Lifelong process – It involves co-curricular activities and they come with a lot of practice and training. Informal education is a lifelong learning process that happens naturally, this cannot be forced onto students.
- No fees– For the learning, there are no extra fees leveraged on the informal curriculum as it is embedded in the existing curriculum — its cost efficient and complimentary on school.
3. Hidden Curriculum
Hidden curriculum is the unspoken lesson learnt in the classroom environment or school environment such as values, behaviour norms, social norms and attitude management.
These lessons are often considered as a lifelong learning which may not explicitly be significant but contribute a lot in students character and behaviour development.
Here are some characteristics of hidden curriculum:
- Unintentional – Hidden curriculum is designed in a way that it incorporates a set of lessons that are not usually taught in school in traditional setup.
- Informal – Hidden curriculum is to be taught formally as it can only be explicitly shared in a social interaction or in a situation where exceptions are considered not in the traditional classroom setup.
- Concepts – Hidden curriculum includes several other concepts other than syllabus subjects like friendship, honesty, fairness and even work ethics. This gives them another definition of perspective for understanding the differences whether it be cultural or personal.
4. Spiral Curriculum
Spiral curriculum is designed to revisit the important topics at increasing levels of complexity overtime this ensures that learners build a prior knowledge of the topic.
In order to depend on the understanding and the thought process it is better to take the smallest steps of learning to a very complex topic making it easy to understand as the progress in the education.
Some characteristics of a spiral curriculum are:
- Repetition: Students in a spiral curriculum are supposedly suggested to revisit a topic multiple times making it monotonous though helping them grasp and internalize the concepts better.
- Progression: It is like a ladder where students move from simple to complex ideas and build their knowledge over the existing knowledge learning new things to put in context.
- Critical thinking: With this reputative model students tend to develop a stronger critical thinking and problem solving skills that retains information for a longer time helping them in solidifying their knowledge.
5. Integrated Curriculum
Integrated curriculum combines multiple subjects in one classroom making it a cohesive learning experience for students.
This encourages skills that are interdisciplinary and also motivate students to learn as they grow. It helps students see the connection between the different fields of knowledge and find reliability in them.
An integrated curriculum has several characteristics, including:
- Holistic learning – Integrated curriculum uses the concepts that connect different areas of studying in a way that contributes to a child’s overall development making the learning more interactive and fun. It allows all students to learn in a holistic way and develop similarly.
- Interdisciplinary or multidisciplinary – Integrated curriculum can be disciplinary which means that they include multiple subjects or multiple disciplines integrated in one curriculum for an academic year. The integration of multiple topics within the same subject can help students relate with the overall existence of the content and implement it.
- Collaboration – Integrated curriculum encourages collaboration between students and teachers fostering peer-to-peer interaction, and here students collaborate on a different theme and different subject matters.
6. Core Curriculum
Core curriculum is very similar to the formal curriculum, as it refers to a set of essential subjects and courses that are compulsory for all students and are required to study in a particular class or standard.
This ensures a common foundation of knowledge and skills for learners, so they find competition fairer when growing.
Characteristics to a core curriculum include:
- Focused learning experience – The core curriculum focuses on the learning experiences of a student where the process is to master a particular course and be a responsible member of society as they grow.
- Problem-solving – The core curriculum also emphasizes group problem solving activities across all disciplines across all fields that helps students gain all the necessary problem solving and analytical skills.
7. Subject-Centered Curriculum
Subject centered curriculum focuses on specific subjects that are to be taught independently to students apart from their whole syllabus.
This curriculum emphasized on mastery of subject matter rather than the whole course or syllabus which is commonly used in traditional education systems in higher studies in colleges for masters or post graduate diploma.
A subject-centered curriculum has the following characteristics:
- Content emphasis – The focus is on mastering knowledge and skills. It’s very similar to those educational models followed in colleges for higher education.
- Subject specialization – Students enroll in specialized learning experiences to meet a subject requirement. This helps in becoming a learned professional and grow in their work life.
8. Learner-Centered Curriculum
Learner centred curriculum that focuses on the needs and interest of a student prioritising their abilities. This ensures active participation from Students and promotes personal growth for them fostering fun in learning.
Some characteristics of learner-centered curriculum include:
- Skill Development – Learner centred approach in a curriculum helps students develop important skills like problem solving, analytical skills, evaluation skills and even critical thinking skills giving them a control over their own learning progress and motivating them to accept responsibility and work beyond their classroom experience.
