If you are a student who is preparing for higher studies internationally, you must have come across A-level which is short for Advanced Level qualifications.
A-Levels are subject-based qualifications that students in the United Kingdom and a few other countries typically take at the end of their secondary school education.
Table of Contents
- What are A-Levels?
- Why Choose A-Levels?
- How Do A-levels Work?
- What Subjects do A Level Students Take?
- Tips for Choosing A-Level Subjects
- How are A Levels Assessed?
- What is the Structure and Format of A Level Qualification?
- A-Level Exam Boards: Cambridge vs. Edexcel
- A-Levels Entry Requirements
- After A-Levels: What Can You Do?
- Conclusion
What are A-Levels?
A-Levels or Advanced Level Qualifications are subject-based qualifications which are taken as the final academic courses before university.
A-Levels is a two year program in which students between 16 and 18 years old can apply for university entry globally, particularly in the UK.
The exam is a popular choice for students seeking higher education abroad. It provides a specialized and in-depth study of chosen subjects.
To clear the exam, one must read A-Level past papers.
Why Choose A-Levels?
A-Levels nowadays are a popular choice among students for secondary education. Because of its depth of knowledge, global recognition, and flexibility in subject choice.
Let’s elaborate the key reasons of choosing A-Levels:
- Global Recognition:
A-Levels has a global recognition which means it is acceptable internationally in different schools and colleges.
This recognition stems from their rigorous curriculum, standardized assessments, and the depth of knowledge they require students to acquire.
- Depth of Knowledge:
A-Levels is popular for their in depth knowledge provided to students through various subjects. It is an advantageous part of the exam.
Students preparing for higher education or specialized careers can get the benefit of A-Levels.
- Flexible Subject Choice:
One of the ideal reasons why students choose this exam instead of others is flexible subject choices for everyone.
This enables students to customize their learning based on their personal interests and future aspirations.
- Academic Excellence:
Each student works hard to achieve academy excellence and A-Levels fulfil this desire.
It is a popular choice due to their rigorous curriculum, in-depth subject knowledge, and global recognition.
- University Preparation:
For university preparations A-Levels is an ideal choice for students due to their rigorous curriculum, focus on subject depth, and global recognition.
They are a strong foundation of independent learning in diverse subjects and analytical thinking builds interests and career aspirations.
How Do A-levels Work?
A-levels exams aiming for higher education or certain career paths which helps students to get a brighter future.
Here’s a breakdown of the key components how A-levels work:
1. Coursework and Examinations
A-levels have a mix of coursework and examinations, though the balance depends on the subject and exam board.
- Exams: These are mostly held at the end of the course or usually in the second year. Remember, they carry the most weight in most subjects.
- Coursework: It majorly considers subjects like English, Art, and some sciences. However, it can be in various ways like essays, reports, experiments, or practical work submitted and marked under exam conditions.
2. Exam Boards
A-level qualifications are offered by various UK-based exam boards. These exam boards includes:
- Cambridge Assessment International Education (CAIE)
- Edexcel (Pearson)
- AQA (Assessment and Qualifications Alliance)
- OCR (Oxford, Cambridge and RSA Examinations)
3. Grading System
A-levels use a standardized grading scale which is determined by the exam boards. It topically includes A* to E.
Here, A* is highest and E signifies minimum pass. However, U is unclassified.
4. UCAS Points
UCAS points is a method used by the UK’s university application system. Let’s see each A-level grade has a specific number of points, such as:
A* = 56 points, A = 48 points and E = 16 points. It is an ideal method which determines the eligibility of students. Explore more about A-Levels grading system a guide for students.
5. University Entry
A-levels are a primary qualification used for entry into universities in the UK and worldwide.
Most degree programs have specific subject requirements (e.g., Engineering may require Maths and Physics).
What Subjects do A Level Students Take?