- Collaboration – A learner centred approach also equips students with the skills of collaboration where they work in a team to build on the strength and come up with new ideas in the classroom.
- Flexibility and reflection – It allows students to reflect on their learning journey where they can take time to pause and think about everything that they have done in an academic year and that can be done in future. It also promotes learning styles and processes as other students need.
9. Teacher-Centered Curriculum
Teacher-Centred curriculum is a curriculum that focuses on the learning process where the teacher is at the centre deciding how, what and when students will learn about a certain topic — basically they are the decision maker in the entire learning process.
This often involves direct instruction and structured lessons for students in an academic year which helps them bro and learn more.
Characteristics and features ended curriculum or the traditional education system could have includes:
- Teacher centric – The entire model is teacher centric where the teacher is the primary source of knowledge and authority in a classroom. The teacher decides what topics to be taught and what activities to be conducted.
- Passive students – Students in this model are the passive listeners who just receive information from the teacher. This is a one way approach where students are independent and they work alone, individually.
- Memorization and limited opportunity – This type of curriculum has very limited opportunities for students to develop skills like problems solving critical thinking as it restricts them from interacting in class under the control of the authority. And the major activity that takes place in the classroom in such an environment is memorizing and recalling the information from the lecture that they have received.
10. Activity-Based Curriculum
Activity based curriculum emphasis on hands-on learning experience is for students to make their learning experience more engaging and entertaining for them to promote knowledge retention and better engagement in the classroom.
It is a creative approach commonly known as ABC, mere characteristics to this activity based curriculum is :
- Hands on learning – Students here participate and take tasks instead of passive listening like happening in the traditional classroom setup that tends to connect with the real world using their skills and mindset to apply in the real world challenges.
- Problem solving – Problem solving skill is a dominant method in ABC as it allows practical applications and makes learning easier than the theoretical information encouraging students to be independent, inquisitive and think critically.
- Social development – Activity based curriculum helps students develop social skills and teamwork.
11. National Curriculum
National curriculum is a standard set of curriculum designed and mandated by the government of India for students to promote a quality in the education sector for all students particularly in one educational board.
Some of the examples of the national curriculum could be CBSE — Central board of secondary education and ICSE — Indian certificate of secondary education, these two are the most prominent and dominant educational boards and the curriculum that exists in India.
12. Competency-Based Curriculum
Competency based curriculum is a specifically designed curriculum that helps students and focuses on development of specific skills and competencies in students lives.
This kind of curriculum ensures that the student achieves proficiency in all the areas that are essential for a students academy and professional growth along with their skill development.
Competency-based education (CBE) has several characteristics, including:
- Learner-centric – Competency where education focuses on students allowing them to learn at their own pace and takes ownership of the learning, it facilitates self awareness and modernization for learning.
- Continuous assessment – Students are expected to perform and they are regularly assessed to determine if they have mastered the required material or not.
- Real-world relevance – Exposure to real world experience is when students learn they grow with time implementing the learner skills into the real world application.
13. Montessori Curriculum
The Montessori curriculum developed by Mariam Montessori is a curriculum that focuses and emphasizes self-directed learning with hands-on experiences, activities and instructions in a prepared environment for students.
14. International Curriculum
International curriculum such as IGCSE — international general certificate of secondary education GCSE — general certificate of secondary education and IB — international baccalaureate are designed to meet the global education standard and prepare students for opportunities across the globe in terms of higher education and looking for colleges for graduation post graduation and diploma.
Incase if somebody wants to know about the comparison between the curriculums, one can read about; IGCSE vs GCSE and IB vs IGCSE
Another question that circulates among students is IGCSE vs CBSE: Which Board Is Better for Academic Excellence? — this basically has a lot to do with the comparison between national and international curriculums.
- International Recognition: International curriculum provides qualifications that are accepted by universities and employers worldwide, oftentimes internationally accepted curriculum is something parents are looking for in their children’s schooling.
- Skill Development: The curriculum places a strong emphasis on analytical skills,soft skills, team bonding, communication, and practical learning.
- Assessment Flexibility: The curriculum offers a variety of assessment methods for enrolled students, including coursework, practical tests, and written exams.
15. Vocational Curriculum
Vocational curriculum focuses on training and practical learning to contribute to skilled development in specific industries and career opportunities.
Under this curriculum students are prepared and geared towards the future to be well suited for the workforce.
Vocational curriculums are designed to teach practical skills that students can use in their chosen field or profession.
Some characteristics of vocational curriculums include:
- Hands-on learning: Vocational learning programs and curriculum help students gain practical knowledge skills and training that they can use immediately in their workplace contributing to the development.
- Certifications based program: Combine on the job training with classroom instructions and on certifications and degrees based on that which can be used when considering jobs which or positions which are in the workforce.
- Work-based learning: Vocational training is a complete work of learning where the programs are designed in a way that a person learns from their experiences.
What is the Difference Between Curriculum and Syllabus?
While in certain cases they are interchangeable, curriculum and syllabus have distinct components for themselves in the education industry where curriculum is a broader term that encompasses all the other educational frameworks and includes elements like content, goals, teaching methodologies, assessment strategies and sub standard assessments.
And on the other hand, the syllabus is a detailed outline of all the topic assignments and assessments in a particular subject that is offered to a student under a curriculum in an academic year.
| Curriculum | Syllabus | |
| Definition | A comprehensive plan that outlines the overall educational content, goals, and framework for a course or program. | A detailed outline of the topics, concepts, and lessons covered in a particular subject or course. |
| Scope | Broader in scope; includes objectives, content, teaching methods, assessments, and resources. | Narrower in scope; focuses only on subject-specific topics to be taught. |
| Focus | Focuses on overall learning goals, educational philosophy, and skills development. | Focuses on the specific topics and content to be studied within a subject. |
| Created By | Typically developed by education boards, ministries, or institutions. | Usually prepared by individual teachers or subject specialists. |
| Duration | Designed for a complete course, program, or level of education (e.g., K-12 curriculum). | Designed for a specific subject or course for a limited timeframe (e.g., one academic term). |
| Flexibility | Less flexible as it forms the foundation of an educational system. | More flexible; teachers can adapt it based on classroom needs. |
| Components | Includes learning objectives, content, assessment strategies, resources, and teaching methodologies. | Lists topics, chapters, assignments, and timelines for a particular subject. |
| Purpose | Ensures overall educational consistency, development of skills, and achievement of learning outcomes. | Helps students prepare for exams and track what will be taught in a specific subject. |
| Example | National Curriculum Framework (NCF), CBSE Curriculum, IB Curriculum. | Mathematics syllabus for Grade 10, Science syllabus for a semester. |
Components of a Curriculum
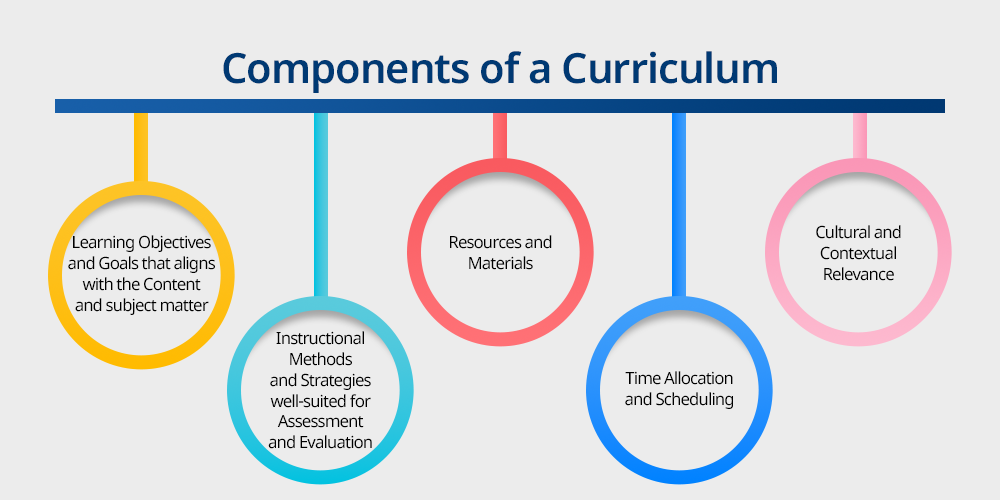
Major component to list for a curriculum includes :
- Learning Objectives and Goals that aligns with the Content and subject matter
There are many key features and components to a curriculum, but the most important part is that they are intended to achieve objectives and goals in an educational setup making sure that every student completes a course or program with knowledge and skills that makes them a better individual.