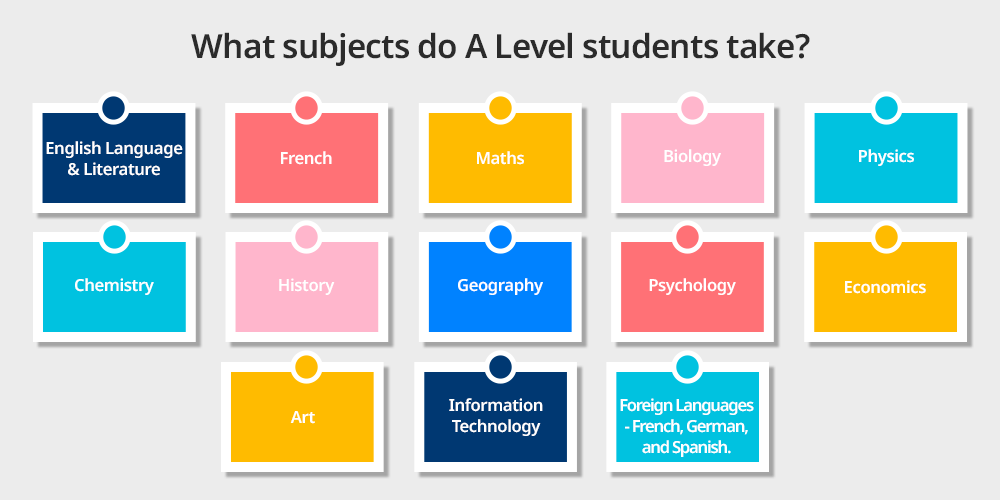
For A Level qualification, learners are free to choose subjects that hold their interest or they feel the topics are going to help them in their future studies or career. There are no compulsory subjects with A Levels.
The most popular subjects include:
- English Language & Literature
- French
- Maths
- Biology
- Physics
- Chemistry
- History
- Geography
- Psychology
- Economics
- Art
- Information Technology
- Modern Foreign Languages such as French, German, and Spanish.
If you are looking for a complete list of A-Level subjects, refer to the Cambridge International Education’s (CIE) official website.
Tips for Choosing A-Level Subjects
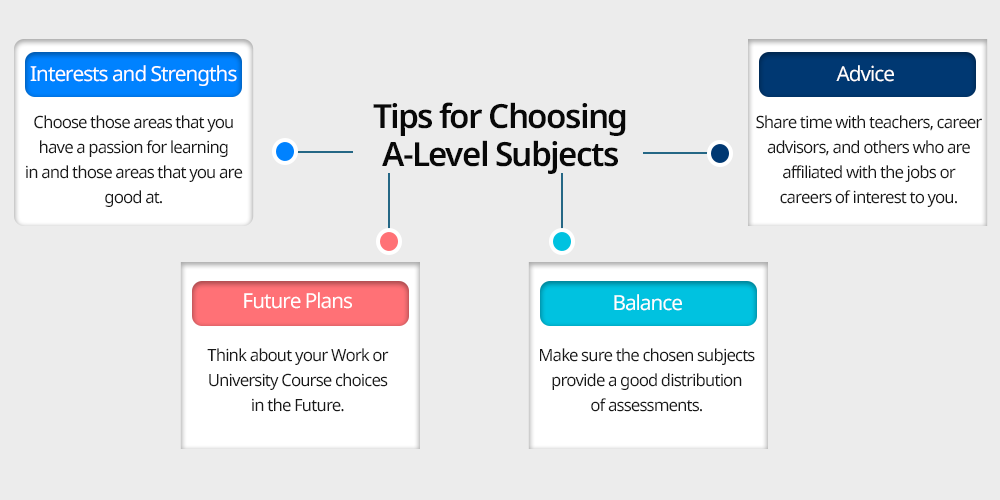
Selecting the right A-level subjects is crucial as it can influence your university options and career path.
Here we have listed below some advice that help you to make an informed decision:
- Interests and Strengths: Choose those areas that you have a passion for learning in and those areas that you are good at. When students enjoy a subject, there is a chance for them that they can perform well and achieve greater lesson fulfillment.
- Future Plans: Think about your Work or University Course choices in the Future. Some professions and university programs require specific A-level subjects for the applicant. Check the requirements in your preferred area of specialization so that you may be aware of the subjects you need to take.
- Balance: Make sure the chosen subjects provide a good distribution of assessments. Combining the sciences with humanities/arts can give a more balanced education and leave more doors open for the future.
- Advice: Share time with teachers, career advisors, and others who are affiliated with the jobs or careers of interest to you. Their ideas may help you resolve some of the difficulties and help you make wiser decisions regarding your choices of subjects.
How are A Levels Assessed?
A Levels are assessed through a combination of exams and, in some cases, coursework or practical assessments.
An overview of how a levels are commonly assessed:
1. Written Exam
Most A Level subjects are assessed externally through final exams conducted at the end of the two-year program.
Exams test subject knowledge, critical thinking, analysis, and application.
Wanted to explore A-Level exams? Before applying, you must read the A-Level curriculum.
2. Coursework
Some subjects such as English, History, or Art may include coursework, which can contribute to the final grade.
3. Practical Assessments
Science subjects like Biology, Chemistry, and Physics may involve a practical component or endorsement.
The practical endorsement does not affect the final grade but appears as a separate pass or fail notation on the certificate.
4. Exam Boards
There are two main exam boards popular with students such as Cambridge International Education, and Edexcel.
However, some other common choices are AQA, OCR, and WJEC.
5. Grades/UCAS Points
A Level exams consider grades or UCAS points range from A* (A-star) to E. Here, A* denoting exceptional performance of students.
For example, an A* is worth 56 points, an A is worth 48, and so on.
6. Standardized Qualifications
A Levels exams offer standardized qualifications which are widely accepted by universities in the UK and other countries.
What is the Structure and Format of A Level Qualification?
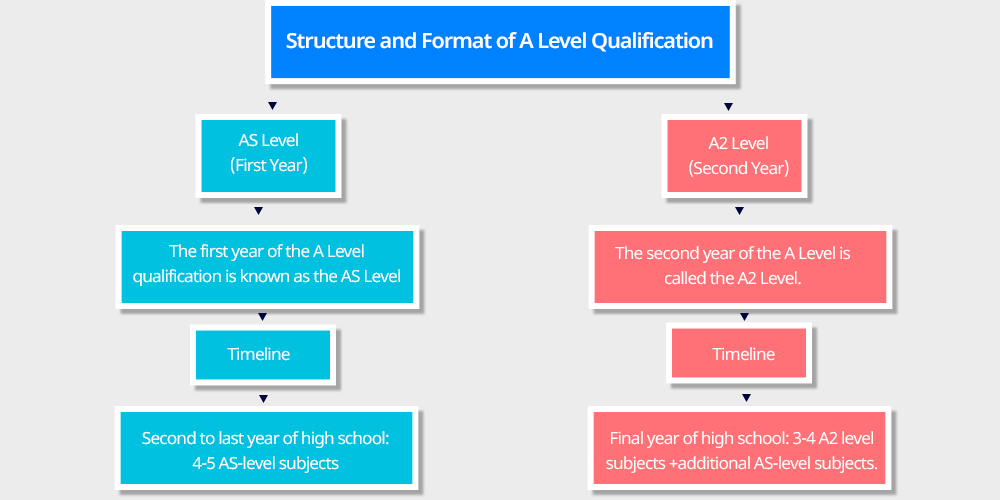
A Level Qualification has two main parts:
- AS Level (First Year)
- A2 Level (Second Year).
The first year of the A Level qualification is known as the AS Level, where students will study courses that provide enough understanding to progress to A-level.
The second year of the A Level is called the A2 Level. A2 Level courses are the second half of the A-level courses, and build on the curriculum included during the first year that is AS level.
Here’s a summary of typical timeline of an international A-levels student:
Second to last year of high school: 4-5 AS-level subjects
Final year of high school: 3-4 A2 level subjects +additional AS-level subjects.
A-Level Exam Boards: Cambridge vs. Edexcel
Choosing one is a crucial life changing decision for any kid. Cambridge and Edexcel are two of the leading exam boards offering A-Level qualifications.
Both of them have different characteristics. Edexcel A Levels have a single exam paper, on the other hand Cambridge A Levels offer a tiered system with separate foundation and higher levels.
1. What is the Cambridge Exam Board?
The exam board is a part of the University of Cambridge which offers international qualifications like IGCSEs and A Levels. It is globally recognized for academic excellence.