- Instructional Methods and Strategies well-suited for Assessment and Evaluation
Another aspect to this is that a curriculum includes knowledge concepts and skills that a student is expected to learn in a given specific time and is often assessed at the end of every academic year where the progress determines the effectiveness of a curriculum.
- Resources and Materials
These curricula are often backed up with a proper set of resources and material available in the educational setup like text book digital tools laboratory equipment and well learned educators.
- Time Allocation and Scheduling
Every curriculum is designed for a specific duration of time and has limitations over the duration of lessons periods and terms which ensures coverage of a proper content which reflects equally on the performance of the student.
- Cultural and Contextual Relevance
The curriculum is a designed framework which incorporates cultural societal and historical concepts for the learners in a very systematic manner to make education more meaningful.
Curriculum Development
What is Curriculum Development?
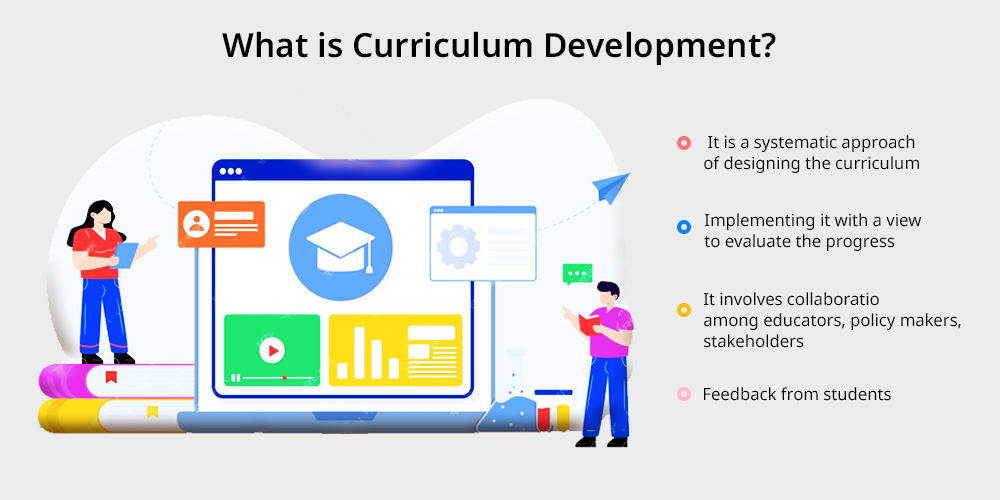
Curriculum Development is a systematic approach of designing the curriculum and also implementing it with a view to evaluate the progress in order to meet all the educational objectives and the needs of students.
It involves collaboration among educators, policy makers, stakeholders and feedback from students and fares to create a comprehensive and engaging educational framework.
7 Steps of Curriculum Development
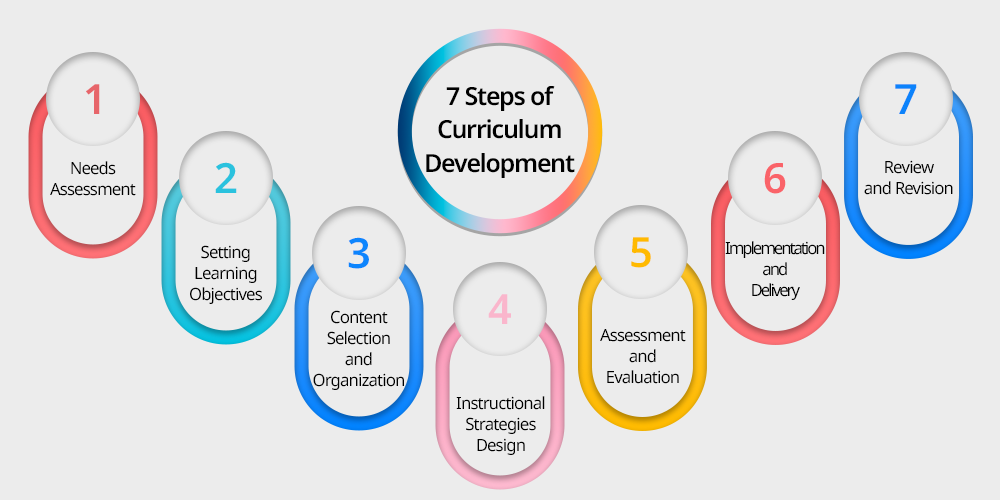
There are seven crucial steps to curriculum development which ensures that every need of a student is taken into consideration and a proper implementation of the curriculum takes place putting in the delivery response channels like lesson plans, teaching learning activities, co-curricular activities etc.