2. What is the Edexcel Exam Board?
It is a UK-based exam body under Pearson. It provides academic and vocational qualifications including GCSEs and A Levels. It is widely accepted in the UK and internationally.
Selecting one between both depends on individual preferences, academic goals, and subject suitability. Let’s understand the difference through a table:
| S.No. | Particulars | Edexcel A Levels | Cambridge A Levels |
| 1. | Assessment Structure | In the Edexcel A Levels exam students get a mix of modular and linear assessments. | On the other hand, Cambridge A Levels includes a linear model with final exams in the end. |
| 2. | Question Paper Structure | The structure in Edexcel includes a single set of question papers for most subjects. It includes both difficult and easy questions. | The structure of Cambridge works with the tiered system with separate foundation and higher levels for few subjects. |
| 3. | Emphasis | Edexcel emphasizes on knowledge, understanding and application. | Cambridge focuses on independent thinking, problem-solving, and analytical skills. |
| 4. | Coursework | Edexcel A Levels includes coursework and practical assessments in a few subjects. | While Cambridge A Levels focus on the main exams. |
| 5. | Subject Offering | Edexcel A Levels offers a wide range of subjects, however generally fewer than Cambridge. | Cambridge A Levels consists of over 55 subjects. It gives students the flexibility to choose combinations based on their interests and career requirements. |
| 6. | Teaching & Learning Style | Edexcel uses structured questions, case studies, and practical scenarios in their learnings. | Cambridge motivates students for independent research, conceptual understanding of topics, and long-answer writing. |
| 7. | Flexibility | For flexibility a linear structure is used. It means you are assessed mostly at the end of two years. | Here you can take AS and A Levels separately (modular structure). It means you have the option to spread out exams. |
A-Levels Entry Requirements
A-Levels or Advanced Level qualifications is a subject-based qualification in the UK, which is taken after GCSEs. And are used as a basis for university admissions.
Before enrolling, students need to meet specific entry requirements. Let’s explore in detail:
1. General Entry Requirements
For admission many schools and colleges require:
- A minimum of 5 GCSEs or equivalent at grades 9 to 4 (A* to C).
- Including English and Mathematics.
- Remember minimum grades in subjects relevant to your A-Level choices which are usually grade 6 or above.
2. Subject-Specific Requirements
Few subjects in A-Level have specific requirements such as:
- Maths or Further Maths requires high grades usually 7 or above in GCSE Maths.
- Subjects like Science need a strong performance and sometimes Maths.
- Economics or Business: GCSE in Maths and English, sometimes Business Studies.
- Previous study of the language is often required.
3. International Students
If you’re applying from outside the UK:
- Equivalent qualifications like IGCSEs, CBSE, ICSE, etc. are usually accepted by schools and colleges.
- English proficiency tests such as IELTS or TOEFL may be required if English isn’t your first language.
- Some schools might mandate entrance tests or conduct interviews as part of their admission process. However, it is optional.
4. Selective or Private Schools
Entry into highly competitive institutions sometimes requires:
- Entrance Tests
- Interviews
- Predicted Grades
- Reference Letters
These schools often look for higher academic performance mostly grade 7 to 9 GCSEs or equivalent.
After A-Levels: What Can You Do?
When students complete A-Levels, they have several options depending on their career goals and interests:
- University: Most learners prefer to further their education and they sit for university intakes in order to get courses of their desire. A-Levels are required when joining university and they are the determinant of whether one will get into a preferred course in a university.
- Vocational Training: For all the persons that are looking forward to the learning of particular hands-on skills vocational training or apprenticeship forms a more concrete pragmatic alternative rather than the university routes. Such an organized program usually leads to placing people in several fields of employment.
- Employment: Some students enter into work after A-Levels and work in different capacities for different organisations. A-level qualifications are appreciated by a lot of companies and many of them provide their employees promotions.
Conclusion
It is important to understand that A-level is important if planning for educational and career paths.
Among the various options available when you complete your A-level, it is important to proceed with an option that is suitable in terms of the desired goal.
Further, 21K schools are here to also assist you in your A–level education and help you prepare for further learning and a profession path.