- Needs Assessment: This is to identify the needs of the students and the objectives of education for that particular academic year or course plan, focusing on creating a relevant and effective curriculum, for the long run.
- Setting Learning Objectives: It simply meant to define clear goals that are measurable, and achievable for students.
- Content Selection and Organization: When considering a nationwide audience it is equally important to choose appropriate subject matter wisely and organise it logically and sequentially, for the betterment of students and ease of learners.
- Instructional Strategies Design: The strategies involved in Developing teaching methods and curriculum are very complex and need proper time and patience for implementation, the activities are there to deliver the curriculum effectively, this requires proper coordination and supportive functionality across all departments.
- Assessment and Evaluation: For implementing a curriculum on such a wise level, it is important to understand that specifically designed tools would be required to measure student performance and curriculum structures in an academic year to ensure that the strategies designed and the people involved are working efficiently and effectively for the same goal.
- Implementation and Delivery: Now and everything has been curated wisely, it is the moral responsibility of the institution to put forward the curriculum into practice through less in plants teaching learning activities and other classroom activity to promote education in a most strategic and standardized manner to support learners and their learning journey.
- Review and Revision: It is equally important to regularly evaluate the curriculum and make necessary adjustments to keep it relevant and effective for students in such a dynamic world where things change every second and people introduce new trends and style every other minute.
7 Roles of Educators in Shaping the Curriculum
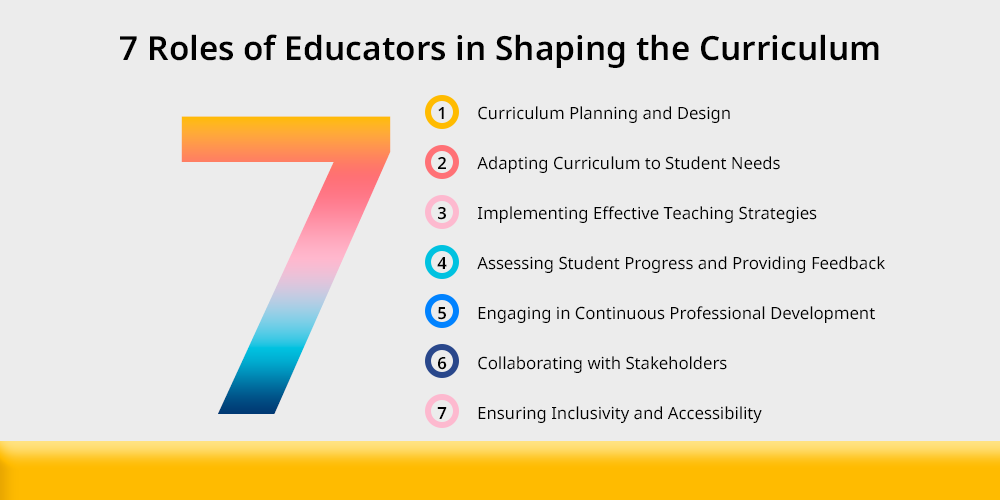
Educators in the whole educational environment play very crucial roles in shaping everything from curriculum to the students life. They make sure that the curriculum meets students needs and educational goals in every possible way.
The responsibilities start from planning and continuously keep growing as at every step of life they need to collaborate and engage with their peers and even with the stakeholders involved in the process to ensure accessibility and inclusivity.
It is their responsibility to implement effective teaching strategies for teachers to employ techniques that deliver curriculum effectively and keeps students motivated and engaged in the classroom.
7 major roles and responsibilities of educators in shaping curriculum are:
- Curriculum Planning and Design
- Adapting Curriculum to Student Needs
- Implementing Effective Teaching Strategies
- Assessing Student Progress and Providing Feedback
- Engaging in Continuous Professional Development
- Collaborating with Stakeholders
- Ensuring Inclusivity and Accessibility
Factors Influencing Curriculum Design
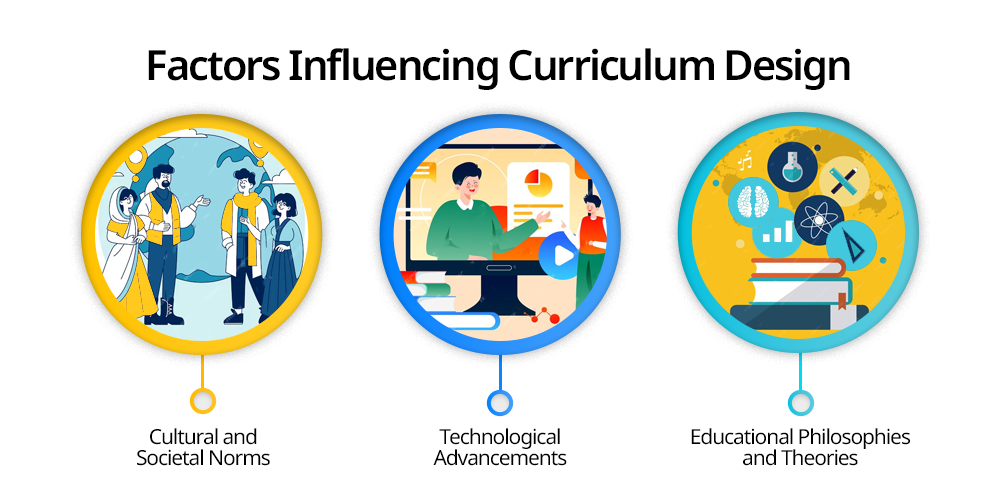
There are several factors that influence the curriculum design as they help in shaping the design and implementation of the curriculum in the education system as they reflect on certain values and beliefs of the society revolutionising the platform for delivering education.
Some of the factors that influence curriculum design are :
1. Cultural and Societal Norms
The culture and society of a nation or country reflects on the curriculum for that particular nation as it is fully invaded with the values, tradition and beliefs of the society ensuring that students are well connected with their cultural heritage as they grow to survive and hustle in the globalised world.
2. Technological Advancements
The rise of technology in the recent world has completely revolutionized the education system all over the world as online platforms have taken the education system and traditional classroom by storm.
These technology advance education systems have promoted blended learning virtual classroom and digital assessments making an environment that is engaging and keeps students motivated.
It is very important to know how technology can support students’ success.
3. Educational Philosophies and Theories
The educational philosophies and theories affect the curriculum where a curriculum is structured to promote meaning for learning experience.
There are some educational theories such as behaviourism, constructivism and humanism that affect the flow of curriculum.
Role of Curriculum in Teaching and Learning
Yet another catalyst in the journey of teaching and learning is curriculum where it is a fundamental element that affects both the directions and structures contributing equally in them.
A major role of curriculum in teaching is to design daily lesson plans and ensure consistency and uniformity in the educational content to achieve the institutional as well as the curriculum goal.
Three major roles of the curriculum in teaching and learning are:
1. Guiding Educators in Lesson Planning
Educators preserve direction and ensure that students learn what is important about the concepts, skills and knowledge concepts that schooling is meant to impart.
In schools, the curriculum predicts a range of content areas such as math, science, language arts as well as academic and co – curricular activities and programs.
2. Providing Structure and Consistency
Learning is the process through which an individual acquires knowledge through teaching activities that are expected to take place in educational institutions, schools for instance.
It is a complete structural construction that outlines the subject matter, course objectives, and instructional approaches to support and direct the instructor and the student.
They preserve direction and ensure that students learn what is important about the concepts, skills and knowledge concepts that schooling is meant to impart.
In schools, the curriculum predicts a range of content areas such as math, science, language arts as well as academic and co – curricular activities and programs.
Curriculum on the other hand is a documented plan for learning that breaks down knowledge and skills into teachable units which are agreed to be developmentally appropriate for students and necessary for the growth of the learners as well as the society.
3. Aligning Educational Outcomes with Goals
Educators Align Educational Outcomes with Goals to preserve direction and ensure that students learn what is important about the concepts, skills and knowledge concepts that schooling is meant to impart.
In schools, the curriculum predicts a range of content areas such as math, science, language arts as well as academic and co – curricular activities and programs.
An educational activity in a curriculum means a single event or activity through which the learning objectives of the curriculum are achieved.
Last is the National Curriculum Framework which is a set of purpose, approach, and procedure for determining and establishing a national curriculum for a nation as the framework for formulating and implementing education policies and programmes at national level.
Challenges in Curriculum Implementation
The exciting and challenging course of implementing curriculum adopted as a professional adventure as the experienced and novice educators may face.
1. Balancing Diverse Student Needs

One major challenge is balancing the nurturing of students’ learning capacities with the various other demands that come when learners come from different backgrounds.
This implies that each and every learner holding his or her own characteristics such as abilities, interests, and cultural endowment should have an equal chance for learning but differ in the proportion of attention given where required.
2. Bridging Theory and Practical Application

Another challenge is to bridge that distance between theory and the practical application where teachers aim to produce students who are intellectually equipped and have the power to learn from both theory and practice integrated well in their curriculum.
The challenging aspect to this is to maintain a coherent environment where there is a deeper understanding of knowledge that is being provided to the student and they effectively apply them outside the regular classroom representing a bigger picture
3. Ensuring Inclusivity for All Learners

Lastly, it should also be taken in concern to aim for a curriculum that is favourable for all students. It even considers those with special abilities, low income winners and one with linguistic barriers they may require some help which can be considered under special education.
Some of these factors have a significant effect on the planning and often required resources that may sometimes go beyond the reach of the stakeholders.
But they are very essential when it comes to setting up the classroom in such a way that every child can learn without undue hindrance from his or her classmates.
And there many Challenges and Benefits of Inclusive Education which is also to be taken in consideration for implementing a successful curriculum.
4. Overcoming Challenges with Proactive Efforts

Therefore, it can be said that the achievement of effective curriculum implementation is invariably filled with challenges although these challenges are the building blocks or the pathways to a better learning environment for learners with appropriate provisions for achievement of equality for all.
All of these challenges can be faced if the necessary effort is invested in overcoming them and be translated into a proactive opportunity for learning and improvement.
Tips for Effective Curriculum Planning
Effective curriculum is ensured with proper support from all the stakeholder involved. It ensures proper implementation of the curriculum.
The entire curriculum planning process is done to make sure that the educational process is smooth, impactful and relevant for the students, pursuing education across the globe or country.
Key tips to ensure an effective curriculum planning process are:
- For effective curriculum planning, it is suggested to keep engaging educators, parents, and students in the planning process to understand diverse perspectives and make necessary alterations or changes as per the need and demand of the system.
- Also, when considering an effective implementation, regularly reviewing and updating the curriculum to keep it aligned with technological and societal changes is also important.
- Integrating experiential learning opportunities can also be game changing, the learning opportunities such as field trips, workshops, and hands-on activities can help students earn skills and practically apply studies and the acquired knowledge to real life problems and situations .
- For a curriculum to make changes and be impactful for the world it is suggested to incorporate feedback from students and teachers to refine instructional strategies and materials.
- It is equally important to ensure flexibility in the curriculum to address emerging challenges and opportunities.
Examples of Curriculum Models
The curriculum model is designed to provide frameworks for organizing and delivering educational content to all students with equality and promotes inclusivity. Three major curriculum models include and its examples are:
1. Subject-Centered Curriculum

A traditional model of education that offers a standardised set of information and knowledge to students regardless of anything.
The model mainly focuses on common and sometimes specific subjects such as: mathematics, science and literature. Now these subjects are taught differently and are considered separate disciplines.
2. Learner-Centered Curriculum
This model is systematically designed to cater to the needs of learners.
The model focuses on the needs and interests of students, encouraging active participation and promoting knowledge retention in them. This model teaches students self-learning and inculcates the culture of self-directed learning.
3. Problem-Centered Curriculum
problem- centered learning is an approach proposed to students that equips them with several life saving skills preparing them for the future.
The approach uses real-world problems and issues, incorporating them in the studying manual and encouraging critical thinking and problem solving skills in students with the help of interdisciplinary learnings.
Conclusion
The curriculum is considered to be the backbone of education.
It not only defines an educational perspective but also saves knowledge skills and discipline that is important to students.
From formal to informal there is a lot of curriculum that exists and every part of the curriculum is well structured that provides a road map to educators on how to approach the learning journey of a student contributing to the overall success.
And it is no fun or one man’s job to implement an effective curriculum – it requires an army to collaborate and continuously access the curriculum and integrate adoption as per the society and technological advancements.
21K School is a formally recognized and accredited K-12 School offering Indian curriculum and British Curriculum online for learners aged 3 to 18 years in India and abroad, British Curriculum includes both Pearson Edexcel and Cambridge Assessment International Education (CAIE).
The 21K School also follows the National Curriculum Framework of India up-to middle school curriculum.